Figure 1 From Chronic Heart Failure Part 1 Pathophysiology Signs And

Figure 1 From Chronic Heart Failure Part 1 Pathophysiology Signs And Abstract. chronic heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from impaired cardiac relaxation or contraction. patients with chronic heart failure may experience multiple debilitating symptoms, such as fatigue, pain, and peripheral oedema. however, breathlessness may be considered the most debilitating symptom. this is. Serum nt pro bnp, sst2 and galectin 3 levels in patients with chronic heart failure (ef<40%) were expressed at significantly high levels and so which one can be need for early or help in diagnosis.

Chronic Heart Failure Part 1 Pathophysiology Signs And Sym Chronic heart failure (chf) is a clinical syndrome involving reduced cardiac output because of impaired cardiac contraction. typical clinical symptoms of chf include shortness of breath, fatigue and ankle swelling. 1. chf prevalence is 1 2%, rising to 10% in over 70 year olds. 4. for more information on the acute presentation of heart failure. Heart failure is an epidemic disease which affects about 1% to 2% of the population worldwide. both, the etiology and phenotype of heart failure differ largely. following a cardiac injury (e.g., myocardial infarction, increased preload or afterload) cellular, structural and neurohumoral modulations occur that affect the phenotype being present. The pathophysiology of the condition, its causes, assessment, and signs and symptoms are outlined, including pharmacological strategies, device implantation, lifestyle modification, cardiac rehabilitation and palliative care. chronic heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from impaired cardiac relaxation or contraction. patients with chronic heart failure may. Doi: 10.7748 ns.2017.e10349 corpus id: 33125553; chronic heart failure part 1: pathophysiology, signs and symptoms. @article{brake2017chronichf, title={chronic heart failure part 1: pathophysiology, signs and symptoms.}, author={rebecca brake and ian jones}, journal={nursing standard (royal college of nursing (great britain) : 1987)}, year={2017}, volume={31 19}, pages={ 54 63 } }.
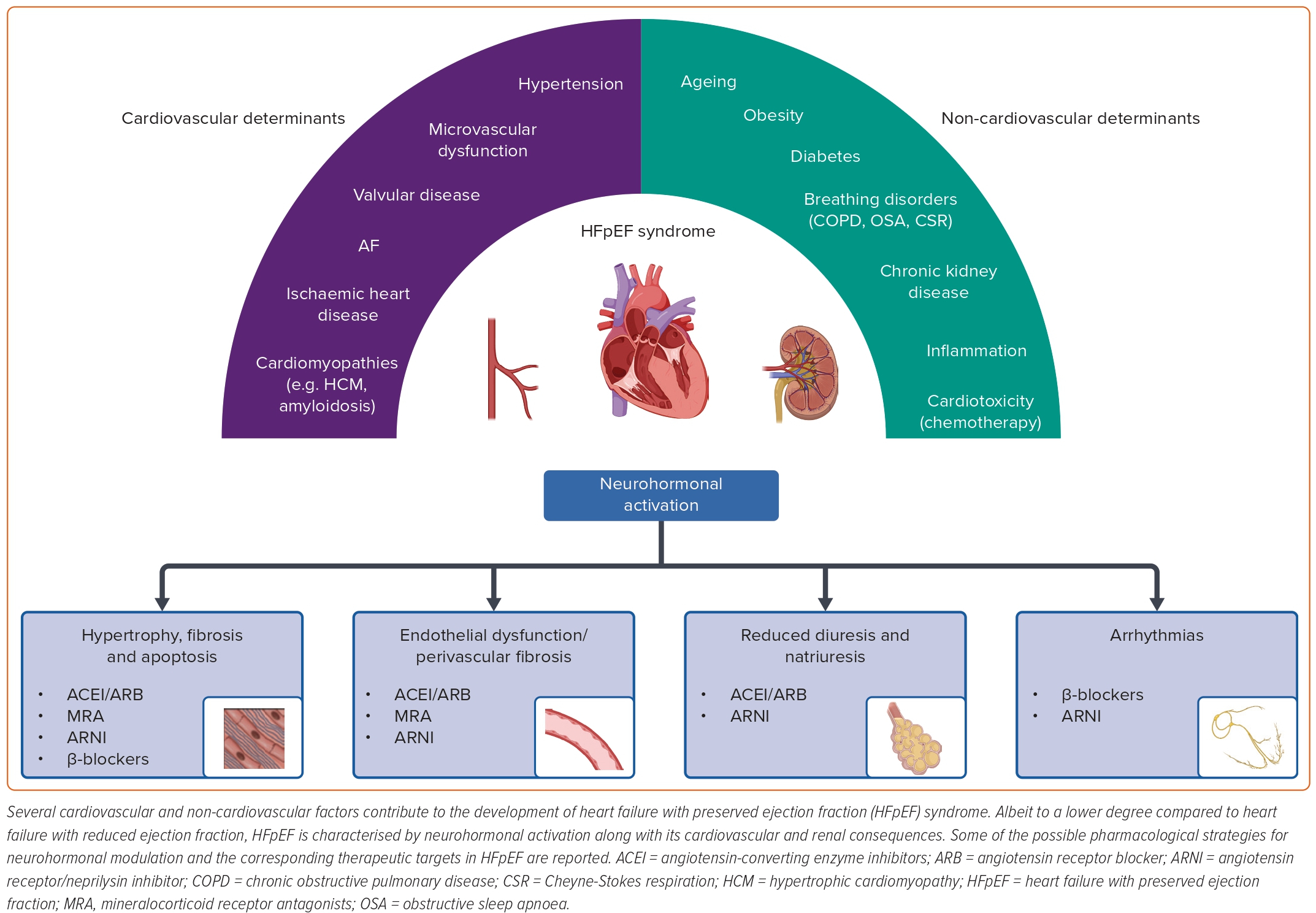
Figure 1 Pathophysiology Of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection The pathophysiology of the condition, its causes, assessment, and signs and symptoms are outlined, including pharmacological strategies, device implantation, lifestyle modification, cardiac rehabilitation and palliative care. chronic heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from impaired cardiac relaxation or contraction. patients with chronic heart failure may. Doi: 10.7748 ns.2017.e10349 corpus id: 33125553; chronic heart failure part 1: pathophysiology, signs and symptoms. @article{brake2017chronichf, title={chronic heart failure part 1: pathophysiology, signs and symptoms.}, author={rebecca brake and ian jones}, journal={nursing standard (royal college of nursing (great britain) : 1987)}, year={2017}, volume={31 19}, pages={ 54 63 } }. 2 introduction. go to: 2.1. diagnosis and definition of chronic heart failure. heart failure is a common complex clinical syndrome of symptoms and signs caused by impairment of the heart’s action as a pump supporting the circulation 11,74,337. it is caused by structural or functional abnormalities of the heart. As a consequence, the heart is unable to perfuse the tissues adequately. the resulting clinical syndrome (see table 2) can be explained by compensatory measures, such as cardiac hypertrophy and activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin–angiotensin system. table 1. causes of heart failure. table 2.
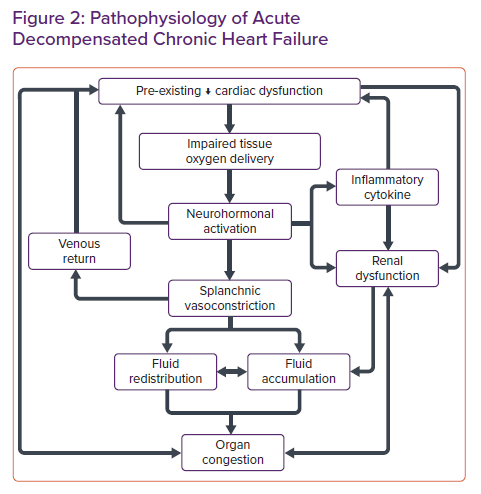
Pathophysiology Of Chronic Heart Failure 2 introduction. go to: 2.1. diagnosis and definition of chronic heart failure. heart failure is a common complex clinical syndrome of symptoms and signs caused by impairment of the heart’s action as a pump supporting the circulation 11,74,337. it is caused by structural or functional abnormalities of the heart. As a consequence, the heart is unable to perfuse the tissues adequately. the resulting clinical syndrome (see table 2) can be explained by compensatory measures, such as cardiac hypertrophy and activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin–angiotensin system. table 1. causes of heart failure. table 2.

Comments are closed.