Internal Combustion Engine Docx Internal Combustion Engine
Internal Combustion Engine Simple Diagram An internal combustion engine (ice or ic engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. in an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high temperature and high pressure gases produced by combustion. Internal combustion engines, lecture 20 turbocharging. pdf. 1 mb. internal combustion engines, lecture 21 hydrogen, fuel cell and battery. pdf. 847 kb. internal combustion engines, lecture 22 bio fuels and hybrids. mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. ocw is open and available to the world and is a.

Internal Combustion Engine Docx Internal Combustion Engine The Heywood, mit) modern gasoline ic engine vehicle converts about 16% of the chemical energy in gasoline to useful work. the average light duty vehicle weighs 4,100 lbs. the average occupancy of a light duty vehicle is 1.6 persons. if the average occupant weighs 160 lbs, 0.16x((1.6x160) 4100) = 0.01. An internal combustion engine is a type of heat engine that is widely used in various applications, particularly in transportation. this engine acts as the primary power source for automobiles, motorcycles, airplanes, boats, and many other machines. the engine works by turning the stored energy in fuel into useful energy that makes these. The first modern internal combustion engine, known as the otto engine, was created by a german engineer, nicolaus otto in 1876. “internal combustion engine” typically refers to engines where combustion occurs intermittently. the diesel engine was invented by a german mechanical engineer and inventor in 1897. rudolf diesel. This course studies the fundamentals of how the design and operation of internal combustion engines affect their performance, efficiency, fuel requirements, and environmental impact. topics include fluid flow, thermodynamics, combustion, heat transfer and friction phenomena, and fuel properties, with reference to engine power, efficiency, and emissions. students examine the design features and.

Diagram Internal Combustion Engine Diagram Of A Show How A Works The first modern internal combustion engine, known as the otto engine, was created by a german engineer, nicolaus otto in 1876. “internal combustion engine” typically refers to engines where combustion occurs intermittently. the diesel engine was invented by a german mechanical engineer and inventor in 1897. rudolf diesel. This course studies the fundamentals of how the design and operation of internal combustion engines affect their performance, efficiency, fuel requirements, and environmental impact. topics include fluid flow, thermodynamics, combustion, heat transfer and friction phenomena, and fuel properties, with reference to engine power, efficiency, and emissions. students examine the design features and. Examples: lhv gasoline cnh1.87n 44 mj kg diesel fuel cnh1.75n 43 mj kg natural gas (mostly methane) ch3.8 45 mj kg coal cnh0.8n 30 mj kg methanol ch3oh 20 mj kg. ethanol c2h5oh 26 mj kg. (lhv = energy released per unit mass of fuel without recovery of the heat of vaporization of the water vapor in the combustion products) stoichiometric. The internal combustion engine is any heat engine that obtains mechanical energy by burning chemical energy (fuel) in confined space (combustion chamber). the invention and development of the internal combustion engine in the nineteenth century has had a profound impact on human life. the internal combustion engine offers a relatively small.

Doc Internal Combustion Engine рђр рµрєсѓр рѕрґсђ р сѓрґрёрє Academia Edu Examples: lhv gasoline cnh1.87n 44 mj kg diesel fuel cnh1.75n 43 mj kg natural gas (mostly methane) ch3.8 45 mj kg coal cnh0.8n 30 mj kg methanol ch3oh 20 mj kg. ethanol c2h5oh 26 mj kg. (lhv = energy released per unit mass of fuel without recovery of the heat of vaporization of the water vapor in the combustion products) stoichiometric. The internal combustion engine is any heat engine that obtains mechanical energy by burning chemical energy (fuel) in confined space (combustion chamber). the invention and development of the internal combustion engine in the nineteenth century has had a profound impact on human life. the internal combustion engine offers a relatively small.

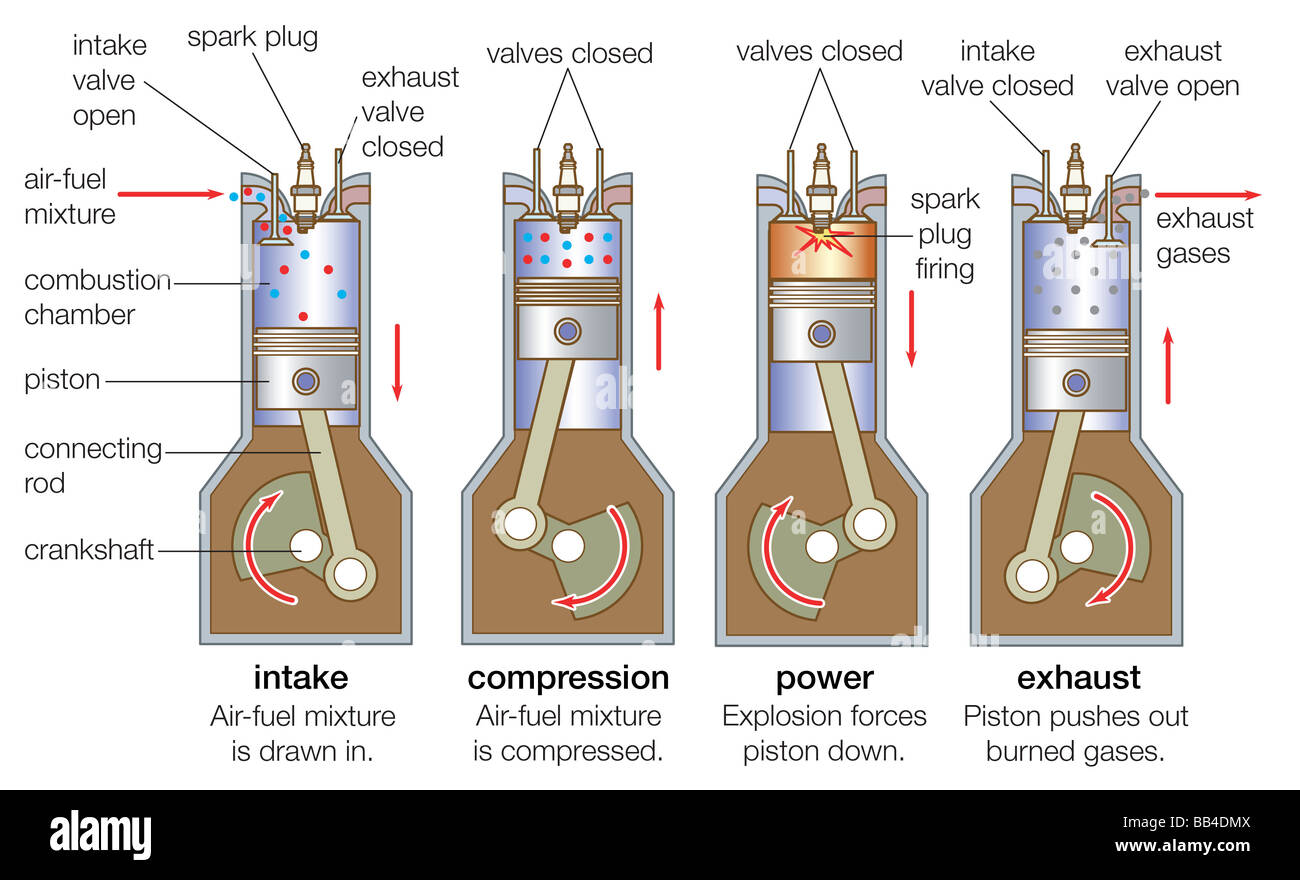
Mechanical Engineering Internal Combustion Engine Detailed Section

Comments are closed.