Heating Curves Phase Diagrams Mr Pauller

Heating Curves Phase Diagrams Mr Pauller Youtube This video discusses the heating curve and phase diagram for water. What is a phase diagram? fully explained phase diagrams. fully explained heating curves of any substance.

Heating And Cooling Curves Explained The basics of the phase diagram and the heating curve are explained, including in the latter case, the concept of latent heat. these are two different types. Boil water. heat steam from 100 °c to 120 °c. the heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: q = m × c × Δ t (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). the heat needed to induce a given change in phase is given by q = n × Δ h. using these equations with the appropriate values for specific. The energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 2.5.1 2.5. 1. Δ h is positive for any transition from a more ordered to a less ordered state and negative for a transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state. previously, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical processes. The compound cholesteryl benzoate is a rod like molecule that undergoes a phase change from the solid to the liq uid crystal phase at 145.5 °c. when cholesteryl benzoate is mixed with cholesteryl oleyl carbonate, a molecule with a curved shape, the temperature of the solid to liquid crys tal transition changes.
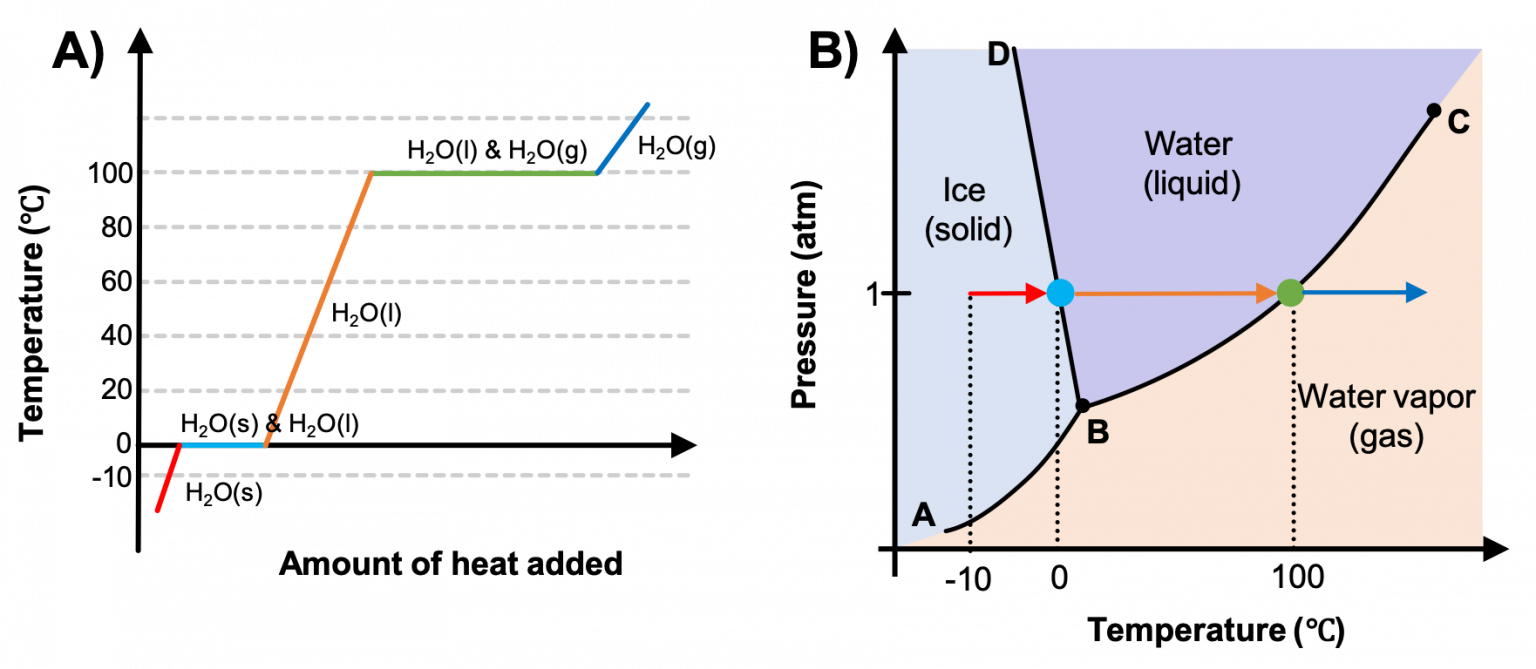
M11q2 Heating Curves And Phase Diagrams вђ Chem 103 104 Resource Book The energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 2.5.1 2.5. 1. Δ h is positive for any transition from a more ordered to a less ordered state and negative for a transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state. previously, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical processes. The compound cholesteryl benzoate is a rod like molecule that undergoes a phase change from the solid to the liq uid crystal phase at 145.5 °c. when cholesteryl benzoate is mixed with cholesteryl oleyl carbonate, a molecule with a curved shape, the temperature of the solid to liquid crys tal transition changes. Phase diagrams (plots of pressure vs. temperature) were correlated with heating curves (plots of temperature vs. energy). these two types of plots provide complementary information on the phase transitions of substances. while a heating curve provides information on the phase changes at a single pressure, the phase diagram depicts the phase. Key concepts and summary. phase diagrams (plots of pressure vs. temperature) were correlated with heating curves (plots of temperature vs. energy). these two types of plots provide complementary information on the phase transitions of substances. while a heating curve provides information on the phase changes at a single pressure, the phase.

Comments are closed.