Factoring Sums And Differences Of Perfect Cubes
Factoring Sum And Difference Of Cubes For the difference of cubes, the "minus" sign goes in the linear factor, a − b; for the sum of cubes, the "minus" sign goes in the quadratic factor, a2 − ab b2. advertisement. some people use the mnemonic " soap " to help keep track of the signs; the letters stand for the linear factor having the "same" sign as the sign in the middle of. This algebra video tutorial focuses on factoring sums and differences of cubes. this video contains plenty of examples and practice problems factoring sums.

Factoring Cubes Using Sum And Difference Youtube The sum of two perfect squares, a2 b2, does not factor under real numbers. in algebra 2, we will extend our factoring skills. to factoring both the difference and the sum of two perfect cubes. factor the sum of perfect cubes: a3 b3 = (a b) (a2 ab b2) factor the difference of perfect cubes: a3 b3 = (a b) (a2 ab b2) when trying. Step 2. write them as squares. (a)2 − (b)2 step 3. write the product of conjugates. (a − b)(a b) step 4. check by multiplying. it is important to remember that sums of squares do not factor into a product of binomials. there are no binomial factors that multiply together to get a sum of squares. Step 2. write them as squares. (a)2 − (b)2 step 3. write the product of conjugates. (a − b)(a b) step 4. check by multiplying. it is important to remember that sums of squares do not factor into a product of binomials. there are no binomial factors that multiply together to get a sum of squares. The process for factoring the sum and difference of cubes is very similar to that for the difference of squares. we first identify \(a\) and \(b\) and then substitute into the appropriate formula. the separate formulas for sum and difference of cubes allow us to always choose \(a\) and \(b\) to be positive.
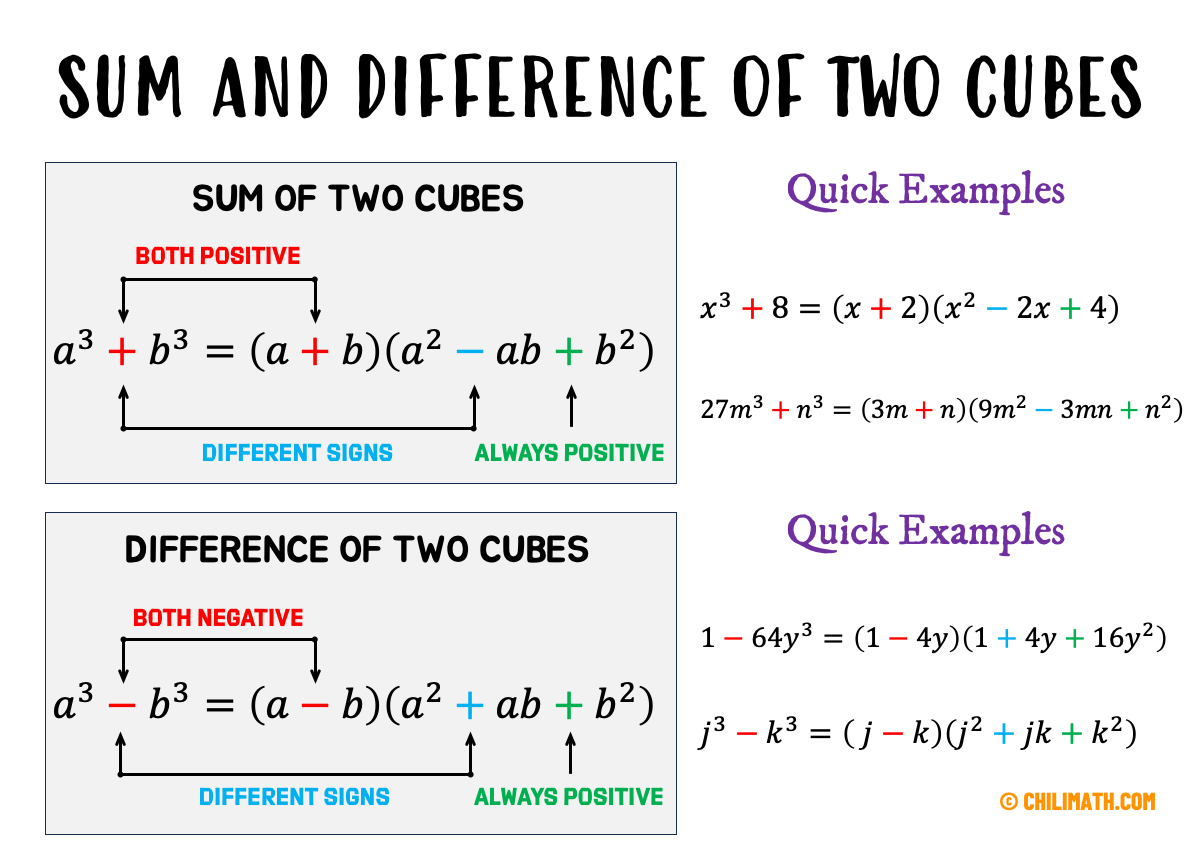
Factoring Sum And Difference Of Two Cubes Chilimath Step 2. write them as squares. (a)2 − (b)2 step 3. write the product of conjugates. (a − b)(a b) step 4. check by multiplying. it is important to remember that sums of squares do not factor into a product of binomials. there are no binomial factors that multiply together to get a sum of squares. The process for factoring the sum and difference of cubes is very similar to that for the difference of squares. we first identify \(a\) and \(b\) and then substitute into the appropriate formula. the separate formulas for sum and difference of cubes allow us to always choose \(a\) and \(b\) to be positive. Factor the sum or difference of cubes. step 1. does the binomial fit the sum or difference of cubes pattern? is it a sum or difference? are the first and last terms perfect cubes? step 2. write them as cubes. step 3. use either the sum or difference of cubes pattern. step 4. simplify inside the parentheses. step 5. check by multiplying the factors. How to. given a sum of cubes or difference of cubes, factor it. confirm that the first and last term are cubes, a3 b3 a 3 b 3 or a3 − b3 a 3 − b 3. for a sum of cubes, write the factored form as (a b)(a2 − ab b2) (a b) (a 2 − a b b 2). for a difference of cubes, write the factored form as (a −b)(a2 ab b2) (a − b) (a 2.

Comments are closed.