Food Chains Food Webs Exploringthe Temperatewoodland Vrogue Co
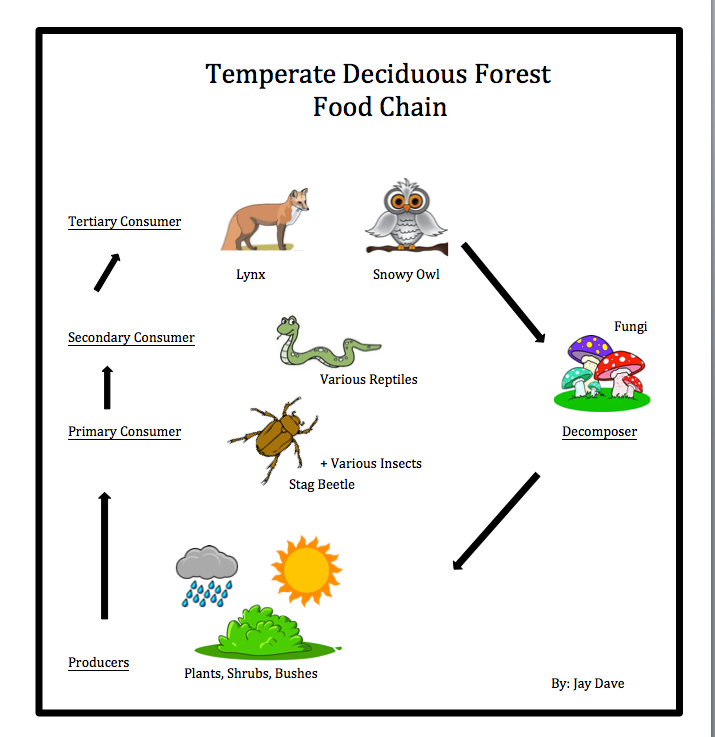
Food Chains Food Webs Exploringthe Temperatewoodland Vrogue Co If you were an animal, where do you believe you'll stand in this biome? would you hold all of the power and be a quantiary concumer, or be the one who provides for everyone as the producer? this page. The specific producers in a temperate woodland and shrubland food web may vary depending on the location and ecosystem. however, here are five examples of common producers found in this type of ecosystem: oak trees: oak trees are large, long lived producers that dominate the canopy in many temperate woodland and shrubland ecosystems.
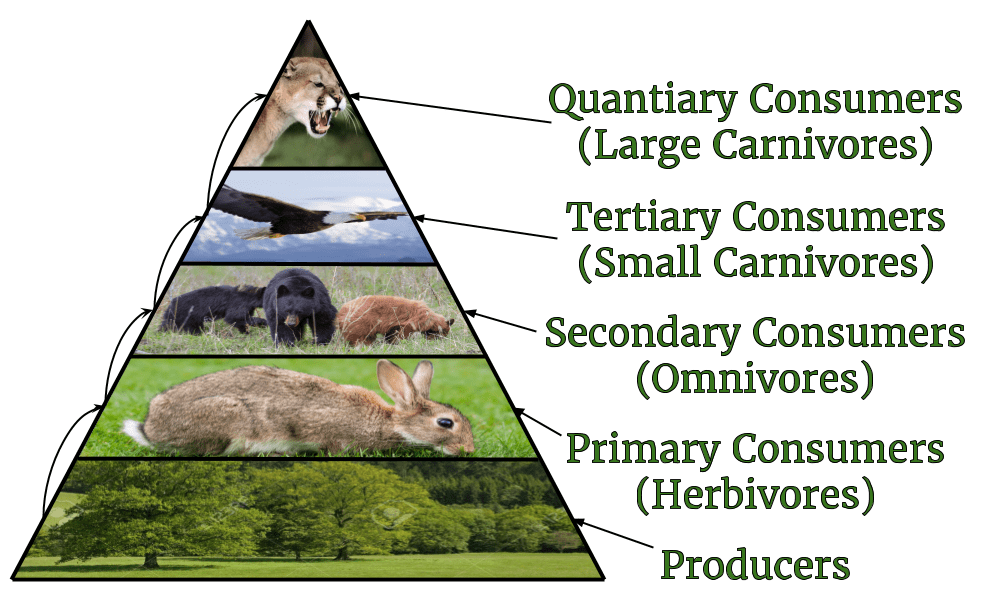
Food Chains Food Webs Exploringthe Temperatewoodland Vrogue Co A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. A terrestrial food chain that includes four feeding levels juventu and web meaning diagrams examples teachoo what is the difference between web? species extinction? happens when goes extinct? 6 4: chains webs biology libretexts can any be complete without plants? byju s neet science of for kids: circle life flow 25 best with 5 organisms 14 1: marine environments geosciences free vector. A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. The idea to apply the food chains to ecology and to analyze its consequences was first proposed by charles elton (krebs 2009). in 1927, he recognized that the length of these food chains was.

Food Chains Food Webs Exploringthe Temperatewoodland Vrogue Co A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. The idea to apply the food chains to ecology and to analyze its consequences was first proposed by charles elton (krebs 2009). in 1927, he recognized that the length of these food chains was. A food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the transfer of energy in food between. Food webs. simply put, a food web describes all of the food chains in a given ecosystem. rather than forming a straight line that goes from the sun to the plants to the animals that eat them, food.
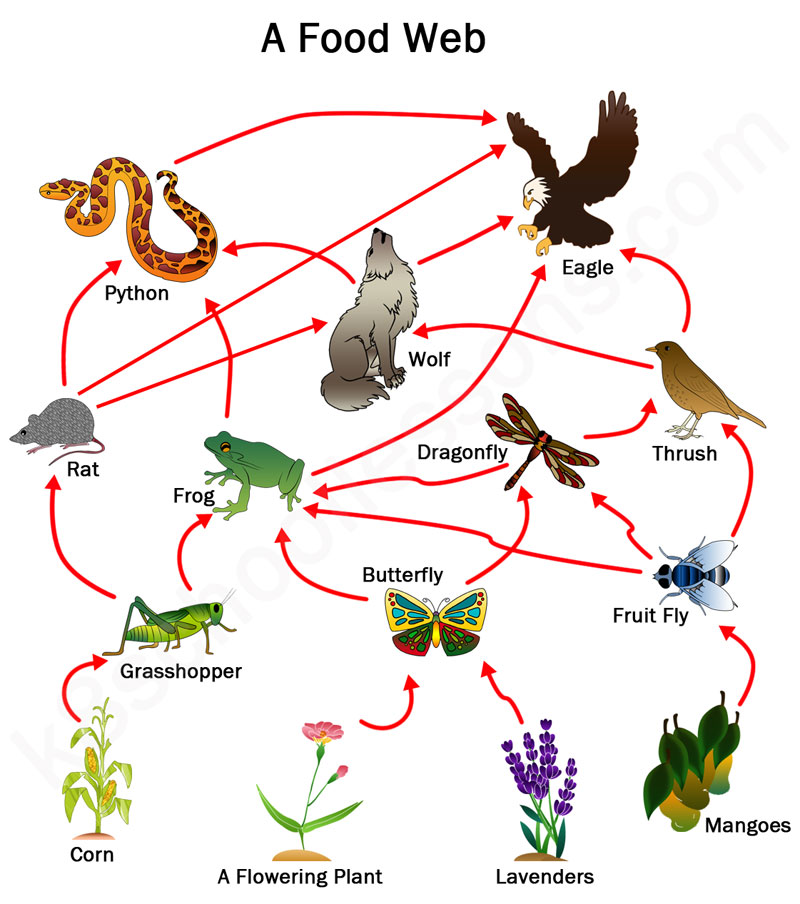
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food A food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the transfer of energy in food between. Food webs. simply put, a food web describes all of the food chains in a given ecosystem. rather than forming a straight line that goes from the sun to the plants to the animals that eat them, food.

Comments are closed.