Food Webs Taiga Forest Vrogue Co
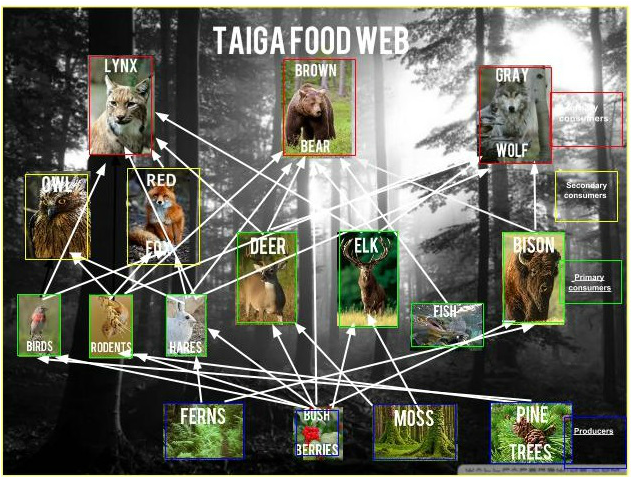
Food Webs Taiga Forest Vrogue Co Taiga food web: interconnected relationships between flora and fauna. scarlett dennis. july 7, 2023. the taiga, also known as the boreal forest, is the largest land biome on earth, stretching across north america, europe, and asia in the high northern latitudes. characterized by its dense coniferous forests, long, cold winters, and short, wet. A taiga biome food web shows the feeding relationships and how energy flows between organisms at different trophic levels. 1. producers: it mainly consists of coniferous trees like spruce, fir, and pine. these trees are well adapted to the cold climate, with needle like leaves that reduce water loss through transpiration.

Food Web Taiga Biome Vrogue Co The taiga biome food web is a complex network of interconnected relationships between organisms living in the taiga. it illustrates how energy flows through the ecosystem, from producers (plants) to consumers (animals) and decomposers (fungi and bacteria). each organism plays a specific role in maintaining the balance of this unique ecosystem. 2. Introduction. a food web is the representation of the interconnected feeding relationship among various components of an ecosystem. it transfers energy through various producers, consumers, and decomposers. in the taiga biome, the food web is complex and includes various organisms. Examples of primary consumers in the food chain of taiga biome are insects, birds, mice, rats, chipmunks, squirrels, porcupines, deer, moose and elk. secondary consumers (carnivores) these are heterotrophs and consume the herbivores for deriving their nutrients. in short, secondary consumers are heterotrophs that rely on organisms of the second. We detected widespread changes in c assimilation by small mammals exposed to long term warming in a boreal forest, highlighted by a significant shift from plant to fungal based food webs (fig. 1a.
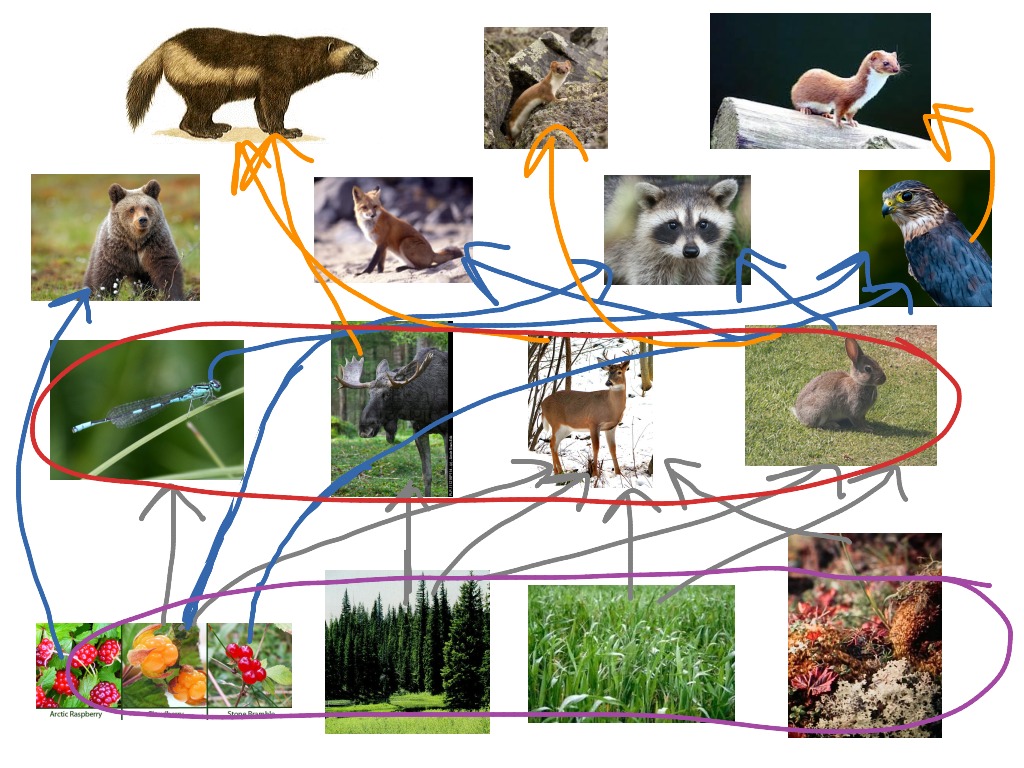
Food Web Taiga Coniferous Forest Vrogue Co Examples of primary consumers in the food chain of taiga biome are insects, birds, mice, rats, chipmunks, squirrels, porcupines, deer, moose and elk. secondary consumers (carnivores) these are heterotrophs and consume the herbivores for deriving their nutrients. in short, secondary consumers are heterotrophs that rely on organisms of the second. We detected widespread changes in c assimilation by small mammals exposed to long term warming in a boreal forest, highlighted by a significant shift from plant to fungal based food webs (fig. 1a. The food web is extremely important to ecology because it balances the many biomes it affects. it also demonstrates how an animal adapts or changes to their environment. if that is the case, the food web will also adapt and change according to the organisms. the food web is what primarily makes the world go round. Taiga forest: home; species. symbiotic relationships; coevolution; food webs; climate and challenges. powered by create your own unique.

Comments are closed.