Goal Directed Medical Therapy For Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction

Guidelineвђђdirected Medical Therapy For Patients With Heart Failure W Guideline directed medical therapy: hf: heart failure: hfimpef: heart failure with improved ejection fraction: hfmref: heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction: hfpef: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: hfref: heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: icd: implantable cardioverter defibrillator: ife: immunofixation. Introduction. heart failure (hf) is a common clinical syndrome in which symptoms result from a structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the ventricle to fill with or eject blood. hf may be caused by disease of the myocardium, pericardium, endocardium, heart valves, vessels, or by metabolic disorders [1].
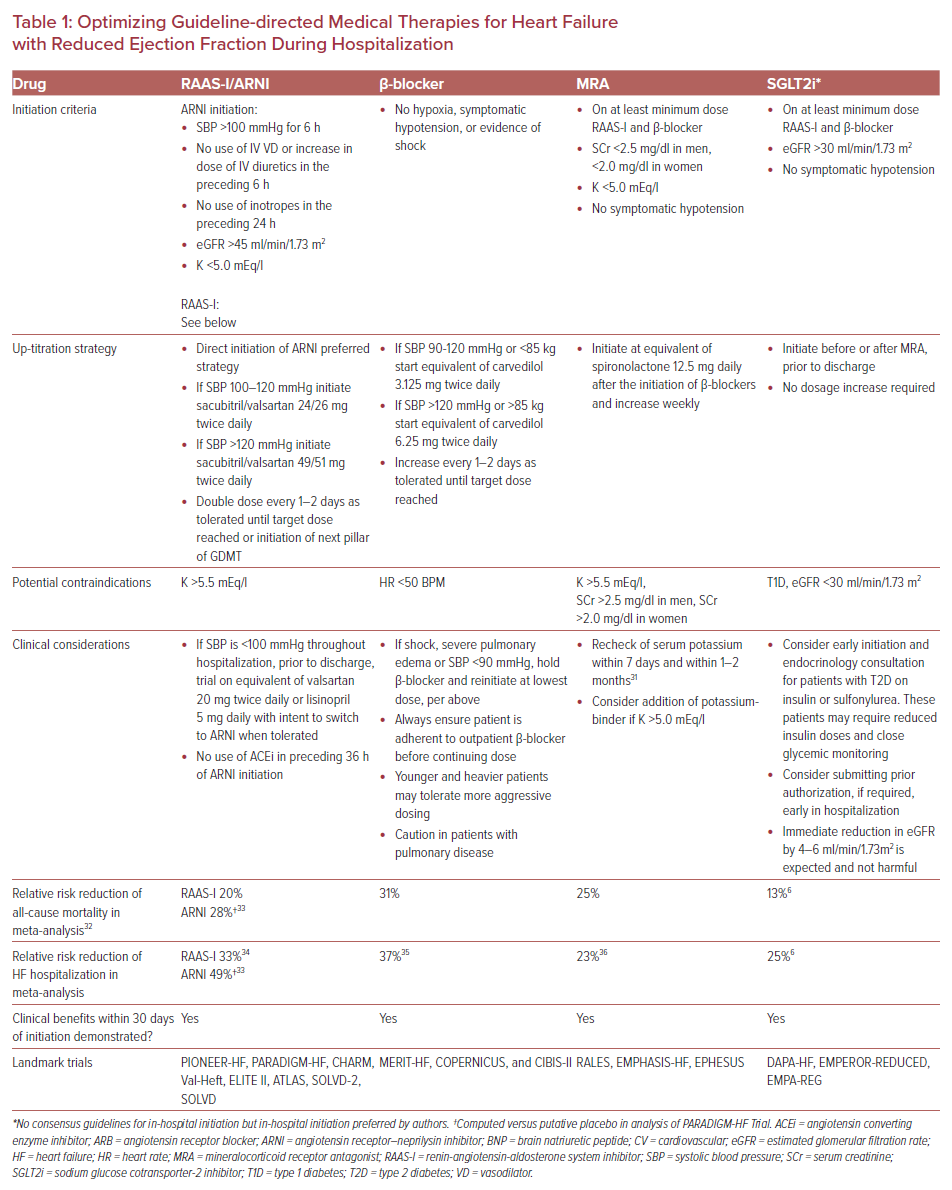
Optimizing Gdmt For Hfref During Hospitalization Guideline directed medical therapy (gdmt) for heart failure (hf) with reduced ejection fraction (hfref) now includes 4 medication classes that include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (sglt2i). Heart failure (hf) encompasses a broad range of left ventricular (lv) function. new treatment guidelines address the entire spectrum of hf. the classification of hf is as follows: hfref (hf with reduced ejection fraction [ef]): lvef ≤40%; hfimpef (hf with improved ef): previous lvef ≤40% and follow up measurement of lvef >40%; hfmref (hf. The 2022 guideline from the american college of cardiology, american heart association, and heart failure society of america provides practical recommendations for preventing, diagnosing, and managing patients with heart failure. this article summarizes the most important of these recommendations, specifically for managing patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (hfref), and. Guideline directed medical therapy (gdmt) for heart failure (hf) with reduced ejection fraction (hfref) now includes 4 medication classes which include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (sglt2i). patients with advanced hf who wish to prolong survival should be referred to a team specialized in hf.
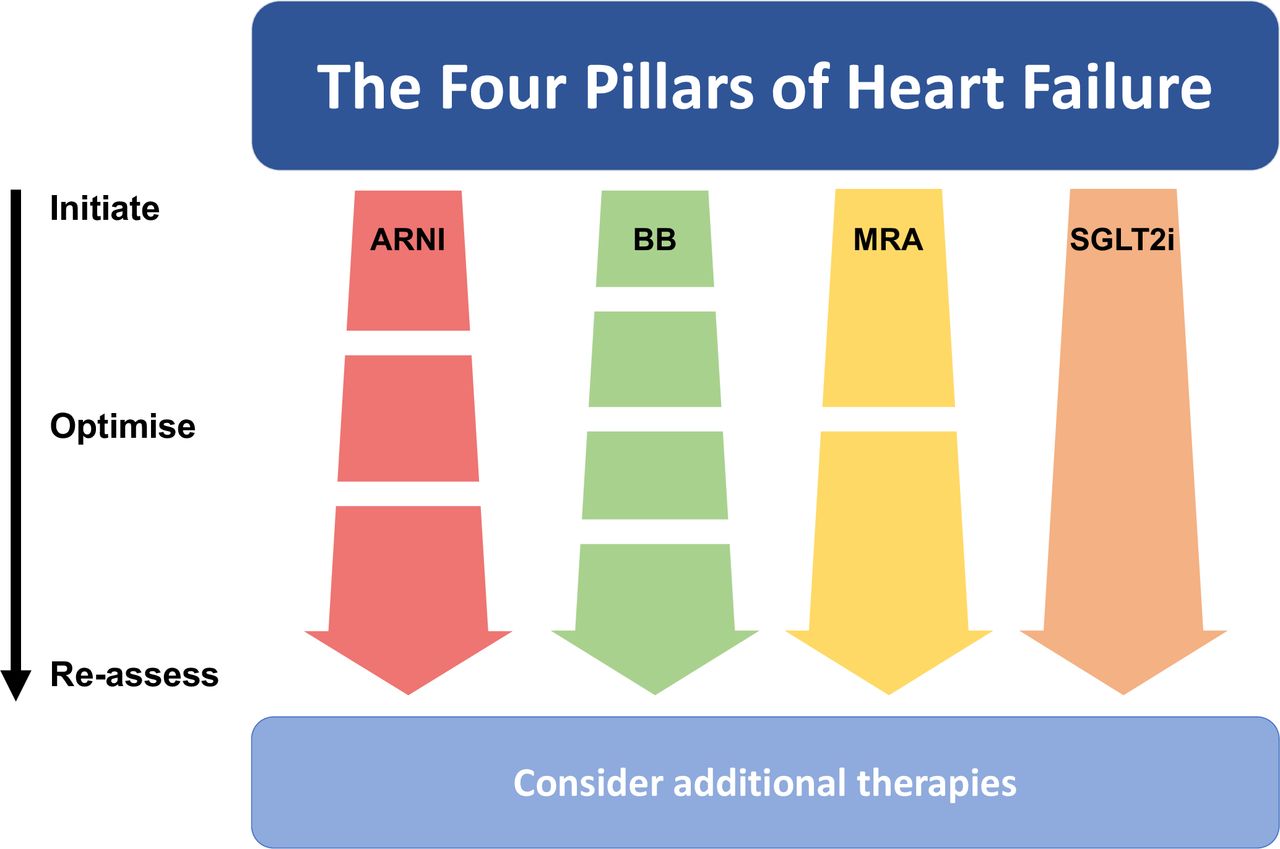
Four Pillars Of Heart Failure Contemporary Pharmacological Therapy For The 2022 guideline from the american college of cardiology, american heart association, and heart failure society of america provides practical recommendations for preventing, diagnosing, and managing patients with heart failure. this article summarizes the most important of these recommendations, specifically for managing patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (hfref), and. Guideline directed medical therapy (gdmt) for heart failure (hf) with reduced ejection fraction (hfref) now includes 4 medication classes which include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (sglt2i). patients with advanced hf who wish to prolong survival should be referred to a team specialized in hf. 1. guideline directed medical therapy (gdmt) for heart failure (hf) with reduced ejection fraction (hfref) now includes 4 medication classes which include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (sglt2i). 5. It is well known that neurohormonal antagonists (β‐blocker, renin‐angiotensin system blocker [rasb], and aldosterone antagonist [aa]) reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (hfref). 1 β‐blocker and rasb are recommended as class ia indications (unless contraindicated or not tolerated) in all symptomatic patients by the current.

Comments are closed.