Hyponatremia Approach
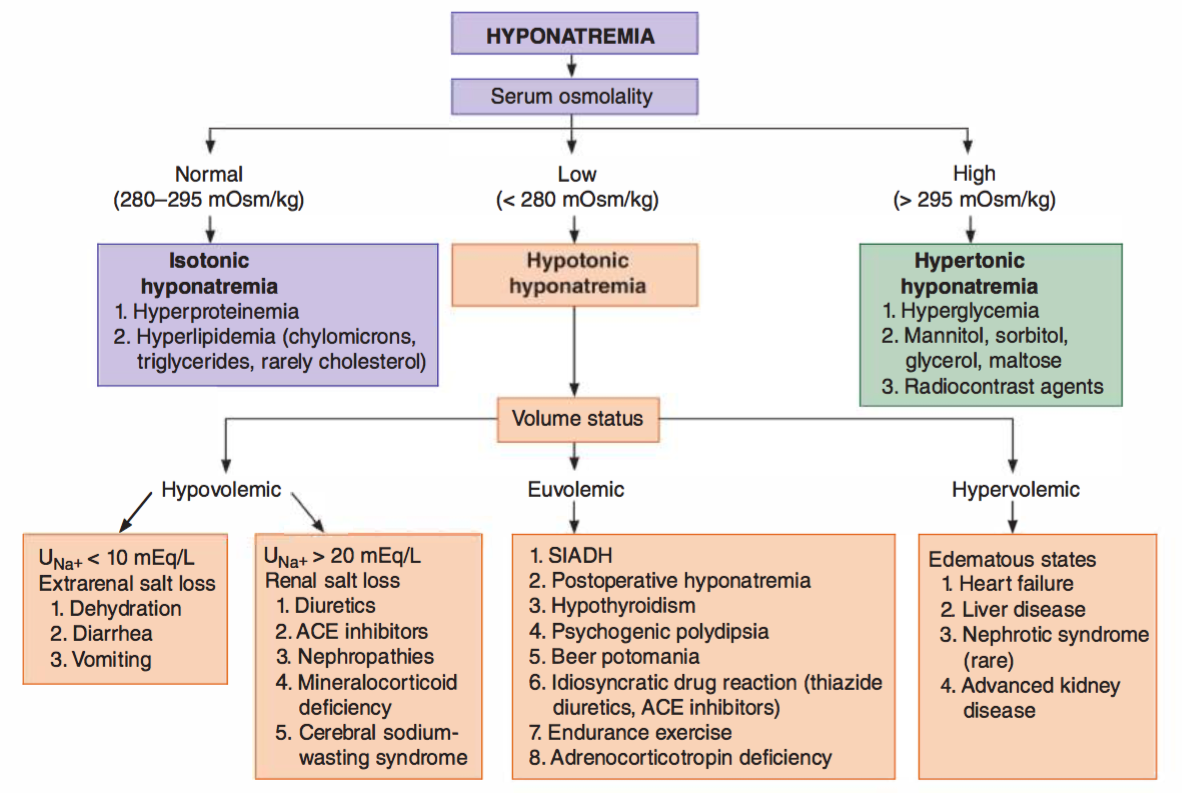
Hyponatremia Flowchart Hyponatremia can be classified according to the volume status of the patient as hypovolemic, hypervolemic, or euvolemic. koay es. cases in chemical pathology: a diagnostic approach. 3d ed. Mild hyponatremia is characterized by gastrointestinal tract symptoms nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite. sometimes, subtle neurologic abnormalities may be present when the serum sodium is between 120 and 130 meq l. hyponatremia in the elderly may manifest with frequent falls and gait disturbances.
Hyponatremia Harrison S Manual Of Medicine Learn how to diagnose the causes and treatment of hyponatremia, a low serum sodium concentration, in adults. this article reviews the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnostic approach of hyponatremia. Learn how to evaluate and treat adults with hyponatremia, a condition of low serum sodium caused by water excess or deficit. find out the goals, rates, and methods of correction, as well as the common pitfalls and complications. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l but can vary to some extent depending upon the set values of varied laboratories.[1] hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality caused by an excess of total body water in comparison to that of the total body sodium content. edelman approved of the fact that serum sodium concentration does not depend on total. Hyponatremia is a secondary cause of osteoporosis. when evaluating patients, clinicians should categorize them according to their fluid volume status (hypovolemic hyponatremia, euvolemic hyponatremia, or hypervolemic hyponatremia). for most patients, the approach to managing hyponatremia should consist of treating the underlying cause.
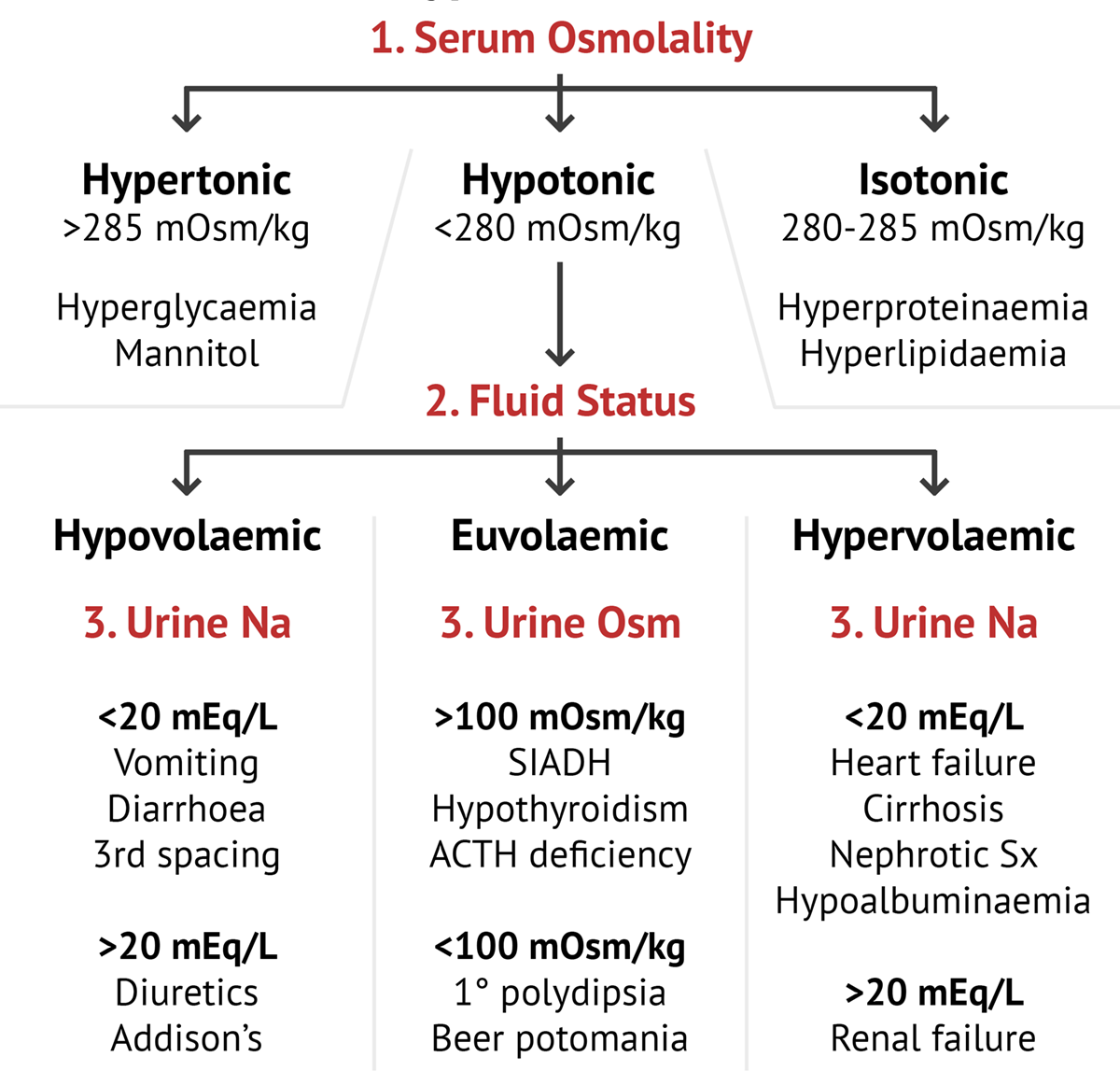
Hyponatraemia Test Findings Medschool Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l but can vary to some extent depending upon the set values of varied laboratories.[1] hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality caused by an excess of total body water in comparison to that of the total body sodium content. edelman approved of the fact that serum sodium concentration does not depend on total. Hyponatremia is a secondary cause of osteoporosis. when evaluating patients, clinicians should categorize them according to their fluid volume status (hypovolemic hyponatremia, euvolemic hyponatremia, or hypervolemic hyponatremia). for most patients, the approach to managing hyponatremia should consist of treating the underlying cause. Learn how to diagnose and treat sodium disorders based on volume status, plasma osmolality, and symptoms. find evidence based recommendations, clinical pearls, and patient handouts for hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Hyponatremia, the most common electrolyte disorder encountered, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality even in its milder forms.1 despite novel pathophysiologic insights, diagnostic approaches, and management options, hyponatremia remains a challenge for clinicians.2,3 in a recent article copublished in the european journal of endocrinology, intensive care medicine, and.
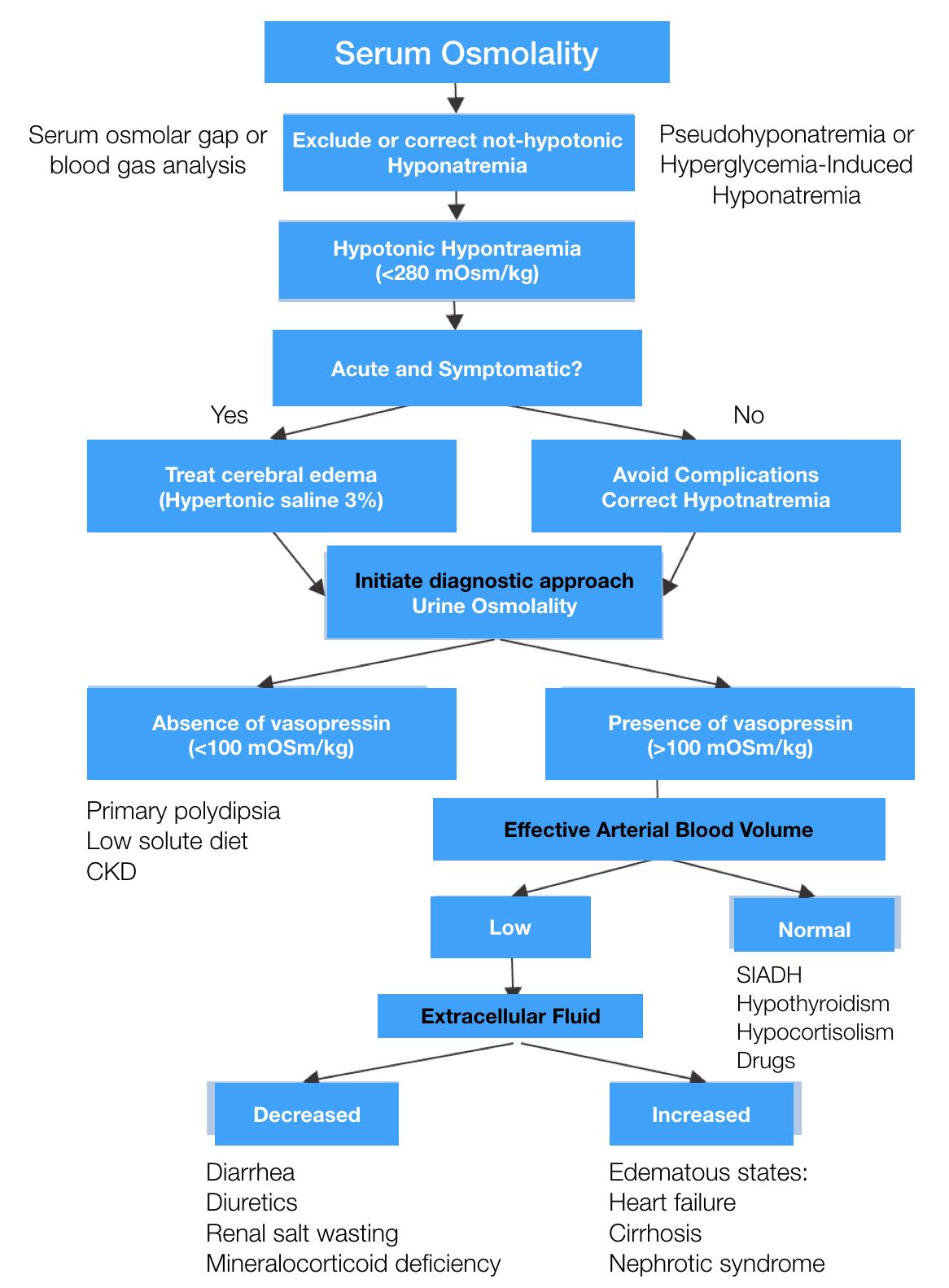
Pathophysiology Based Approach To Hyponatremia Diagnostic Grepmed Learn how to diagnose and treat sodium disorders based on volume status, plasma osmolality, and symptoms. find evidence based recommendations, clinical pearls, and patient handouts for hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Hyponatremia, the most common electrolyte disorder encountered, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality even in its milder forms.1 despite novel pathophysiologic insights, diagnostic approaches, and management options, hyponatremia remains a challenge for clinicians.2,3 in a recent article copublished in the european journal of endocrinology, intensive care medicine, and.

Hyponatremia A Lazy Man S Classification Deranged Physiology

Comments are closed.