Flow Chart Of Blood Clotting
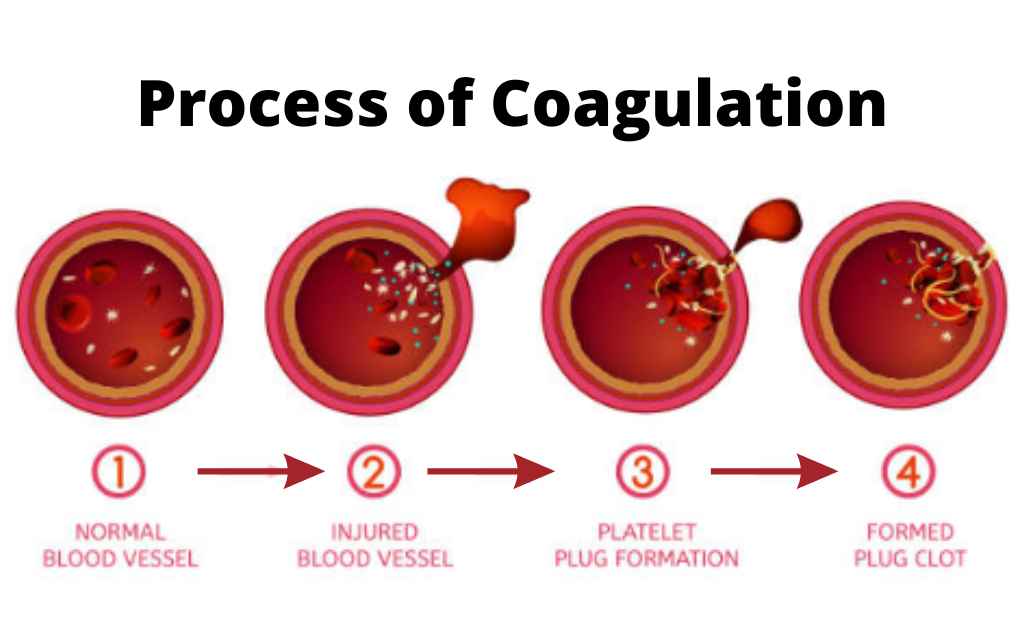
Blood Coagulation Mechanism And Process Pathways Blood is a necessary component of the human body, and the loss of this fluid may be life threatening. blood is generated via hematopoiesis and ultimately becomes the delivery method for oxygen to the tissues and cells. the human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. vascular mechanisms, platelets, coagulation factors, prostaglandins, enzymes, and proteins are the. Blood clotting process. blood flows through the blood vessels to deliver the needed oxygen and nutrients to the different cells in the body. the blood clotting process or coagulation is an.
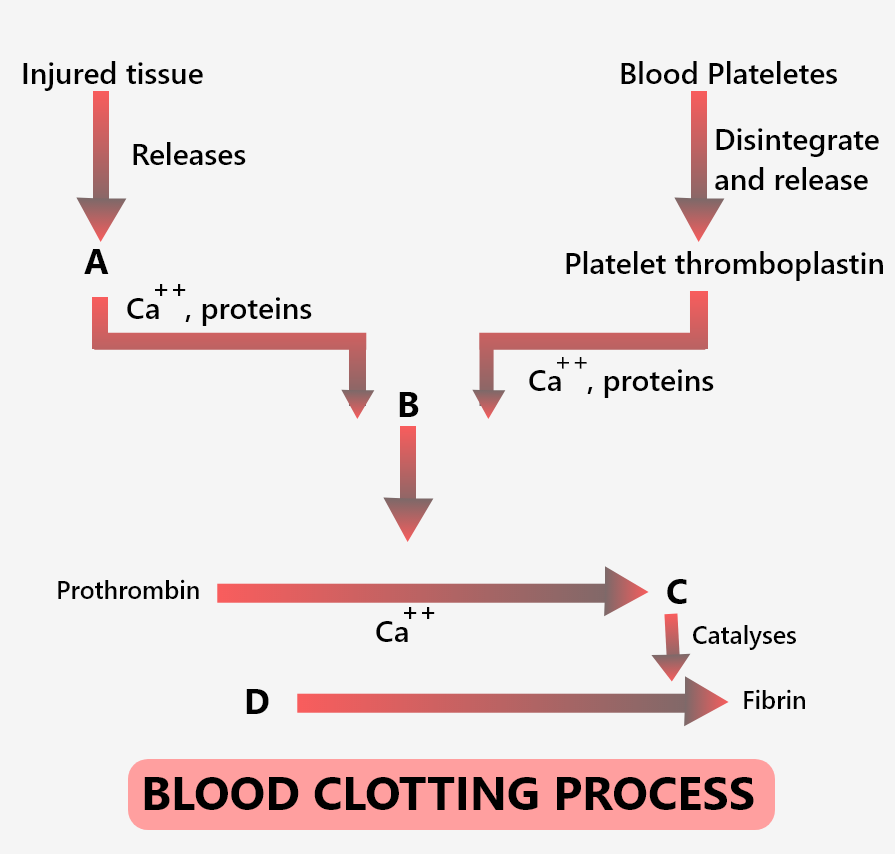
Blood Clotting Process Flow Chart Flowchart Examples Hemostasis is the body's way of stopping injured blood vessels from bleeding. hemostasis includes clotting of the blood. an abnormality in any part of the system that controls bleeding can lead to excessive bleeding or excessive clotting, both of which can be dangerous. when clotting is poor, even a slight injury to a blood vessel may lead to. Flow chart blood clotting process diagram: the science of the heart and circulatory system louise spilsbury,richard spilsbury,2017 07 15 what makes our hearts pump how does blood circulate throughout our bodies curious readers will love this innovative look at the human heart and. For example, if a blood clot blocks the supply of blood to the brain, it can cause a stroke. a blood clot that forms within the blood vessels is called a thrombus. on the right hand side of figure 5, you can see how a blood clot can block the normal flow of blood in a blood vessel. The coagulation cascade refers to the series of steps that occur during the formation of a blood clot after injury by activating a cascade of proteins called clotting factors. there are three pathways: intrinsic, extrinsic, and common. the intrinsic pathway is activated by factors in the blood, while extrinsic is activated by tissue factor.
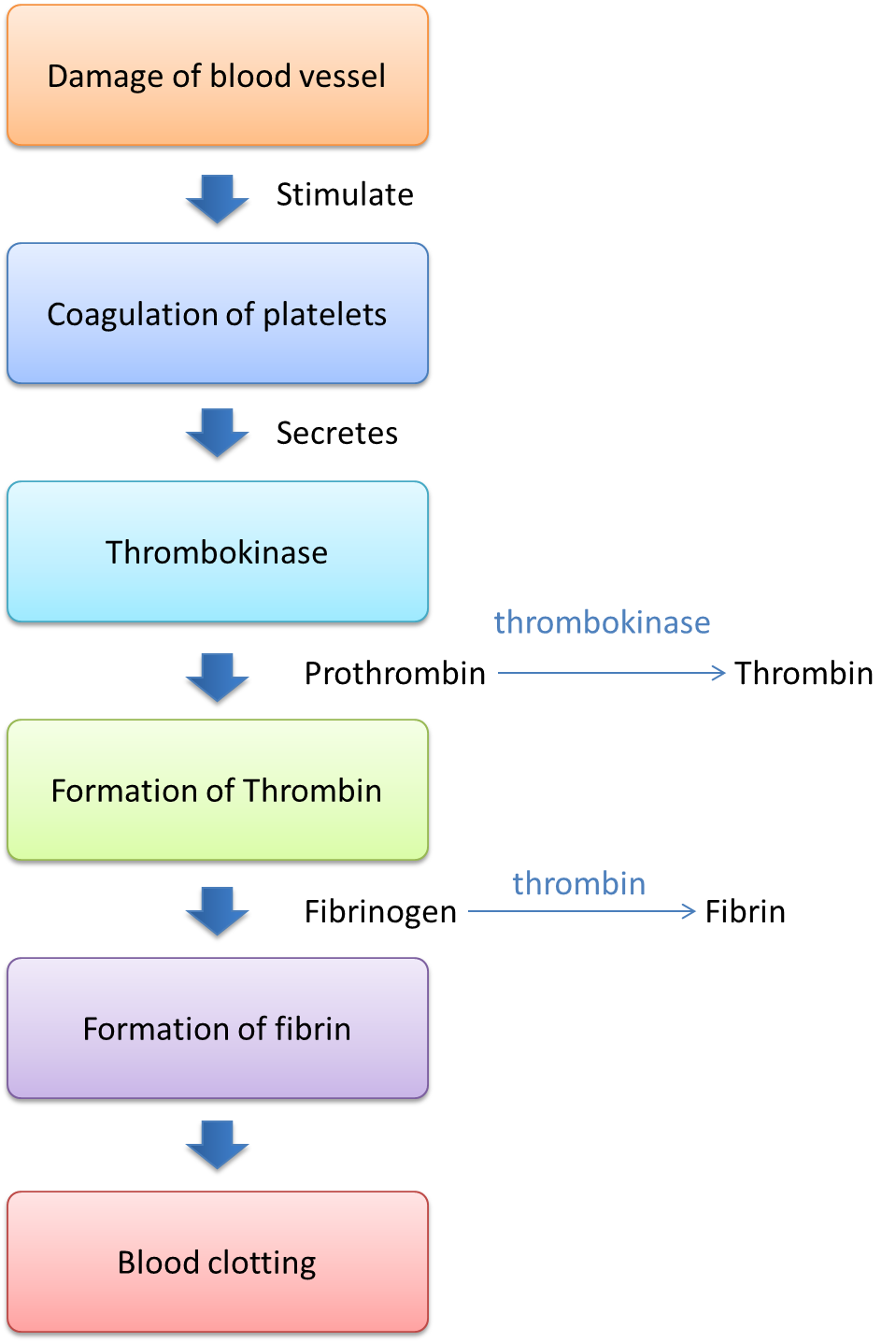
1 3 1 Mechanism Of Blood Clotting Spm Biology For example, if a blood clot blocks the supply of blood to the brain, it can cause a stroke. a blood clot that forms within the blood vessels is called a thrombus. on the right hand side of figure 5, you can see how a blood clot can block the normal flow of blood in a blood vessel. The coagulation cascade refers to the series of steps that occur during the formation of a blood clot after injury by activating a cascade of proteins called clotting factors. there are three pathways: intrinsic, extrinsic, and common. the intrinsic pathway is activated by factors in the blood, while extrinsic is activated by tissue factor. Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting) primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. to accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and activate. that activation means they can “recruit” more platelets to form a platelet “plug” to stop blood loss from the damaged area. Coagulation is the formation of a blood clot (or thrombus), and is essential to haemostasis. haemostasis is the body’s physiological response to stop or prevent bleeding.the coagulation process is characterised by a cascade where one event sets off another and so on. in this cascade, proteins called clotting factors initiate reactions which activate yet more clotting factors. therefore, as.

Function Of Blood Biology Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting) primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. to accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and activate. that activation means they can “recruit” more platelets to form a platelet “plug” to stop blood loss from the damaged area. Coagulation is the formation of a blood clot (or thrombus), and is essential to haemostasis. haemostasis is the body’s physiological response to stop or prevent bleeding.the coagulation process is characterised by a cascade where one event sets off another and so on. in this cascade, proteins called clotting factors initiate reactions which activate yet more clotting factors. therefore, as.
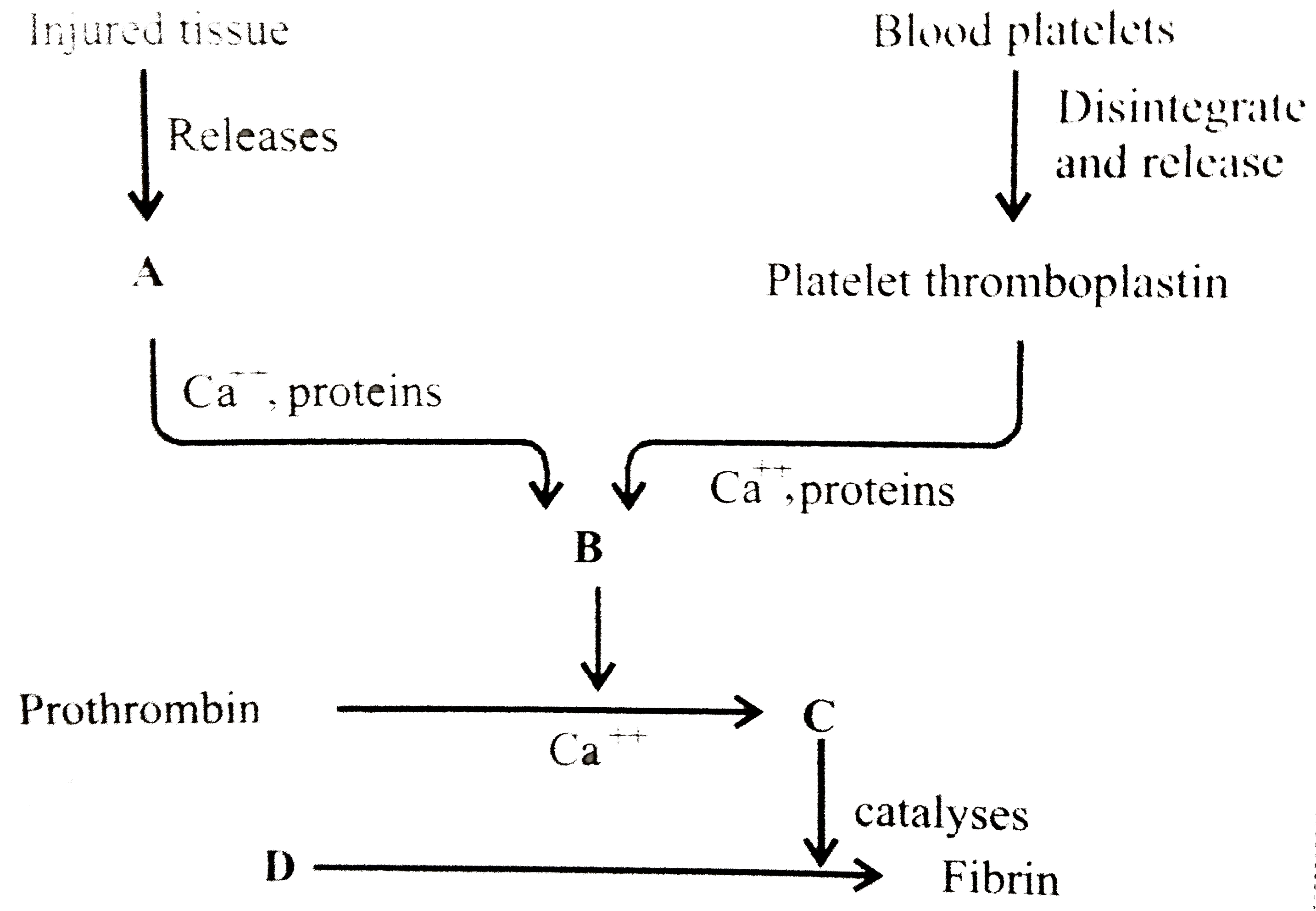
Describe The Process Of Blood Clotting

Comments are closed.