Hyponatremia Approach Definition Classification Symptoms Diagnostic
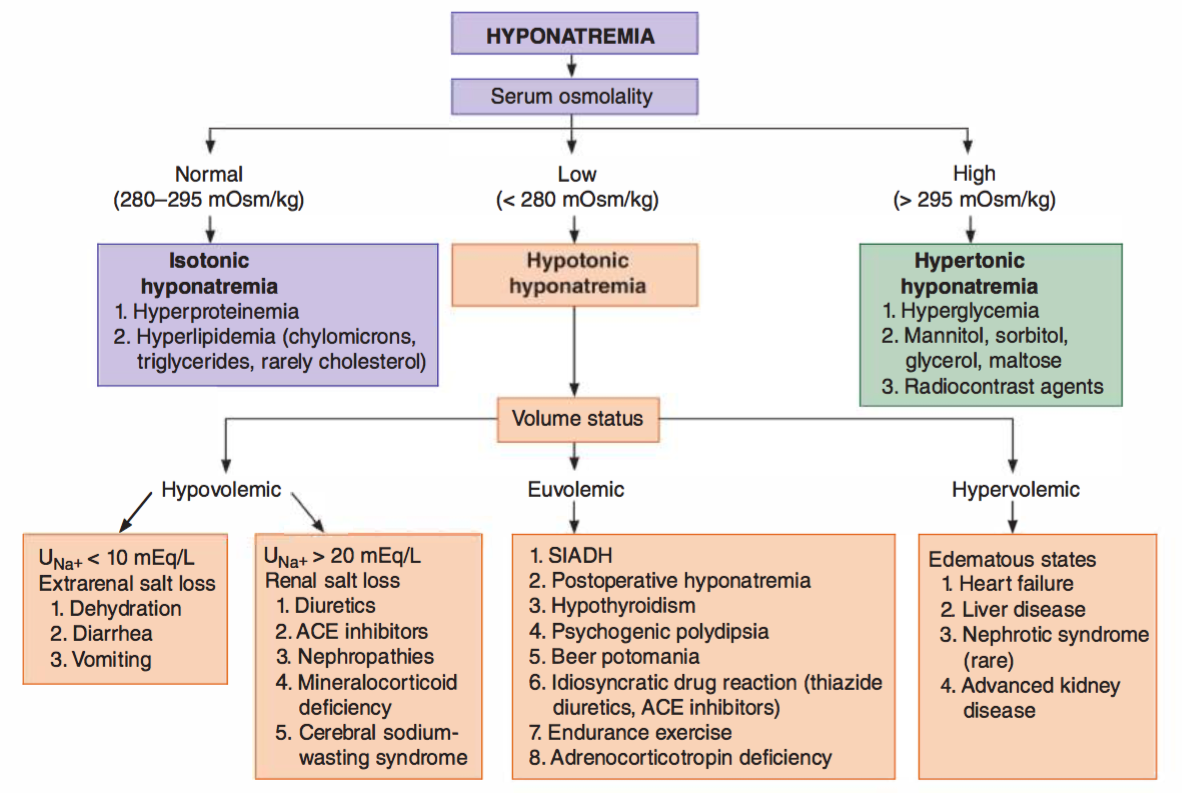
Hyponatremia Flowchart Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l but can vary to some extent depending upon the set values of varied laboratories.[1] hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality caused by an excess of total body water in comparison to that of the total body sodium content. edelman approved of the fact that serum sodium concentration does not depend on total. Hyponatremia and hypernatremia are classified based on volume status (hypovolemia, euvolemia, and hypervolemia). sodium disorders are diagnosed by findings from the history, physical examination.
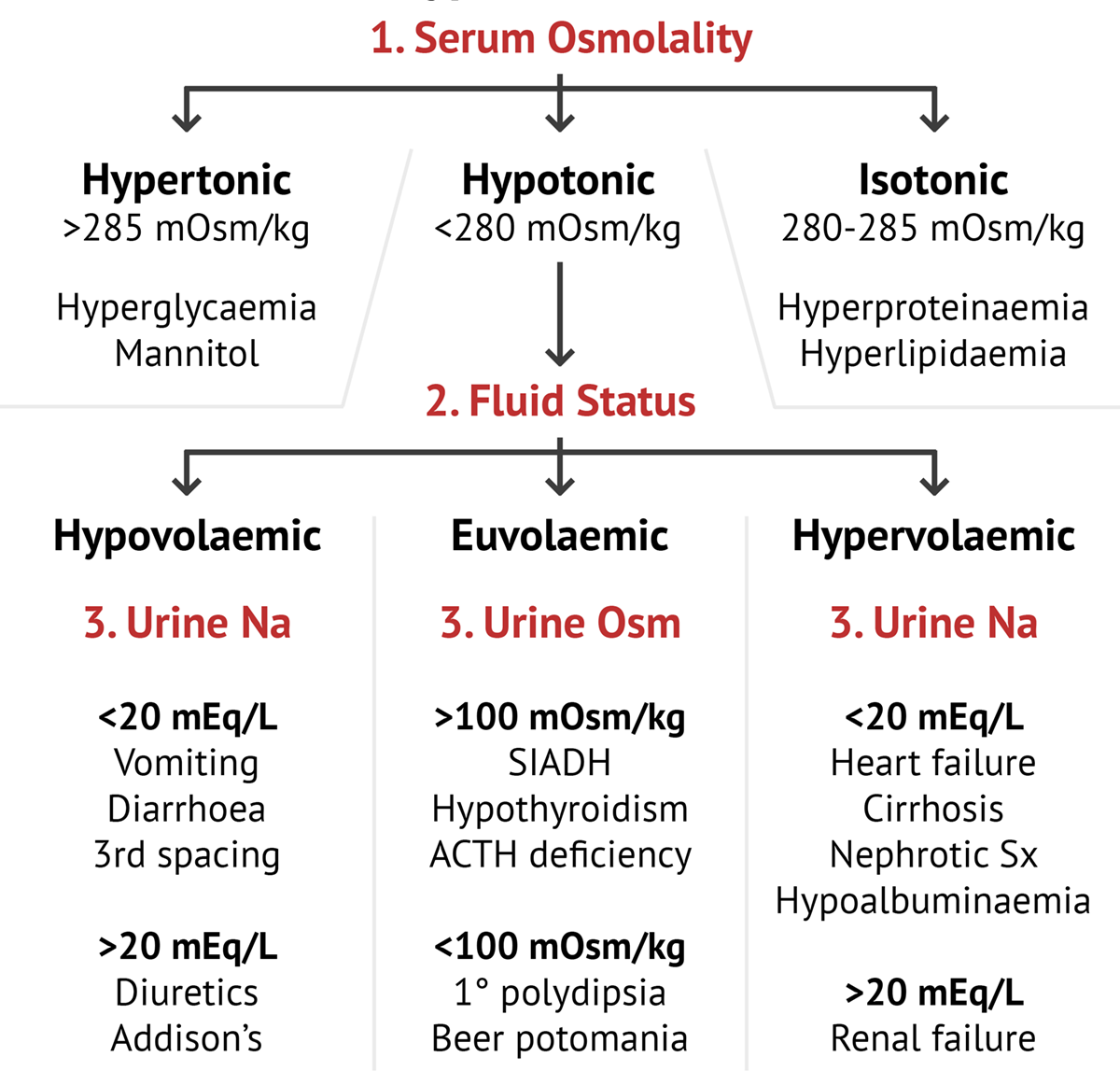
Diagnostic Approach To Hyponatremia Download Scientif Vrogue Co Hyponatremia is an important and common clinical problem. the etiology is multifactorial. hyponatremia may be euvolemic, hypovolemic or hypervolemic. proper interpretation of the various laboratory tests helps to differentiate the various types of hyponatremia. treatment varies with the nature of onset acute or chronic, severity and symptoms. The diagnostic approach to the patient with hyponatremia will be reviewed here. many patients with hyponatremia have a single cause, but multiple factors sometimes contribute to the fall in plasma sodium. as an example, when a patient infected with hiv becomes hyponatremic, volume depletion, the syndrome of inappropriate adh secretion (siadh. Cerebral edema is a medical emergency and occurs more frequently when hyponatremia develops over <48 hours. patients should be treated promptly with hypertonic 3% saline. other treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include fluid restriction and stopping causative medications. overly rapid correction of serum sodium concentration can. Hyponatremia (serum sodium [s na] <136 mmol l) is a common water balance disorder that often poses a diagnostic or therapeutic challenge. 1 this may explain why management of hyponatremia is still suboptimal, as also recently illustrated by a hyponatremia registry. 2 hyponatremia is not a disease but rather a pathophysiologic process indicating disturbed water homeostasis. 3 therefore.
Hyponatremia Harrison S Manual Of Medicine Cerebral edema is a medical emergency and occurs more frequently when hyponatremia develops over <48 hours. patients should be treated promptly with hypertonic 3% saline. other treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include fluid restriction and stopping causative medications. overly rapid correction of serum sodium concentration can. Hyponatremia (serum sodium [s na] <136 mmol l) is a common water balance disorder that often poses a diagnostic or therapeutic challenge. 1 this may explain why management of hyponatremia is still suboptimal, as also recently illustrated by a hyponatremia registry. 2 hyponatremia is not a disease but rather a pathophysiologic process indicating disturbed water homeostasis. 3 therefore. Practice essentials. hyponatremia—defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l—is the most commonly encountered and important electrolyte imbalance that can be seen in isolation or, as is most often the case, as a complication of other medical illnesses (eg, heart failure, liver failure, kidney failure, pneumonia, cancer). [1]. Hyponatremia is primarily a disorder of water balance. a low serum sodium concentration indicates dilute body fluids or an excess of water. the clinical manifestations of hyponatremia depend on the rate of decline of serum sodium. an acute fall in sodium over 24 to 48 hours produces severe cerebral edema, which can be fatal. [5].

Hyponatremia Assessment Practice essentials. hyponatremia—defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l—is the most commonly encountered and important electrolyte imbalance that can be seen in isolation or, as is most often the case, as a complication of other medical illnesses (eg, heart failure, liver failure, kidney failure, pneumonia, cancer). [1]. Hyponatremia is primarily a disorder of water balance. a low serum sodium concentration indicates dilute body fluids or an excess of water. the clinical manifestations of hyponatremia depend on the rate of decline of serum sodium. an acute fall in sodium over 24 to 48 hours produces severe cerebral edema, which can be fatal. [5].

Comments are closed.