General Biology 4 Pdf Meiosis Mitosis

General Biology 4 Pdf Meiosis Mitosis Figure section4.4.1 s e c t i o n 4.4. 1: meiosis and mitosis are both preceded by one round of dna replication; however, meiosis includes two nuclear divisions. the four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct. the daughter cells resulting from mitosis are diploid and identical to the parent cell. Mitosis of that first cell gives rise to clones that make up the rest of the organism’s body. maintenance: some examples: skin cells slough off, rbc’s live 3 months, intestinal cells divide rapidly to replace older cells. repair: damaged cells ranging from skinned knees to post surgical healing is repaired by mitosis.

вїquг Diferencia Mitosis Y Meiosis Curiosoando Outcome. while mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. mitosis: two identical daughter cells. meiosis: four non identical daughter cells with half the chromosome number. Figure 11.1.6 11.1. 6: meiosis and mitosis are both preceded by one round of dna replication; however, meiosis includes two nuclear divisions. the four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct. the daughter cells resulting from mitosis are diploid and identical to the parent cell. Meiosis i: this is also referred to as the reduction division in which the chromosome content of the daughter cell is reduced to half of that of the mother cell. as in mitotic division, meiosis i is preceded by replication of the dna content of the dividing cell. the first phase of meiosis i is the prophase. this goes through 5 stages as follows:. The difference between the two processes is that mitosis occurs in non reproductive cells, or somatic cells, and meiosis occurs in the cells that participate in sexual reproduction, or germ cells. you can navigate to specific sections of this handout by clicking the links below. mitosis: pg. 1 meiosis: pg. 4 mitosis vs. meiosis: pg. 7.
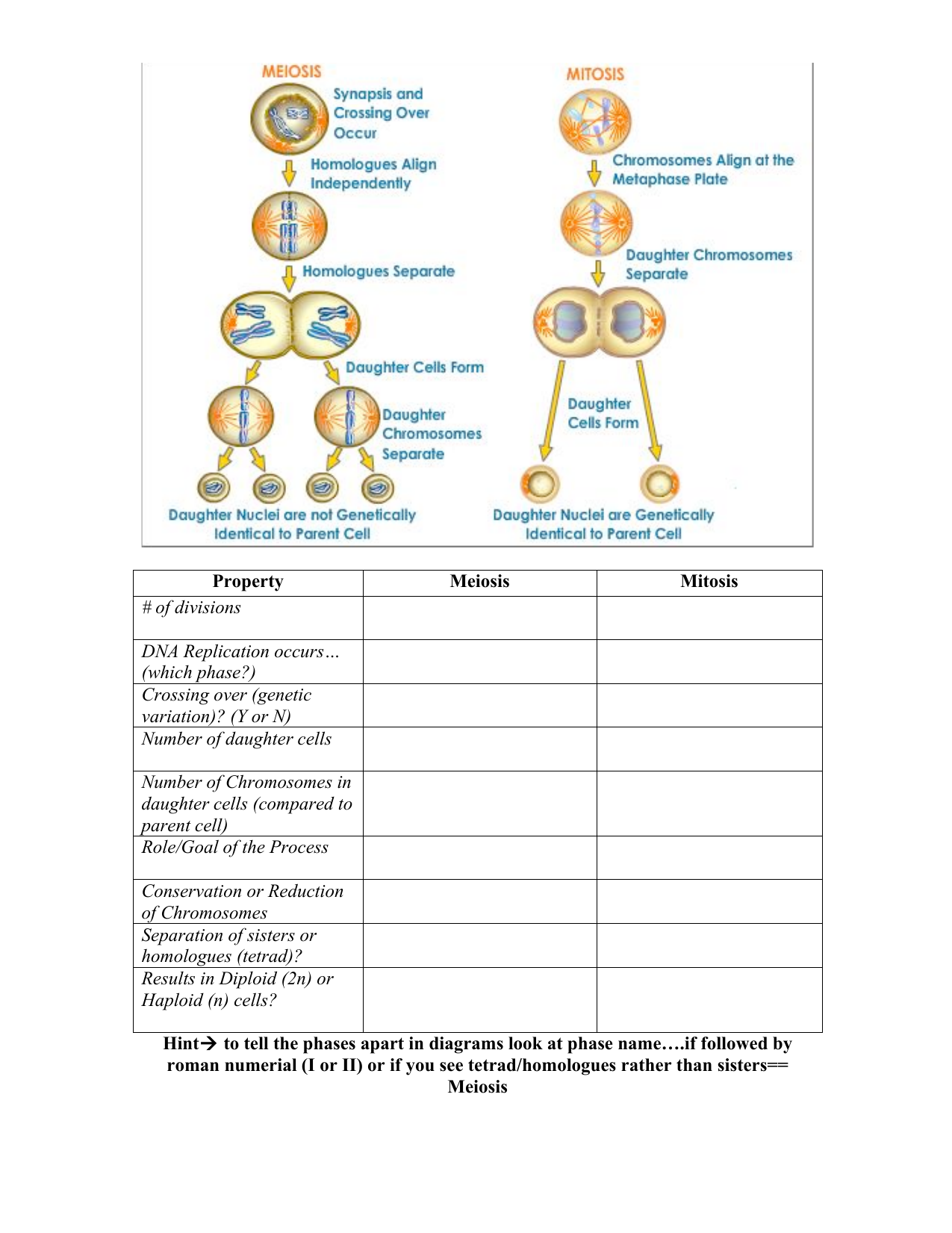
Mitosis And Meiosis Stages Meiosis i: this is also referred to as the reduction division in which the chromosome content of the daughter cell is reduced to half of that of the mother cell. as in mitotic division, meiosis i is preceded by replication of the dna content of the dividing cell. the first phase of meiosis i is the prophase. this goes through 5 stages as follows:. The difference between the two processes is that mitosis occurs in non reproductive cells, or somatic cells, and meiosis occurs in the cells that participate in sexual reproduction, or germ cells. you can navigate to specific sections of this handout by clicking the links below. mitosis: pg. 1 meiosis: pg. 4 mitosis vs. meiosis: pg. 7. Lecture 1: mitosis and meiosis. . 4, # 4 1 – 4 4, 4 7 – 4 10, 4 16in this lecture we review mitosis, the process by which the chromosomes of somatic cells are apportioned equally. to two daughter cells during division. mitosis ensures that all of our cell. inherit the same genetic information. we will compare mitosis with meiosis, which is the. Mitosis: • division of somatic cells for growth repair • parent cell (46 chromosomes 23 pairs) 2 daughter cells each with 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) • one dna replication (copying) followed by one division . draw a diagram in the space below to illustrate this process . meiosis: • production of 4 gametes from one germ line cell.

Assignment 4 Genetics Doc Biology 103 Assignment 4 Meiosis Mitosis Lecture 1: mitosis and meiosis. . 4, # 4 1 – 4 4, 4 7 – 4 10, 4 16in this lecture we review mitosis, the process by which the chromosomes of somatic cells are apportioned equally. to two daughter cells during division. mitosis ensures that all of our cell. inherit the same genetic information. we will compare mitosis with meiosis, which is the. Mitosis: • division of somatic cells for growth repair • parent cell (46 chromosomes 23 pairs) 2 daughter cells each with 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) • one dna replication (copying) followed by one division . draw a diagram in the space below to illustrate this process . meiosis: • production of 4 gametes from one germ line cell.

Comments are closed.