Finite Math Venn Diagram Region Method Youtube

Finite Math Venn Diagram Region Method Youtube Finite math: venn diagram region methodin this video, we learn how to isolate certain regions of the venn diagram using a simple method i teach the students. Finite math 101: venn diagram basicsnot much mystery as to what this video is about; the basics of venn diagrams. in this video, we discuss intersections, un.
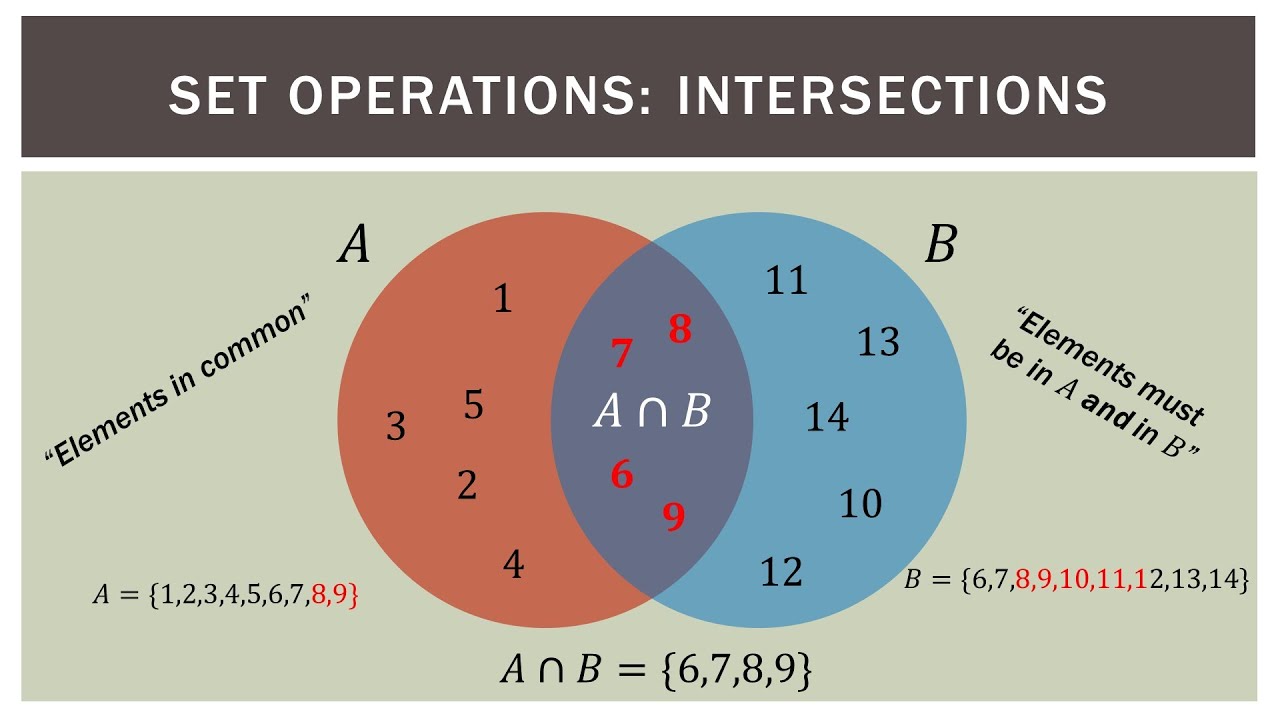
Finite Math Venn Diagram Basics Youtube Finite math: venn diagram practice problemsin this video, we walk through two venn diagram problems that are representative of what you are likely to see in. Recall that this relationship is expressed symbolically as trees ⊂ plants trees ⊂ plants. to create a venn diagram, first we draw a rectangle and label the universal set “u = plants” “u = plants”. then we draw a circle within the universal set and label it with the word “trees.” “trees.”. figure 1. diagram that shows all. This page titled 9.3: venn diagrams is shared under a cc by sa license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by david lippman (the opentextbookstore) . named after john venn, venn diagrams are a way to visually organize information. this section introduces the idea of using venn diagrams to visualize set operations and answer questions. Step 1: first, draw a venn diagram with three intersecting circles to represent the three intersecting sets: notes, flash cards, and review. label the universal set with the cardinality of the class. figure 4. venn diagram for step 1.

5 1 2 Finite Math Applications Of Sets And Venn Diagrams Youtube This page titled 9.3: venn diagrams is shared under a cc by sa license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by david lippman (the opentextbookstore) . named after john venn, venn diagrams are a way to visually organize information. this section introduces the idea of using venn diagrams to visualize set operations and answer questions. Step 1: first, draw a venn diagram with three intersecting circles to represent the three intersecting sets: notes, flash cards, and review. label the universal set with the cardinality of the class. figure 4. venn diagram for step 1. A venn diagram is a diagram that shows the relationship between and among a finite collection of sets. if we have two or more sets, we can use a venn diagram to show the logical relationship among these sets as well as the cardinality of those sets. in particular, venn diagrams are used to demonstrate de morgan's laws. venn diagrams are also useful in illustrating relationships in. Venn diagrams. we now use venn diagrams to illustrate the relations between sets. in the late 1800s, an english logician named john venn developed a method to represent relationship between sets. he represented these relationships using diagrams, which are now known as venn diagrams. a venn diagram represents a set as the interior of a circle.

Brandon Foltz Finite Math Venn Diagram Practice Problems Youtube A venn diagram is a diagram that shows the relationship between and among a finite collection of sets. if we have two or more sets, we can use a venn diagram to show the logical relationship among these sets as well as the cardinality of those sets. in particular, venn diagrams are used to demonstrate de morgan's laws. venn diagrams are also useful in illustrating relationships in. Venn diagrams. we now use venn diagrams to illustrate the relations between sets. in the late 1800s, an english logician named john venn developed a method to represent relationship between sets. he represented these relationships using diagrams, which are now known as venn diagrams. a venn diagram represents a set as the interior of a circle.

Comments are closed.