Hemostasis Blood Clotting Platelet Plug Formation Easy Flowchart

Platelet Plug Formation Primary Hemostasis Video Osmosis Hemostasis is stoppage of bleeding. there are 3 main stages of hemostasis1. vasoconstriction2. platelet plug formation3. coagulation of bloodall the stages a. Introduction. hemostasis is the coordinated physiological mechanisms that prevent and stop blood loss after injury. this coordinated response involves two main phases: 1. primary hemostasis: tiny platelets rush to the scene, sticking to the injured vessel wall and each other (platelet aggregation), forming a temporary plug at the injury site within seconds to stop the ble.

Hemostasis Blood Clotting Platelet Plug Formation Easy Flowchart Summary. platelet plug formation, also known as primary hemostasis, is the first step of hemostasis and is the process where a platelet plug forms to prevent further loss of blood from a damaged vessel. it is divided into five stages: endothelial injury, exposure, adhesion, activation, and aggregation. after the platelet plug is formed, it is. Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting) primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. to accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and activate. that activation means they can “recruit” more platelets to form a platelet “plug” to stop blood loss from the damaged area. Vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) to reduce blood flow to the injured area. platelet plug formation: platelets clump together to form a temporary seal at the injury site. coagulation (blood clotting): a cascade of enzymatic reactions that converts fibrinogen (a soluble protein) into fibrin (an insoluble mesh) to form a stable clot. Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. hemostasis involves three basic steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting factors promote the formation of a fibrin clot. fibrinolysis is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel.
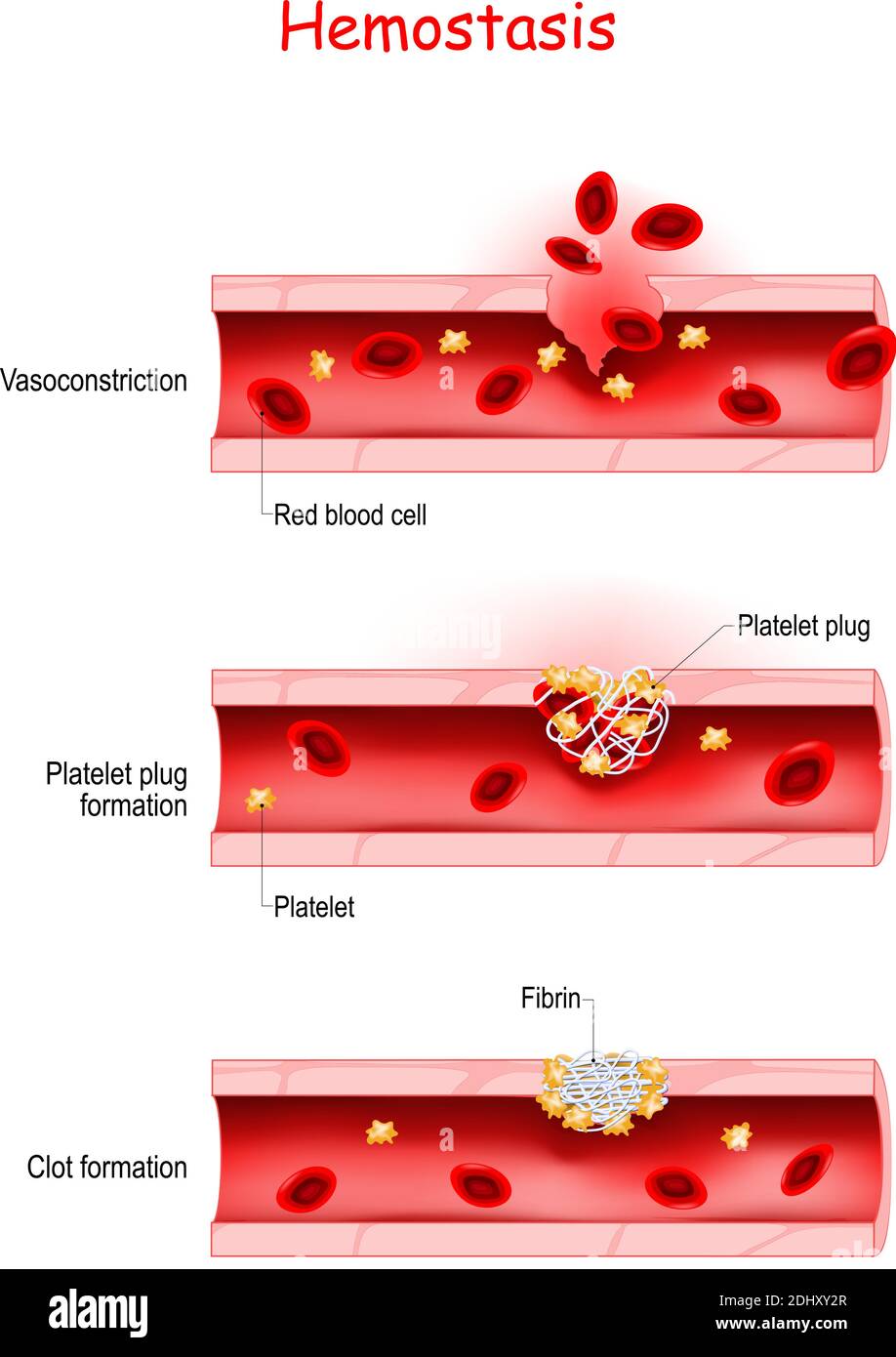
Hemostasis Basic Steps Of Wound Healing Process Platelet Plug Vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) to reduce blood flow to the injured area. platelet plug formation: platelets clump together to form a temporary seal at the injury site. coagulation (blood clotting): a cascade of enzymatic reactions that converts fibrinogen (a soluble protein) into fibrin (an insoluble mesh) to form a stable clot. Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. hemostasis involves three basic steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting factors promote the formation of a fibrin clot. fibrinolysis is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel. 1) constriction of the blood vessel. 2) formation of a temporary “platelet plug." 3) activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot. purpose. hemostasis facilitates a series of enzymatic activations that lead to the formation of a clot with platelets and fibrin polymer. Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. hemostasis involves three basic steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting factors promote the formation of a fibrin clot. fibrinolysis is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel.

Comments are closed.