Gdt Basic Dimensions Ted

Gd T Basic Dimensions Ted Youtube Basic dimensions are typically used within the gd&t framework to control the location or geometry of features. the best example of when basic dimensions are used is when specifying true position. take a look at this drawing below: the basic dimensions are those dimensions in the boxes – the 30 and the 15. they do have tolerances, though, as. As basic dimensions are perfect, there would be no deviations, and they would not be recorded on the report. instead of basic dimensions, we would report the following: flatness for datum a. size of the part (60 0.1 for length and width) thickness of the part (16 0.1) size of the holes (Ø12 0.05) position of the holes (cylindrical.
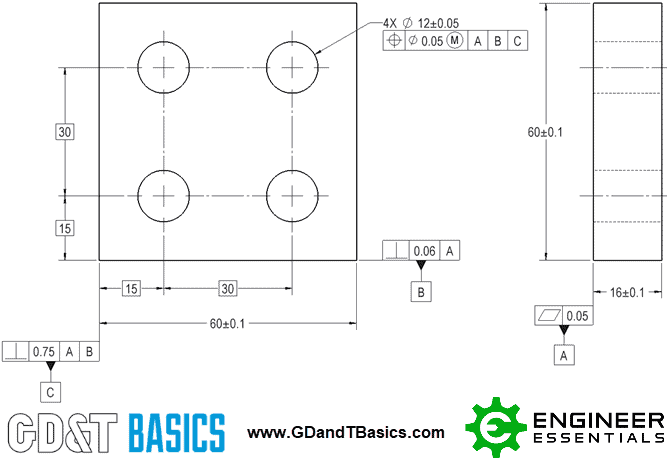
What Are Basic Dimensions And How Do They Work In Gd T Gd T Basi This video is very important for the quality as well production professionals. it will help them after the rejection of the geometric tolerances how much err. The term “basic dimension” is per asme y14.5 2009 or earlier standards and “theoretically exact dimension ted” and the terminology used in iso 1101 or derivative standards. be aware that the definition is an academic one mostly derived from the iso 111 standard. Theoretically exact dimensions (ted), also known as true or boxed dimensions must not be toleranced. the dimension is shown in a rectangular frame. theoretically exact dimensions may only vary by the geometrical tolerance that is stated in the tolerance frame associated with them. theoretically exact dimensions should be used when dimensioning. Basic dimensions are used for calculations. they are used to calculate various geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (gd&t) characteristics such as true position, profile or angularity. in the example above, the 120 degree callout and the 42 diameter bolt circle are the basic dimensions and the true position of 0.2 is the characteristic.

Gd T Basics Introduction To Geometric Dimension And Tolerance Theoretically exact dimensions (ted), also known as true or boxed dimensions must not be toleranced. the dimension is shown in a rectangular frame. theoretically exact dimensions may only vary by the geometrical tolerance that is stated in the tolerance frame associated with them. theoretically exact dimensions should be used when dimensioning. Basic dimensions are used for calculations. they are used to calculate various geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (gd&t) characteristics such as true position, profile or angularity. in the example above, the 120 degree callout and the 42 diameter bolt circle are the basic dimensions and the true position of 0.2 is the characteristic. In a technical drawing, a basic dimension is a theoretically exact dimension, given from a datum to a feature of interest. in geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, basic dimensions are defined as a numerical value used to describe the theoretically exact size, profile, orientation or location of a feature or datum target. [1] allowable. The basic dimensions are considered theoretically exact locations. once the true position is located relative to the datums, the diameter symbol in the feature control frame tells us that the position tolerance zone is cylindrical. the size of the tolerance zone for each hole is dictated by the tolerance stated in the feature control frame.
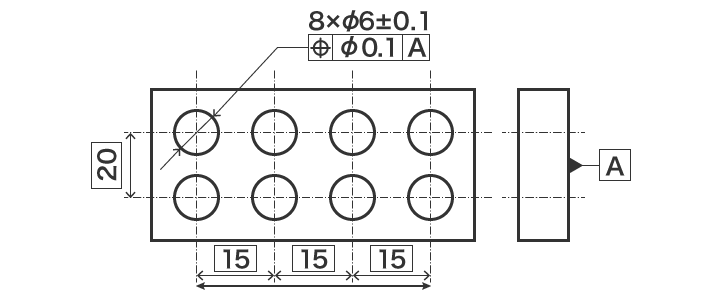
Gd T Drawings And Symbols Gd T Overview Gd T Fundamentals Keyenc In a technical drawing, a basic dimension is a theoretically exact dimension, given from a datum to a feature of interest. in geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, basic dimensions are defined as a numerical value used to describe the theoretically exact size, profile, orientation or location of a feature or datum target. [1] allowable. The basic dimensions are considered theoretically exact locations. once the true position is located relative to the datums, the diameter symbol in the feature control frame tells us that the position tolerance zone is cylindrical. the size of the tolerance zone for each hole is dictated by the tolerance stated in the feature control frame.

Gd T What Is Basic Size And Dimension Youtube

Comments are closed.