Gait Muscular Activity Action

Phases Of Gait And Muscle Activation вђ Adult And Pediatric Printable Gait kinetics investigates the forces and moments of the gait cycle. this includes the study of ground reaction forces (grf), joint torque, plantar pressure distribution and muscle activity. [1] the body should be in equilibrium during gait, therefore, the external ground reaction forces (grf) (external moment) should be balanced by the. After watching this video you be able to describe muscle activation throughout the whole gait cycle. differentiate between concentric and eccentric muscle ac.

Gait Muscular Activity Action Youtube Gait is a multi joint, multi organ activity. muscle contraction and joint mobility are considered to be key elements in the functioning of gait. muscles may contract concentrically (muscles shorten, creating movement and acceleration), eccentrically (controlled muscle lengthening, creating deceleration) or isometrically (muscle contracts without shortening or lengthening, creating stability). Muscle activity during gait. when a person is walking, the walk cycle mechanism is under the influence of external forces (inertia, ground reaction force, and acceleration) and internal forces (muscle contraction). these forces have a direct impact on muscle activity, which produces the final gait cycle pattern 1. Muscle activity. muscle activity during the gait cycle. the movement pattern that we observe in the lower limbs during walking results from the interaction between external forces (joint reaction and ground reaction) and internal forces (produced by muscles and other soft tissue). knowledge of the ground reaction force is especially helpful to. The gait cycle. the action of walking may be summarised by the following sequence: [1] registration and activation of the gait command within the central nervous system. transmission of gait signals to the peripheral nervous system. activation of motor neurons and subsequent muscle fibre engagement. contraction of muscles.

Muscle Activation During Gait Cycle Muscle activity. muscle activity during the gait cycle. the movement pattern that we observe in the lower limbs during walking results from the interaction between external forces (joint reaction and ground reaction) and internal forces (produced by muscles and other soft tissue). knowledge of the ground reaction force is especially helpful to. The gait cycle. the action of walking may be summarised by the following sequence: [1] registration and activation of the gait command within the central nervous system. transmission of gait signals to the peripheral nervous system. activation of motor neurons and subsequent muscle fibre engagement. contraction of muscles. Gait refers to the manner in which a person walks. normally, walking is a very efficient biomechanical process, requiring relatively little use of energy. although the process appears automatic and easy, walking is actually a complex and high level motor function. normal walking requires a healthy body, especially with regard to the nervous and. 1. describe the major functional tasks of the gait cycle and their corresponding subphases. 2. identify the muscle activity, ground reaction forces, and joint angles during each of the subphases of the gait cycle. 3. define the time and distance parameters used to describe and assess normal gait.
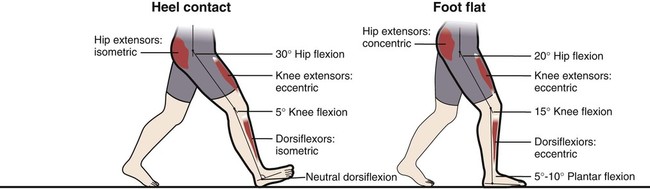
Fundamentals Of Human Gait Musculoskeletal Key Gait refers to the manner in which a person walks. normally, walking is a very efficient biomechanical process, requiring relatively little use of energy. although the process appears automatic and easy, walking is actually a complex and high level motor function. normal walking requires a healthy body, especially with regard to the nervous and. 1. describe the major functional tasks of the gait cycle and their corresponding subphases. 2. identify the muscle activity, ground reaction forces, and joint angles during each of the subphases of the gait cycle. 3. define the time and distance parameters used to describe and assess normal gait.

Comments are closed.