Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of

Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of Four overarching themes were used to explain the qualitative data: integrated and individualised care; formal (including training) vs experiential knowledge; the interaction between dementia and hearing and using the technology. , – the self selecting nature of the sample is a limitation which needs to be taken into account when considering. Abstract. purpose – the purpose of this paper is to explore audiologists, views and experiences of working with older adults with dementia. design methodology approach – an online survey was.
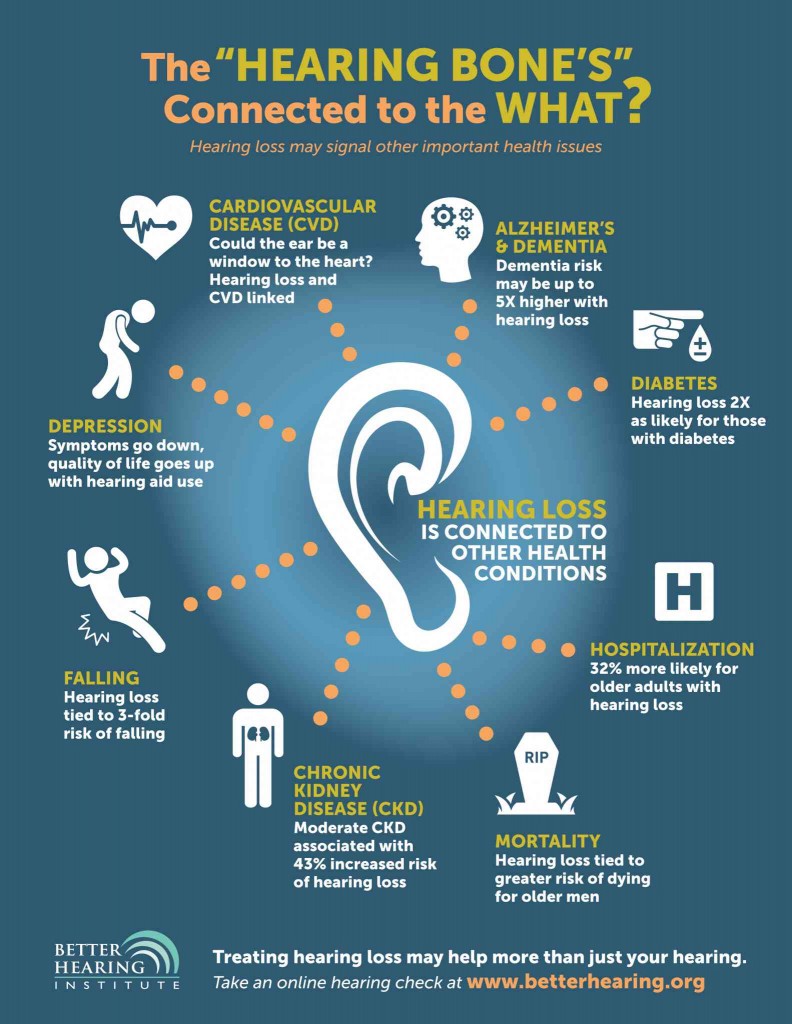
Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of Dive into the research topics of 'hearing loss and dementia: an exploratory study of the views of audiologists'. together they form a unique fingerprint. older adult nursing and health professions 100%. It was demonstrated that the vast majority of audiologists had treated someone with dementia, and 65 per cent of respondents did not feel adequately supported to help this service user population. purpose – the purpose of this paper is to explore audiologists, views and experiences of working with older adults with dementia. design methodology approach – an online survey was distributed to. – given the anticipated increase in rates of dementia within the population and the potential for hearing impairment to exacerbate the symptoms; this study highlights the unique role audiologists have. Introduction. hearing loss in midlife has been estimated to account for 9% of cases of dementia, a huge (but potentially reversible) disease burden given that dementia affects 47 million people worldwide (livingston et al., 2017). acquired hearing loss is most commonly caused by cochlear damage, while dementia is due to cortical degeneration.
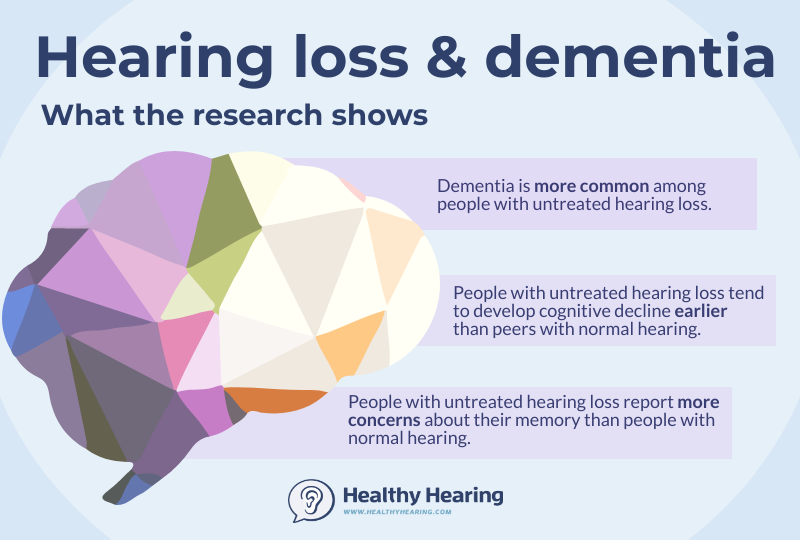
Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of – given the anticipated increase in rates of dementia within the population and the potential for hearing impairment to exacerbate the symptoms; this study highlights the unique role audiologists have. Introduction. hearing loss in midlife has been estimated to account for 9% of cases of dementia, a huge (but potentially reversible) disease burden given that dementia affects 47 million people worldwide (livingston et al., 2017). acquired hearing loss is most commonly caused by cochlear damage, while dementia is due to cortical degeneration. Hearing loss is an important risk factor for the development of dementia, particularly alzheimer's disease (ad). mid life hearing loss increases the risk of developing dementia by double any other single factor. however, given this strong connection between hearing loss and ad, the mechanisms responsible for this link are still unknown. In this prospective population based study, subjective informant based hearing difficulties were associated with development of dementia, whereas objective measures on formal behavioural audiometry were predictive of poorer performance on cognitive testing over time but not the development of dementia. other factors related to central processing might potentiate the effects of peripheral.

Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of Hearing loss is an important risk factor for the development of dementia, particularly alzheimer's disease (ad). mid life hearing loss increases the risk of developing dementia by double any other single factor. however, given this strong connection between hearing loss and ad, the mechanisms responsible for this link are still unknown. In this prospective population based study, subjective informant based hearing difficulties were associated with development of dementia, whereas objective measures on formal behavioural audiometry were predictive of poorer performance on cognitive testing over time but not the development of dementia. other factors related to central processing might potentiate the effects of peripheral.

Hearing Loss And Dementia An Exploratory Study Of The Views Of

Comments are closed.