How Does Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Derifit

How Does Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Derifit In contrast, deserts have the lowest primary productivity. in marine ecosystems, primary productivity is highest in shallow, nutrient rich waters, such as coral reefs and algal beds. to show the flow of energy through ecosystems, food chains are sometimes drawn as energy pyramids. each step of the pyramid represents a different trophic level. As illustrated in figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2, large amounts of energy are lost from the ecosystem from one trophic level to the next level as energy flows from the primary producers through the various trophic levels of consumers and decomposers. figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2: this conceptual model shows the flow of energy through a spring ecosystem in.

How Does Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Derifit Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. This allows chemoautotrophs to synthesize complex organic molecules, such as glucose, for their own energy and in turn supplies energy to the rest of the ecosystem. figure 56.2.1 56.2. 1: swimming shrimp, a few squat lobsters, and hundreds of vent mussels are seen at a hydrothermal vent at the bottom of the ocean. An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their abiotic (non living) environment. ecosystems can be small, such as the tide pools found near the rocky shores of many oceans, or large, such as those found in the tropical rainforest of the amazon in brazil (figure 20.2). Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. [2][3] each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. [1] in order to more efficiently show the quantity.
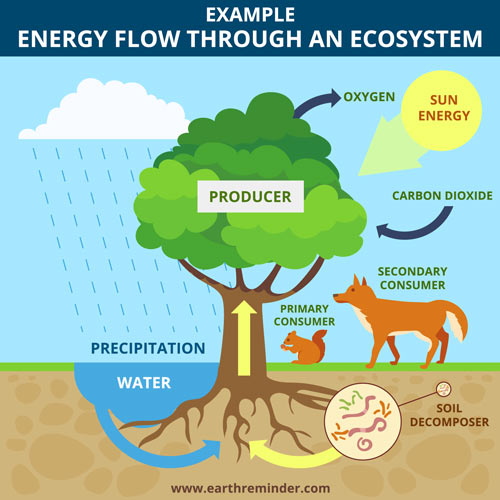
How Does Energy Flow Through An Ecosystem Earth Reminder An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their abiotic (non living) environment. ecosystems can be small, such as the tide pools found near the rocky shores of many oceans, or large, such as those found in the tropical rainforest of the amazon in brazil (figure 20.2). Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. [2][3] each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. [1] in order to more efficiently show the quantity. Energy flow through ecosystems. learning objectives. after studying this chapter, you should be able to: list the levels of organization of living things in the environment. differentiate between food chains and food webs. describe how organisms acquire energy in a food web and in associated food chains. In this section, a variety of ways to depict this movement of energy through an ecosystem will be presented. utilizing multiple representations of data as well as understanding the movement of matter and energy through systems are significant concepts in the ap ® biology course. information presented and the examples highlighted in the section.

Energy Flow Biology Britannica Energy flow through ecosystems. learning objectives. after studying this chapter, you should be able to: list the levels of organization of living things in the environment. differentiate between food chains and food webs. describe how organisms acquire energy in a food web and in associated food chains. In this section, a variety of ways to depict this movement of energy through an ecosystem will be presented. utilizing multiple representations of data as well as understanding the movement of matter and energy through systems are significant concepts in the ap ® biology course. information presented and the examples highlighted in the section.

Comments are closed.