Interior Angles Of A Polygon Examsolutions
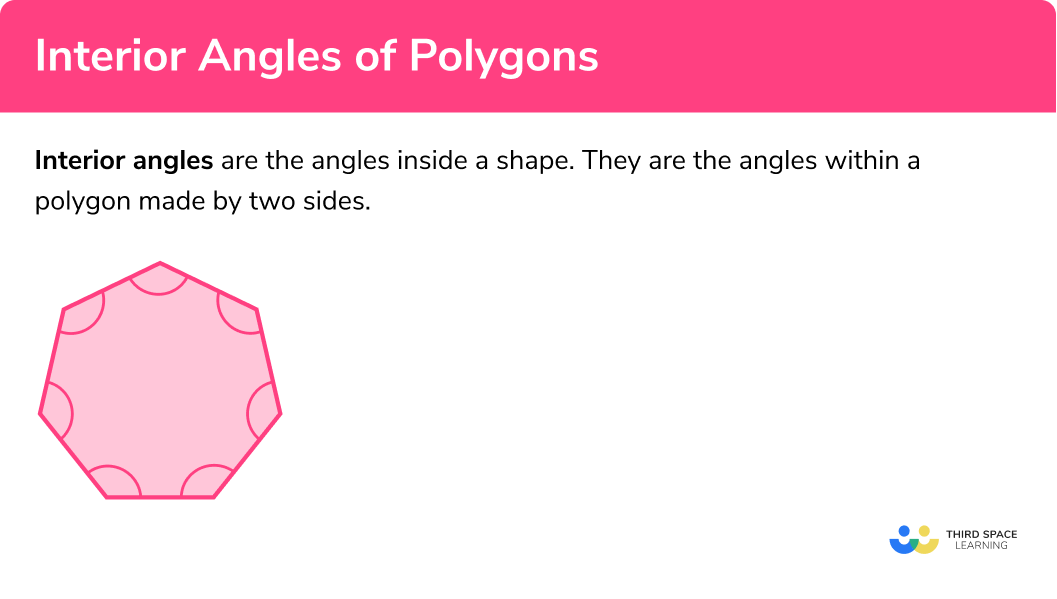
Interior Angles Of A Polygon Gcse Maths Steps Examples In this tutorial, we learn about interior angles and how to calculate the sum of interior angles of any n sided polygon using a special formula.the best th. If it is a regular polygon (all sides are equal, all angles are equal) shape sides sum of interior angles shape each angle; triangle: 3: 180° 60° quadrilateral: 4: 360° 90° pentagon: 5: 540° 108° hexagon: 6: 720° 120° heptagon (or septagon) 7: 900° 128.57 ° octagon: 8: 1080° 135° nonagon: 9: 1260° 140° any polygon: n (n−2.
Interior Angles In Regular Polygons Oryx Learning In a quadrilateral, the sum of the interior angles always totals 360 degrees. this rule applies to all quadrilaterals, whether they are a square, rectangle, paralelogram, rhombus, kite or trapezium. interior angles of a polygon. for any polygon with a number of sides ‘n’, the sum of the interior angles is given by the formula (n 2) × 180. Each interior angle of a regular polygon = (n 2)180° n, where n is the number of sides in the polygon. polygon angle sum theorem. the sum of the angles in any polygon is equal to the number of sides in the polygon minus two, all multiplied by 180 degrees. sum of polygon angles problems may ask you to determine the sum of angles in a particular. We will call these angles x: we know that angles around a point add to 360°. therefore: 60 2x =360 2x =300 x =150 60 2 x = 360 2 x = 300 x = 150. this means that each interior angle of the regular polygon is 150°. so the sum of interior angles is equal to 150 × n or 150n: 150n = (n – 2) × 180. we can now solve for n:. Let us discuss the three different formulas in detail. method 1: if “n” is the number of sides of a polygon, then the formula is given below: interior angles of a regular polygon = [180° (n) – 360°] n. method 2: if the exterior angle of a polygon is given, then the formula to find the interior angle is.

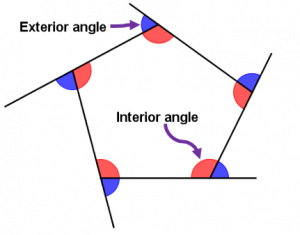
Interior Angles Of Polygons Mr Mathematics We will call these angles x: we know that angles around a point add to 360°. therefore: 60 2x =360 2x =300 x =150 60 2 x = 360 2 x = 300 x = 150. this means that each interior angle of the regular polygon is 150°. so the sum of interior angles is equal to 150 × n or 150n: 150n = (n – 2) × 180. we can now solve for n:. Let us discuss the three different formulas in detail. method 1: if “n” is the number of sides of a polygon, then the formula is given below: interior angles of a regular polygon = [180° (n) – 360°] n. method 2: if the exterior angle of a polygon is given, then the formula to find the interior angle is. The formula for determining one interior angle in a regular polygon is given below: one interior angle = (n 2) x 180° n, here n = total number of sides. let us take an example to understand the concept better, for an equilateral triangle, n = 3. thus, one interior angle = (n 2) x 180° n, here n = 3 = (3 2) x 180° 3 = 60°. Interior angles of parallel lines: the angles that lie in the area enclosed between two parallel lines that are intersected by a transversal are also called interior angles. in the below figure (b), l1 l 1 and l2 l 2 are parallel, and l is the transversal. the angles ∠1, ∠2, ∠3, and ∠4 are interior angles.

Interior Angles Of A Polygon Examsolutions Youtube The formula for determining one interior angle in a regular polygon is given below: one interior angle = (n 2) x 180° n, here n = total number of sides. let us take an example to understand the concept better, for an equilateral triangle, n = 3. thus, one interior angle = (n 2) x 180° n, here n = 3 = (3 2) x 180° 3 = 60°. Interior angles of parallel lines: the angles that lie in the area enclosed between two parallel lines that are intersected by a transversal are also called interior angles. in the below figure (b), l1 l 1 and l2 l 2 are parallel, and l is the transversal. the angles ∠1, ∠2, ∠3, and ∠4 are interior angles.
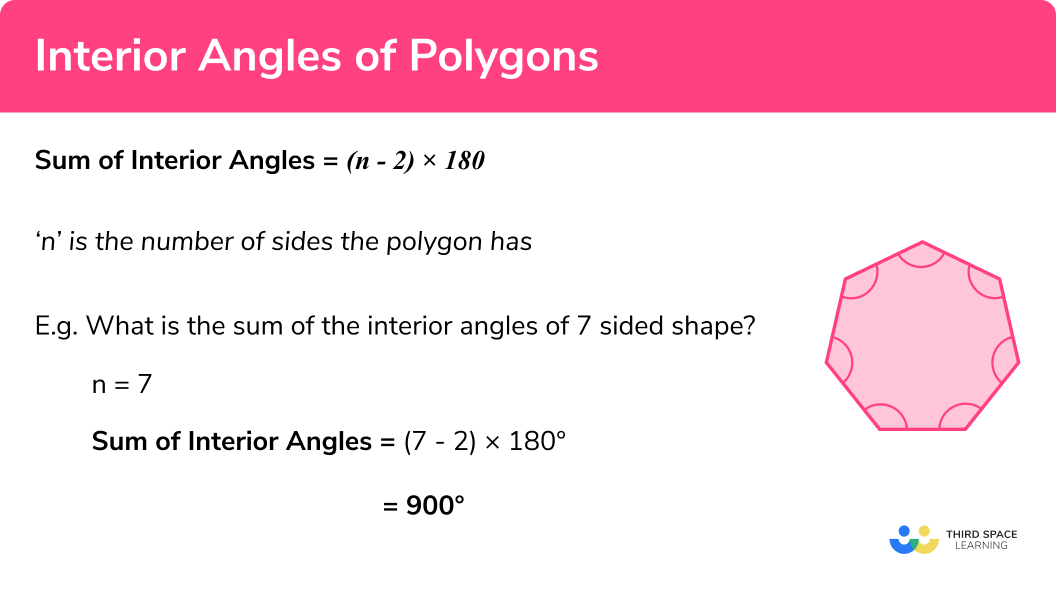
Interior Angles Of A Polygon Gcse Maths Steps Examples

Comments are closed.