How To Do Randomisation In Research Studies

How To Do Randomisation In Research Studies Youtube To enter a woman into the study, the midwife opened the next consecutively numbered envelope." "block randomization was by a computer generated random number list prepared by an investigator with no clinical involvement in the trial. we stratified by admission for an oncology related procedure. Implementation of randomization in clinical trials is due to a. bradford hill who designed the first randomized clinical trial evaluating the use of streptomycin in treating tuberculosis in 1946 [9, 12, 13]. reference [14] provides a good summary of the rationale and justification for the use of randomization in clinical trials.
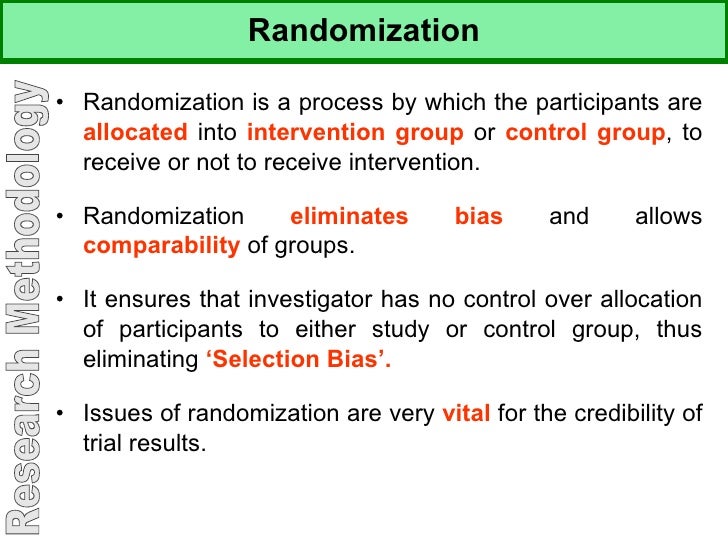
Research Methodology Randomization plays a crucial role in increasing the quality of evidence based studies by minimizing the selection bias that could affect the outcomes. in general, randomization places programming for random number generation, random allocation concealment for security, and a separate random code manager. The randomized controlled trial (rct) has been recognized as the most credible research design for investigations of the clinical effectiveness of new medical interventions [1, 2]. evidence from rcts is widely used as a basis for submissions of regulatory dossiers in request of marketing authorization for new drugs, biologics, and medical. Simple randomisation is a fair way of ensuring that any differences that occur between the treatment groups arise completely by chance. but – and this is the first but of many here – simple randomisation can lead to unbalanced groups, that is, groups of unequal size. this is particularly true if the trial is only small. Studies that use simple random assignment are also called completely randomized designs. random assignment is a key part of experimental design. it helps you ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study: any differences between them are due to random factors, not research biases like sampling bias or selection bias.

Comments are closed.