Fast Neutron Reactor Definition Components Nuclear Power

Fast Neutron Reactor Definition Components Nuclear Power A fast neutron reactor is a nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons. that means the neutron moderator (slowing down) in such reactors is undesirable. this is a key advantage of fast reactors, because fast reactors have a significant excess of neutrons (due to low parasitic absorbtion), unlike pwrs (or. The bn 350 fast neutron reactor at aktau, kazakhstan.it operated between 1973 and 1994. a fast neutron reactor (fnr) or fast spectrum reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons (carrying energies above 1 mev, on average), as opposed to slow thermal neutrons used in thermal neutron reactors.

Fast Neutron Reactor Definition Components Nuclear Power The fast neutron spectrum allows fast reactors to largely increase the energy yield from natural uranium as compared to thermal reactors. this high utilization of fuel can extend nuclear power programmes for thousands of years and provide significant improvements in nuclear waste management. it is for these reasons that fast reactors have been. Fast neutron reactors (fnrs) are a technological step beyond conventional power reactors, but are poised to become mainstream. they offer the prospect of vastly more efficient use of uranium resources and the ability to burn actinides which are otherwise the long lived component of high level nuclear waste. over 400 reactor years of experience. In a fast neutron reactor, the chain reaction is sustained primarily by fast neutrons with an average energy greater than a megaelectron volt. the proportion of nuclear fuel in fast reactors is large, the critical mass is large, and the core is small with a high fuel addition concentration. fast reactors have a high power density, nearly 10. The pressurized water reactor is the most widely used nuclear reactor in the world alongside the boiling water reactor (bwr). this reactor has been developed mainly in the united states, rf germany, france and japan. the nuclear fuel used is enriched uranium in the form of oxide. the moderator and the coolant used can be water or graphite.
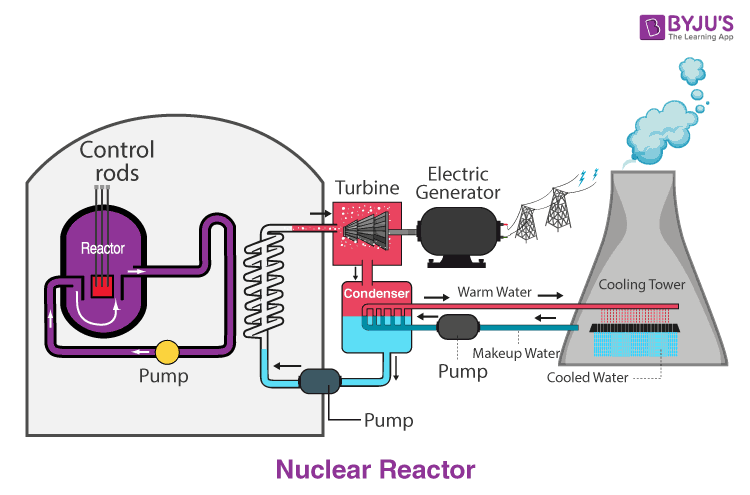
Nuclear Reactor Introduction Main Components And Types Of Nuclear Reactor In a fast neutron reactor, the chain reaction is sustained primarily by fast neutrons with an average energy greater than a megaelectron volt. the proportion of nuclear fuel in fast reactors is large, the critical mass is large, and the core is small with a high fuel addition concentration. fast reactors have a high power density, nearly 10. The pressurized water reactor is the most widely used nuclear reactor in the world alongside the boiling water reactor (bwr). this reactor has been developed mainly in the united states, rf germany, france and japan. the nuclear fuel used is enriched uranium in the form of oxide. the moderator and the coolant used can be water or graphite. When an atom in a nuclear reactor fissions, neutrons are released at high energy (fast speeds). in thermal reactors (nearly all current commercial ones) the fission neutrons are slowed down to low (thermal) energies by collisions with light atoms within the reactor – hydrogen in the water in water cooled reactors, deuterium in heavy water (d2o) in heavy water cooled reactors, or carbon in. This is why many breeder reactors are also fast reactors. fast neutrons are ideal for plutonium production because they are easily absorbed by u. 238. to create pu. 239. , and they cause less.

Comments are closed.