Food Webs And Trophic Cascades

Trophic Cascade Definition Importance Examples Britannica For example, it can be important for understanding the knock on effects of removing top predators from food webs, as humans have done in many places through hunting and fishing. a top down cascade is a trophic cascade where the top consumer predator controls the primary consumer population. in turn, the primary producer population thrives. Consequently, even in tropical rainforests characterized by complex food webs and high primary productivity, where trophic cascades were thought to be inconsequential, the removal of top down.
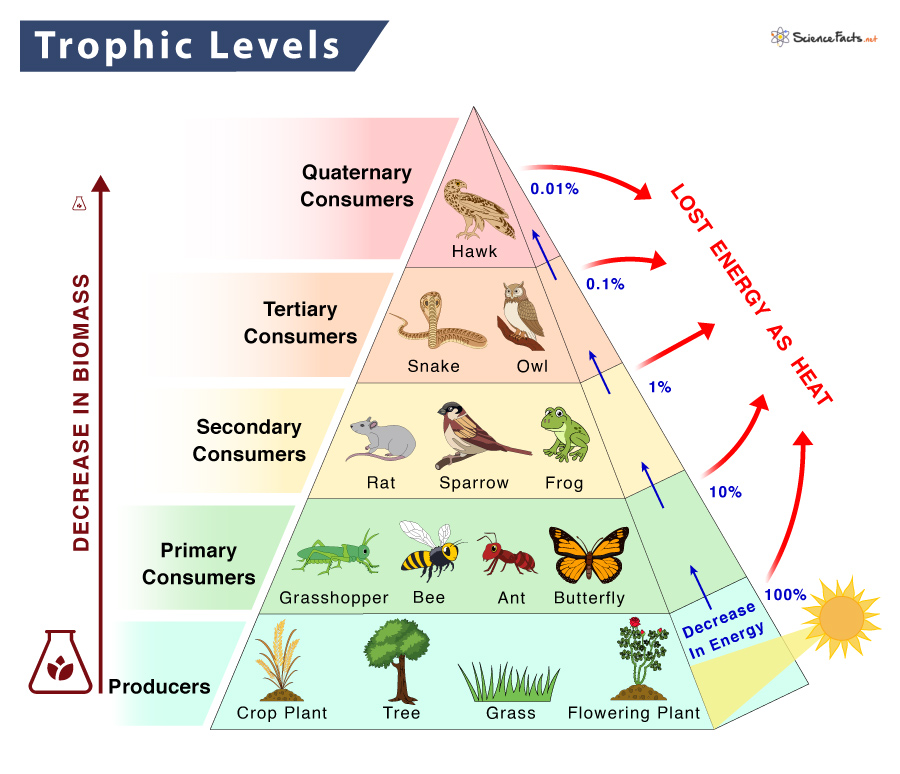
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram Trophic cascade, an ecological phenomenon triggered by the addition or removal of top predators and involving reciprocal changes in the relative populations of predator and prey through a food chain. a trophic cascade often results in dramatic changes in ecosystem structure and nutrient cycling. Trophic cascades are powerful indirect interactions that can control entire ecosystems, occurring when a trophic level in a food web is suppressed. for example, a top down cascade will occur if predators are effective enough in predation to reduce the abundance, or alter the behavior of their prey, thereby releasing the next lower trophic level. Food webs are a way of visualizing relationships between organisms based on their trophic level. an organism’s trophic level is determined by its feeding behavior: top apex predators occupy the highest trophic level. intermediate species occupy the trophic levels between top predators and basal species:. Studies of food web interactions and trophic cascades have traditionally focused on the antagonistic interactions between species 1,2,3,4,8. however, mutualists are also embedded within food webs.

Marine Food Webs вђ Science Learning Hub Food webs are a way of visualizing relationships between organisms based on their trophic level. an organism’s trophic level is determined by its feeding behavior: top apex predators occupy the highest trophic level. intermediate species occupy the trophic levels between top predators and basal species:. Studies of food web interactions and trophic cascades have traditionally focused on the antagonistic interactions between species 1,2,3,4,8. however, mutualists are also embedded within food webs. In a trophic cascade, predators induce effects that cascade down the food chain and affect biomass of organisms at least two links away (ricklefs 2008). and higher trophic levels in food webs. Cascades (bottom up and top down) 2006: ‘a trophic cascade is the process by which a perturbation propagates either up or down a food web with alternating. negative and positive effects at successive levels ’ ([47], p. 253). trends.
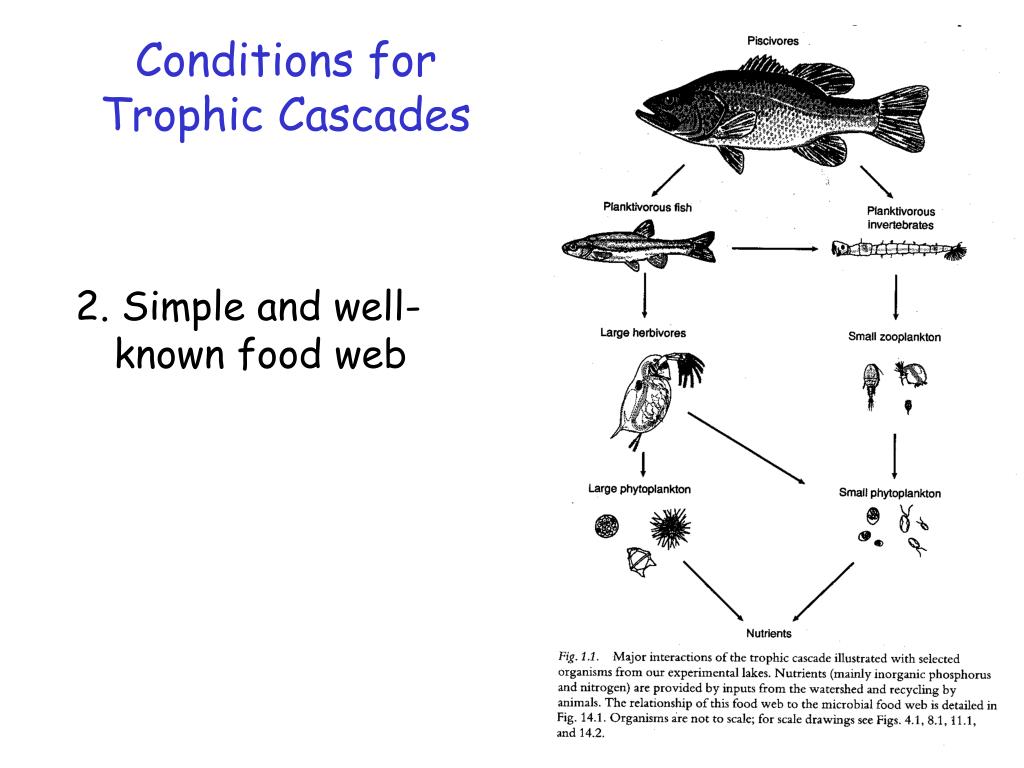
Ppt Food Webs And Trophic Cascades In Lakes Powerpoint Presentation In a trophic cascade, predators induce effects that cascade down the food chain and affect biomass of organisms at least two links away (ricklefs 2008). and higher trophic levels in food webs. Cascades (bottom up and top down) 2006: ‘a trophic cascade is the process by which a perturbation propagates either up or down a food web with alternating. negative and positive effects at successive levels ’ ([47], p. 253). trends.

Trophic Cascade Definition Importance Examples Britannica

Comments are closed.