Gravitation Class 10 Ssc Kepler S Laws Of Planetary Motion Newton S

Gravitation Class 10 Ssc Kepler S Laws Of Planetary Motion Newton S All lectures: playlist?list=plj krueksaznpivm4jpz781u7oxy tm1jtelegram channel: t.me parthmomayaofficialgravitation class 10 ssc. Gravitation class 10 ssc maharashtra state board. kepler's laws of planetary motion, newton's law of gravitation.hello everyone,this is akshay upadhyay wel.

Gravitation Class 10 Ssc Kepler S Laws Of Planetary Motion Newton S Kepler’s law of orbits – the planets move around the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one of the focii. kepler’s law of areas – the line joining a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal interval of time. kepler’s law of periods – the square of the time period of the planet is directly proportional to the cube of. The shorter the orbit of the planet around the sun, the shorter the time taken to complete one revolution. using the equations of newton’s law of gravitation and laws of motion, kepler’s third law takes a more general form. p 2 = 4π 2 [g(m 1 m 2)] × a 3. where m 1 and m 2 are the masses of the two orbiting objects in solar masses. 8.2 kepler’s laws 8.3 universal law of gravitation 8.4 the gravitational constant 8.5 acceleration due to gravity of the earth 8.6 acceleration due to gravity below and above the surface of earth 8.7 gravitational potential energy 8.8 escape speed 8.9 earth satellites 8.10energy of an orbiting satellite 8.11 geostationary and polar satellites. Kepler’s laws question 4: a satellite is orbiting just above the surface of the earth with period t. if d is the density of the earth and g is the universal constant of gravitation, the quantity 3 π g d represents: t. t 2. t 3. √t. answer (detailed solution below) option 2 : t 2.
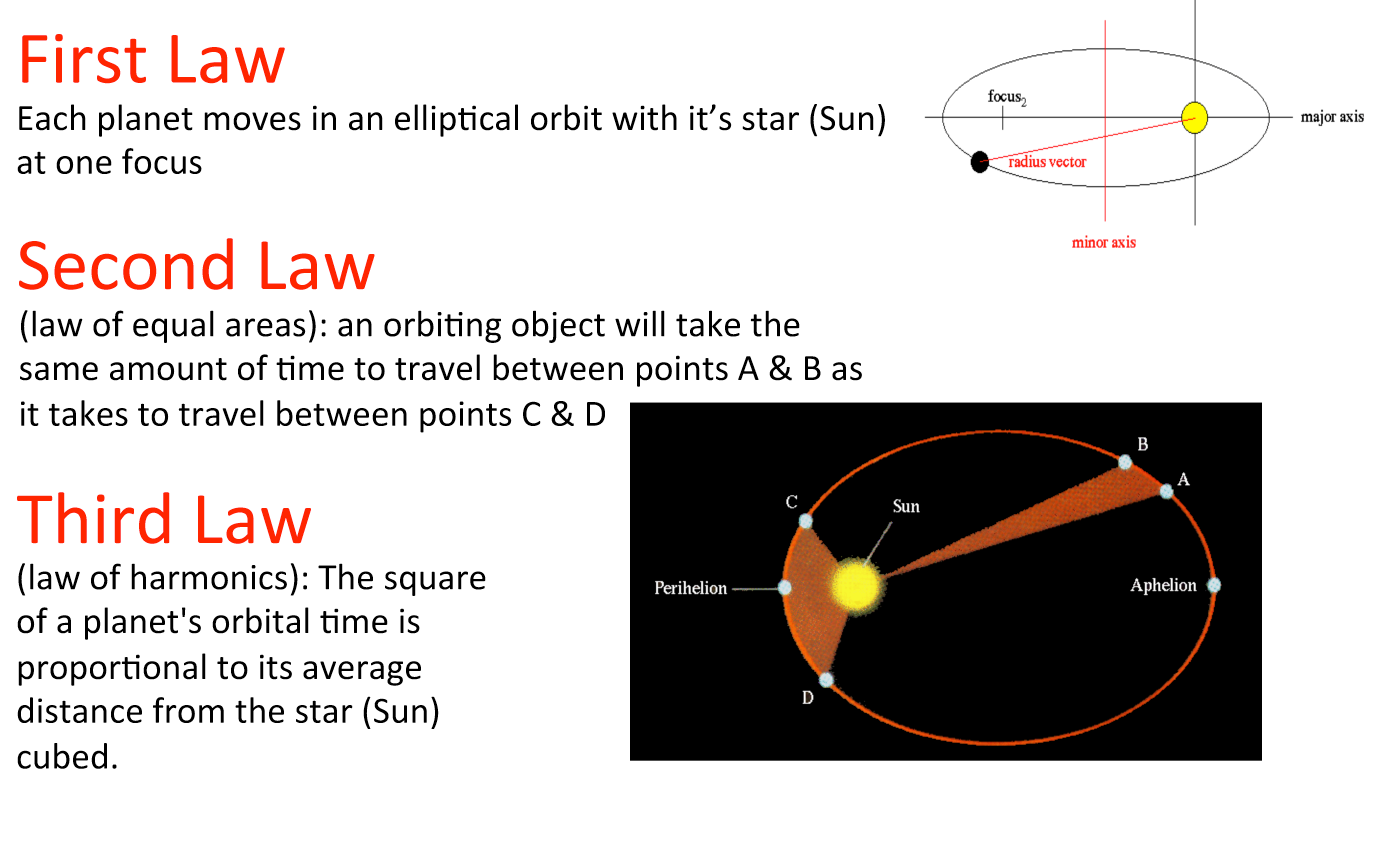
таьюааkeplerюаб юааsюаб юааlawsюаб юааof Planetaryюаб юааmotionюаб таэ Slide Of юааkeplerюабтащюааsю 8.2 kepler’s laws 8.3 universal law of gravitation 8.4 the gravitational constant 8.5 acceleration due to gravity of the earth 8.6 acceleration due to gravity below and above the surface of earth 8.7 gravitational potential energy 8.8 escape speed 8.9 earth satellites 8.10energy of an orbiting satellite 8.11 geostationary and polar satellites. Kepler’s laws question 4: a satellite is orbiting just above the surface of the earth with period t. if d is the density of the earth and g is the universal constant of gravitation, the quantity 3 π g d represents: t. t 2. t 3. √t. answer (detailed solution below) option 2 : t 2. While kepler's law is specific to the motion of celestial bodies, newton's law is a more general principle that extends beyond celestial mechanics. newton's law of universal gravitation applies to any two objects with mass, regardless of their location or size. it is a fundamental law of physics that governs the behavior of objects on earth and. Show how newton’s law of univer sal gravitation can be applied to de riving keplar’s laws of planetary motion. newton’s law of gravitation says that the force on a planet of mass mexerted by another planet (or star) of mass m is given by the familiar inverse square law, and has magnitude f= gmm r2; where ris the distance separating the.

Comments are closed.