Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Atomicspectroscopy
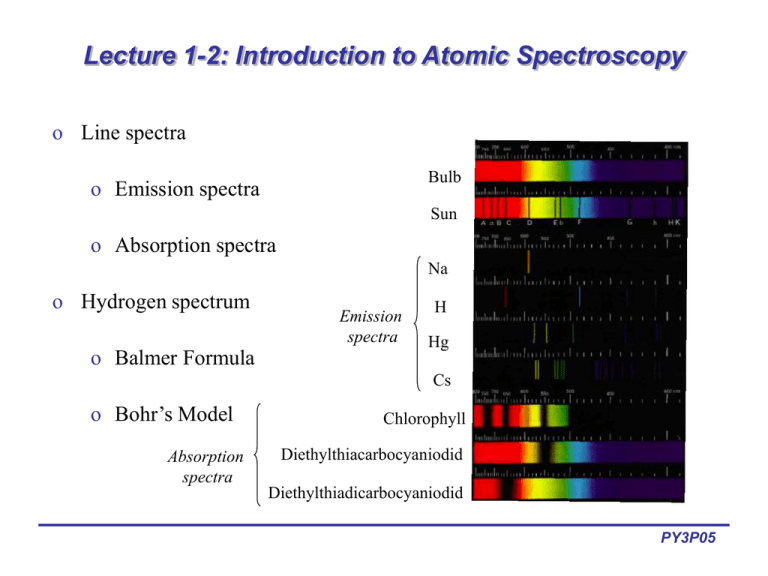
Lecture 1 2 Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Therefore, performing atomic spectroscopy on most samples involves the utilization of an atomization source, which is a device that has the ability to convert molecules to atoms. it is also important to recognize that the absorption or emission spectrum of a neutral atom will be different than that of its ions (e.g., cr 0 , cr 3 , cr 6 all. Atomic spectroscopy. in physics, atomic spectroscopy is the study of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed and emitted by atoms. since unique elements have unique emission spectra, atomic spectroscopy is applied for determination of elemental compositions. it can be divided by atomization source or by the type of spectroscopy used.

Lectures 1 2 Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Types Of Spectra E = mc2 (1.4.1) (1.4.1) e = m c 2. both atomic emission and atomic absorption spectroscopy can be used to analyze samples. atomic emission spectroscopy measures the intensity of light emitted by the excited atoms, while atomic absorption spectroscopy measures the light absorbed by atomic absorption. this light is typically in the visible or. Atomic spectroscopy introduction. 1. introduction. this article outlines the main concepts of atomic structure, with some emphasis on terminology and notation. atomic radiation is discussed, in particular the wavelengths, intensities, and shapes of spectral lines, and a few remarks are made regarding continuous spectra. The photon energy due to an electron transition between an upper atomic level k(of energy ek) and a lower level iis. 2 of 31 3 3 1999 8:09 am atomic spectroscopy: an introduction. e= ek ei= h= hc= hc vac, (1) where is the frequency, the wavenumber in vacuum, and vacthe wavelength in vacuum. This module is designed to introduce the basic concepts of spectroscopy and to provide a survey of several of the most common types of spectroscopic measurement. you will conduct the following measurements. uv vis (ultraviolet visible) spectroscopy of electronic states. fluorescence spectroscopy of electronic states.

Ppt Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Powerpoint Presentation Free The photon energy due to an electron transition between an upper atomic level k(of energy ek) and a lower level iis. 2 of 31 3 3 1999 8:09 am atomic spectroscopy: an introduction. e= ek ei= h= hc= hc vac, (1) where is the frequency, the wavenumber in vacuum, and vacthe wavelength in vacuum. This module is designed to introduce the basic concepts of spectroscopy and to provide a survey of several of the most common types of spectroscopic measurement. you will conduct the following measurements. uv vis (ultraviolet visible) spectroscopy of electronic states. fluorescence spectroscopy of electronic states. Be able to explain the functionality of an atomizer and be able to describe how samples (solid and aqueous) are prepared for eventual atomization. (introduction of analyte (electrothermal vaporization and nebulizers)). this page titled introduction to atomic spectroscopy is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via. Latin: “spectron”—ghost or spirit greek: “ σκοπειν ”—to see. with light, you aren’t looking directly at the molecule—the matter—but its “ghost.”. you observe the light’s interaction with different degrees of freedom of the molecule. each type of spectroscopy—different light frequency—gives a different picture.

Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Atomicspectroscopy Youtube Be able to explain the functionality of an atomizer and be able to describe how samples (solid and aqueous) are prepared for eventual atomization. (introduction of analyte (electrothermal vaporization and nebulizers)). this page titled introduction to atomic spectroscopy is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via. Latin: “spectron”—ghost or spirit greek: “ σκοπειν ”—to see. with light, you aren’t looking directly at the molecule—the matter—but its “ghost.”. you observe the light’s interaction with different degrees of freedom of the molecule. each type of spectroscopy—different light frequency—gives a different picture.

Ppt Introduction To Atomic Spectroscopy Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.