Identifying Nutrient Deficiencies In Plants
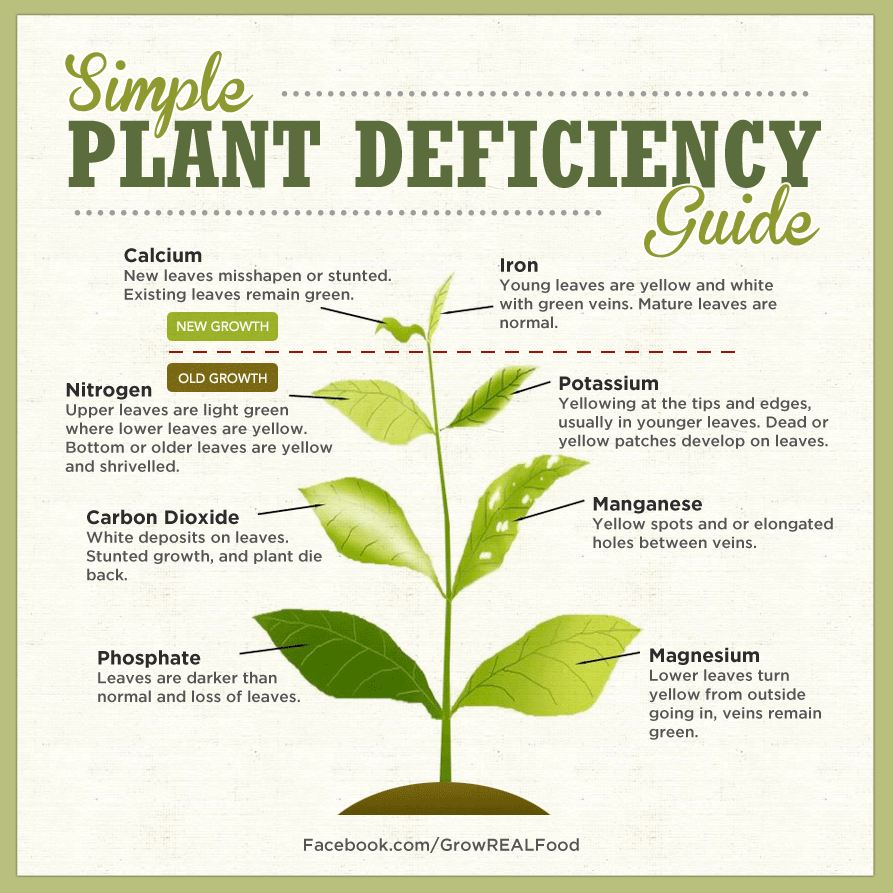
Identifying Plant Nutrient Deficiencies Permablitz Melbourne Calcium deficiency in plants. calcium is an immobile nutrient, so deficiencies will show up on the newer, youngest leaves. a calcium deficiency can also manifest as blossom end rot. blossom end rot on tomato. blossom end rot: a common issue that occurs in the garden when plants are deficient in calcium. this can be due to lack of calcium in the. When identifying common plant nutrient deficiencies, analyze the affected parts (older or newer foliage, or the whole plant). this way, you will find out if the crops suffer from a deficiency of immobile or mobile chemical elements nutrient management. competency area 1: basic concepts of plant nutrition. nrcca.cals.cornell.edu.

Identifying Plant Nutrient Deficiencies Diy Gardening Better Living When managing nutrient deficiencies, it helps to be aware that too many nutrients can be bad. furthermore, some types of plants are more prone to certain deficiencies. leafy greens and some flowers, for example, might need more nitrogen, while root vegetables often require extra phosphorus or potassium. Sulfur deficiency in plants. the micronutrients. iron deficiency in plants. zinc deficiency in plants. boron deficiency in plants. copper deficiency in plants. manganese deficiency in plants. molybdenum deficiency in plants. measuring ph, ec and temperature regularly can help prevent nutrient deficiencies here's how. Identifying a nutrient deficiency in your plant begins by looking where it occurs: oldest leaves or newest growth. once that's established, the most common plant nutrient deficiencies offer these clues: 1,2. scorched edges and speckles on older leaves indicate potassium deficiency. oldest leaves affected first: nitrogen (n) – entire leaves. Table 1. symptoms associated with deficiencies of different nutrients. plants grow poorly and are light green in color. lower leaves turn yellow or light brown and stems are short and slender. plants grow poorly and leaves are dark green with purple tints. lower leaves sometimes turn light bronze with purple or brown spots.
.jpg)
5 Common Nutrient Deficiencies In Plants Identifying a nutrient deficiency in your plant begins by looking where it occurs: oldest leaves or newest growth. once that's established, the most common plant nutrient deficiencies offer these clues: 1,2. scorched edges and speckles on older leaves indicate potassium deficiency. oldest leaves affected first: nitrogen (n) – entire leaves. Table 1. symptoms associated with deficiencies of different nutrients. plants grow poorly and are light green in color. lower leaves turn yellow or light brown and stems are short and slender. plants grow poorly and leaves are dark green with purple tints. lower leaves sometimes turn light bronze with purple or brown spots. Symptoms of deficiency generally appear in older leaves at the lower part of the plants. nitrogen (n) nitrogen is one of the major nutrients commonly applied as fertilisers. plants absorb nitrogen in the form of ammonium or nitrate which can be readily dissolved in water and leached away from soil. Anything withthe word “ calcium”;also gypsum. general yellowing of older leaves ( bottom of plant).therest ofthe p lant isoften light green. most plants absorb nitrogenin t he form of ammonium or nitrate. t heseforms readily dissolve in w ater and leach away. anythingwith the words “ ammonium,” “nitrate,” or “ urea.”.

Macro And Micro Nutrients Functions And Deficiency Symptoms With Figures Symptoms of deficiency generally appear in older leaves at the lower part of the plants. nitrogen (n) nitrogen is one of the major nutrients commonly applied as fertilisers. plants absorb nitrogen in the form of ammonium or nitrate which can be readily dissolved in water and leached away from soil. Anything withthe word “ calcium”;also gypsum. general yellowing of older leaves ( bottom of plant).therest ofthe p lant isoften light green. most plants absorb nitrogenin t he form of ammonium or nitrate. t heseforms readily dissolve in w ater and leach away. anythingwith the words “ ammonium,” “nitrate,” or “ urea.”.

Comments are closed.