How To Read An Nmr Spectrum
How To Read Nmr Spectra 7 Trick Or Basic Steps Chemistry Notes Page id. nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) interpretation plays a pivotal role in molecular identifications. as interpreting nmr spectra, the structure of an unknown compound, as well as known structures, can be assigned by several factors such as chemical shift, spin multiplicity, coupling constants, and integration. 6.6.2 chemical shift. as seen in the 1 h nmr spectrum of methyl acetate (fig. 6.6a), the x axis units of nmr spectrum are in ppm (not in hz as we would expect for frequency), and the two signals stand at different position along the x axis. let’s explain how that works and what information can be obtained.

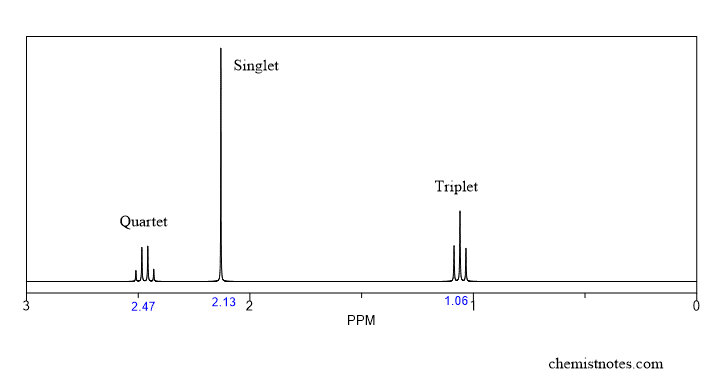
Nmr Spectroscopy An Easy Introduction Chemistry Steps Step 1: ¹h nmr. the first step in structural characterization is 1 dimensional proton ¹h nmr. the chemical shift, multiplicity, coupling constants, and integration are all factors to consider when assigning protons. in this example, only three protons can be assigned by the proton spectrum alone: protons 3, 4, and 6. chemical shift (ppm). Expected product: 1 h nmr: the ratio of protons is 2:3:3. solution. yes, ethyl acetate was synthesized. first, the ratio of protons equals the number of protons in our expected product. the peak at 1.20 ppm is a triplet that integrates to 3 protons. the integration indicates that the peak corresponds to a methyl group. Part 1: nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (nmr spectroscopy) – an overview. the following steps summarize the process: count the number of signals to determine how many distinct proton environments are in the molecule (neglecting, for the time being, the possibility of overlapping signals). use chemical shift tables or charts to. In nmr spectroscopy, predicting resonances and reading an nmr spectrum is crucial for interpreting the structure of unknown compounds. by analyzing factors such as chemical shift, spin multiplicity, coupling constants, and integration, the peaks can provide valuable information about the number of different hydrogen environments present.
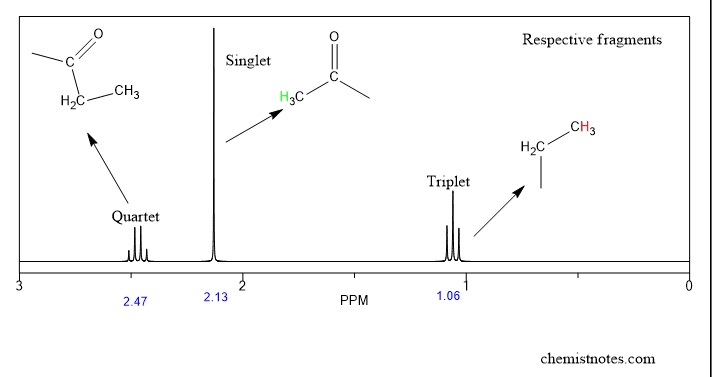
How To Read Nmr Spectra 7 Trick Or Basic Steps Chemistry Notes Part 1: nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (nmr spectroscopy) – an overview. the following steps summarize the process: count the number of signals to determine how many distinct proton environments are in the molecule (neglecting, for the time being, the possibility of overlapping signals). use chemical shift tables or charts to. In nmr spectroscopy, predicting resonances and reading an nmr spectrum is crucial for interpreting the structure of unknown compounds. by analyzing factors such as chemical shift, spin multiplicity, coupling constants, and integration, the peaks can provide valuable information about the number of different hydrogen environments present. 1. 1h nmr is the go to technique to help identify or confirm the structure of organic compounds. a solution state proton spectrum is relatively fast to acquire and a lot of information about the structure of a compound can be deduced from it. with centuries of combined experience in nmr data interpretation, we thought we’d share the basics of. With chemical shift information available, we can now assign the signals in the 1 h nmr spectrum of methyl acetate. according to fig. 6.6c, the protons in the ch 3 group beside the c=o bond are supposed to be in the range of 2–3 ppm, and protons in the ch 3 group connected with o directly have δ value of about 3–4 ppm.

Comments are closed.