How To Find The Conjugate In Math

Conjugate In Math Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript It can help us move a square root from the bottom of a fraction (the denominator) to the top, or vice versa. read rationalizing the denominator to find out more: example: move the square root of 2 to the top: 1 3−√2. we can multiply both top and bottom by 3 √2 (the conjugate of 3−√2), which won't change the value of the fraction: 1 3. Either ˉz or z∗ denotes the complex conjugate of z. the complex conjugate has the same real part as z and the imaginary part with the opposite sign. that means, if z = a ib is a complex number, then z∗ = a − ib will be its conjugate. in the polar form of a complex number, the conjugate of re^iθ is given by re^−iθ.
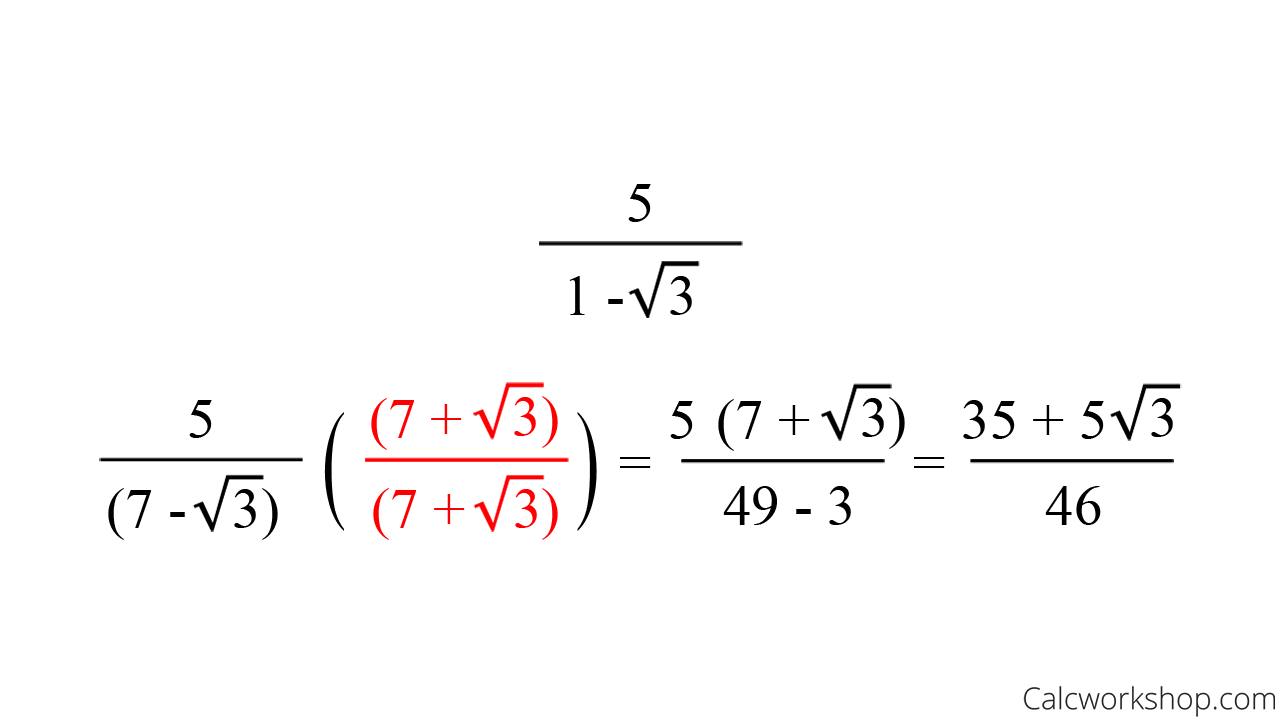
How To Rationalize Using Conjugates 13 Surefire Examples Conjugates in math are two pairs of binomials with identical terms but sharing opposite operations in the middle. below are a few more examples of pairs of conjugates: x – y and x y. 2√2 – 1 and 2√2 1. 3 – 2i and 3 2i. consistent with the definition of conjugates, each pair have identical terms, and each only differs by the sign. The complex conjugate of a complex number z = x iy is x iy (and vice versa) and it is represented by ¯z z ¯ as their sum (2x) and the product x 2 y 2 both are rational numbers. to write the complex conjugate, write the given complex number in the form of x iy (real part first and then the imaginary part) change the middle sign. Rationalize complex numbers by multiplying with conjugate step by step. the conjugate of a complex number has the same real part and the imaginary part has the same magnitude with the opposite sign. the conjugate of a complex number a bi is a bi. to find the conjugate of a complex number change the sign of the imaginary part of the complex. Example 1. multiply x 5 by its conjugate. 1) start by finding the conjugate. since the given binomial has a , its conjugate will have a . the conjugate of x 5 is x − 5. 2) use foil to.

Comments are closed.