Factoring Binomials Sum And Difference Of Perfect Squares

Factoring Binomials Sum And Difference Of Perfect Squares Youtube This algebra video tutorial explains how to factor quadratic expressions in the form of a difference of two squares or sum of squares. it explains when you. The process for factoring the sum and difference of cubes is very similar to that for the difference of squares. we first identify \(a\) and \(b\) and then substitute into the appropriate formula. the separate formulas for sum and difference of cubes allow us to always choose \(a\) and \(b\) to be positive.
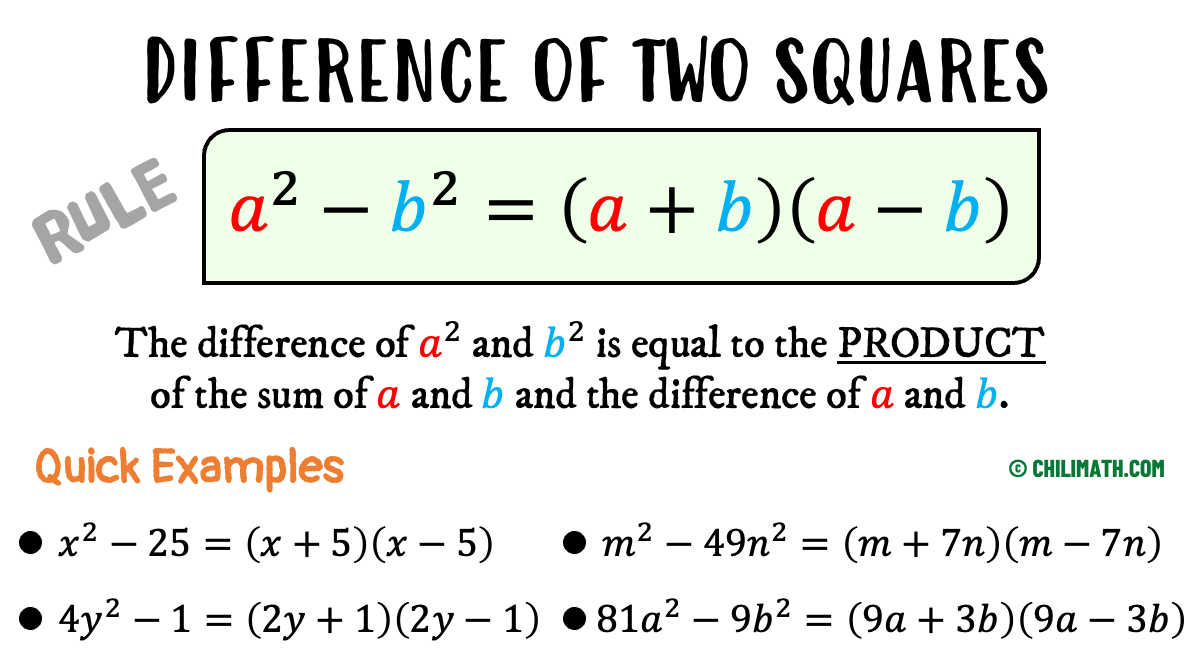
Week 8 Factoring Binomials Difference Of Squares Colegio San Josг In fact, you can go straight from the difference of two squares to its factors. at first, it appears that this is not a difference of two squares. what we need is to try rewriting it in the form that is easily recognizable. for the first term of the binomial, what term when multiplied by itself gives. for the second term, the number when. For the difference of cubes, the "minus" sign goes in the linear factor, a − b; for the sum of cubes, the "minus" sign goes in the quadratic factor, a2 − ab b2. advertisement. some people use the mnemonic " soap " to help keep track of the signs; the letters stand for the linear factor having the "same" sign as the sign in the middle of. Most people find it helpful to memorize the factored form of a perfect square trinomial or a difference of squares. the most important skill you will use in this section will be recognizing when you can use the shortcuts. factoring a perfect square trinomial. a perfect square trinomial is a trinomial that can be written as the square of a binomial. Factor perfect square trinomials. some trinomials are perfect squares. they result from multiplying a binomial times itself. we squared a binomial using the binomial squares pattern in a previous chapter. the trinomial 9 x 2 24 x 16 9 x 2 24 x 16 is called a perfect square trinomial. it is the square of the binomial 3 x 4. 3 x 4.
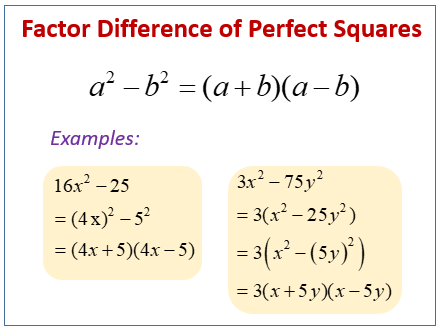
Factoring Expressions Difference Of Two Squares Examples Solutions Most people find it helpful to memorize the factored form of a perfect square trinomial or a difference of squares. the most important skill you will use in this section will be recognizing when you can use the shortcuts. factoring a perfect square trinomial. a perfect square trinomial is a trinomial that can be written as the square of a binomial. Factor perfect square trinomials. some trinomials are perfect squares. they result from multiplying a binomial times itself. we squared a binomial using the binomial squares pattern in a previous chapter. the trinomial 9 x 2 24 x 16 9 x 2 24 x 16 is called a perfect square trinomial. it is the square of the binomial 3 x 4. 3 x 4. There are three factoring formulas that will be used specifically for factoring binomials in this course. they are the difference of squares, the difference of cubes, and the sum of cubes. as the names indicate, we will be working with pairs of either perfect squares or perfect cubes that are either being added (sum) or subtracted (difference). Step 2. write them as squares. (a)2 − (b)2 step 3. write the product of conjugates. (a − b)(a b) step 4. check by multiplying. it is important to remember that sums of squares do not factor into a product of binomials. there are no binomial factors that multiply together to get a sum of squares.

Examples Factoring Binomials Differences Of Squares Youtube There are three factoring formulas that will be used specifically for factoring binomials in this course. they are the difference of squares, the difference of cubes, and the sum of cubes. as the names indicate, we will be working with pairs of either perfect squares or perfect cubes that are either being added (sum) or subtracted (difference). Step 2. write them as squares. (a)2 − (b)2 step 3. write the product of conjugates. (a − b)(a b) step 4. check by multiplying. it is important to remember that sums of squares do not factor into a product of binomials. there are no binomial factors that multiply together to get a sum of squares.

Comments are closed.