Hyponatremia Physiology Calgary Guide

Hyponatremia Physiology Calgary Guide Post views: 34,621 © 2024 the calgary guide to understanding disease disclaimer. Hyponatremia physiology. gfr < 25 ml min, ↓ urine dilution ↑ h2o retention note: • plasma [na ] is regulated by water intake excretion, not by changes in [na ]. • artifactual hyponatremia can be differentiated by a normal or hyperosmolar serum. appropriate adh secretion ↓ eabv hypovolemia: losses via gi, renal, skin, 3rd spacing.
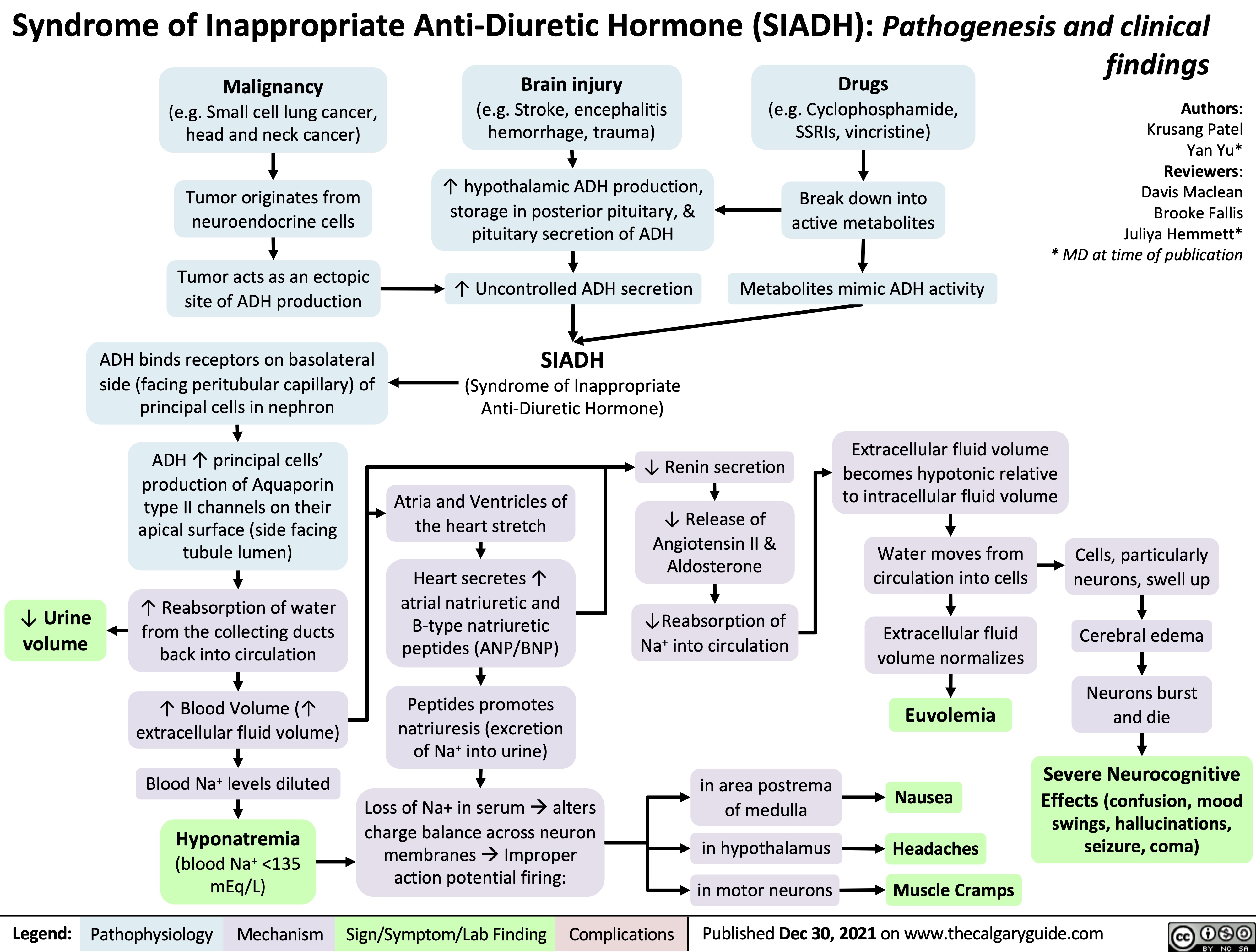
Lung Cancer Hyponatremia Calgary guide. hyponatremia: physiology; 2022 2023. get your blackbook. now on sale in the medical bookstore. reserve your copy today. order by email; 1 877 777 4738;. Cirrhosis causes hyponatremia due to impaired systemic perfusion, as a manifestation of hepatorenal physiology. this is an indication of advanced cirrhosis. cirrhosis rarely causes severe hyponatremia. similar to heart failure, there is usually a fairly stable sodium of ~120 135 mm. There are two possible approaches to the diagnosis of hyponatremia: the classical method and the "lazy man's method". both are offered here. in their most basic form, the approaches require essentially the same tests (serum osmolality, urine osmolality and urinary sodium). in the classical method, one is expected to examine the patient and come to a conclusion regarding their fluid status. the. The management of hyponatremia in patients with hypervolemia can be difficult. water restriction to less than 1.25 l d is essential. sodium restriction to 70 mmol d (with the aid of a dietitian) will help with edema. a loop diuretic should be used to promote sodium and water excretion by the kidneys.

Hyponatremia Diagnosis Flowchart There are two possible approaches to the diagnosis of hyponatremia: the classical method and the "lazy man's method". both are offered here. in their most basic form, the approaches require essentially the same tests (serum osmolality, urine osmolality and urinary sodium). in the classical method, one is expected to examine the patient and come to a conclusion regarding their fluid status. the. The management of hyponatremia in patients with hypervolemia can be difficult. water restriction to less than 1.25 l d is essential. sodium restriction to 70 mmol d (with the aid of a dietitian) will help with edema. a loop diuretic should be used to promote sodium and water excretion by the kidneys. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq l but can vary to some extent depending upon the set values of varied laboratories.[1] hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality caused by an excess of total body water in comparison to that of the total body sodium content. edelman approved of the fact that serum sodium concentration does not depend on total. Hyponatremia is an important and common clinical problem. the etiology is multifactorial. hyponatremia may be euvolemic, hypovolemic or hypervolemic. proper interpretation of the various laboratory tests helps to differentiate the various types of hyponatremia. treatment varies with the nature of onset acute or chronic, severity and symptoms.

Comments are closed.