Isosceles Triangle Properties Formula Theorems Examples

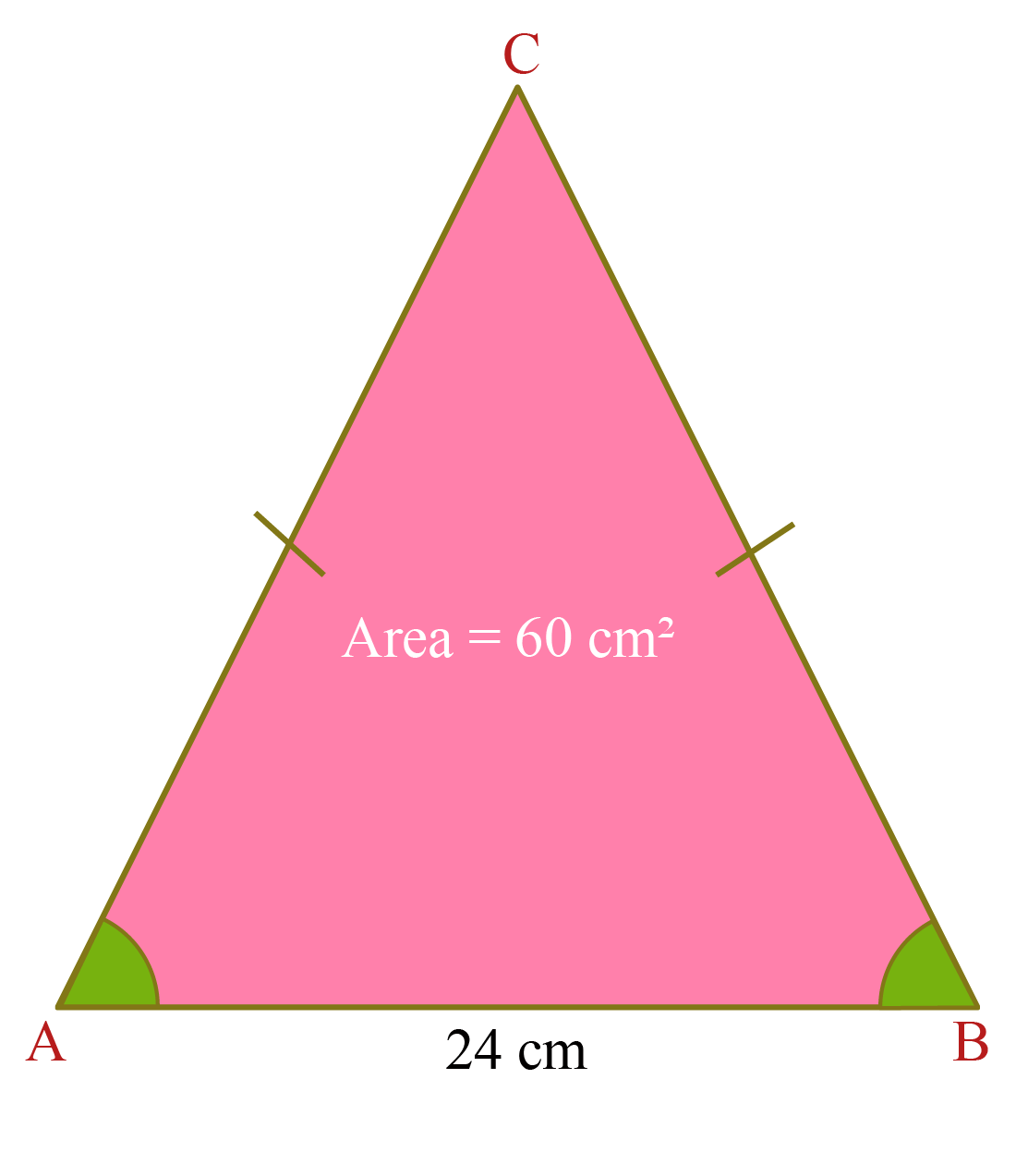
Isosceles Triangle Properties Formula Theorems Examples Now, substitute the base and height value in the formula. area of an isosceles triangle is ½ × b × h. a = ½ × 4 × 6 = 12 cm 2. therefore, the area of an isosceles triangle is 12 cm2. example 2: find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, with a side 6 cm and base 4 cm. solution:. Here, a = 36 inches and b = 24 inches. substituting the values in the perimeter of an isosceles triangle formula, we get, p = 2 (36) 24 = 96 inches. hence, the perimeter of the given triangle is 96 inches. example 3: state true or false: a.) all three angles of an isosceles triangle are equal and measure 60° each.
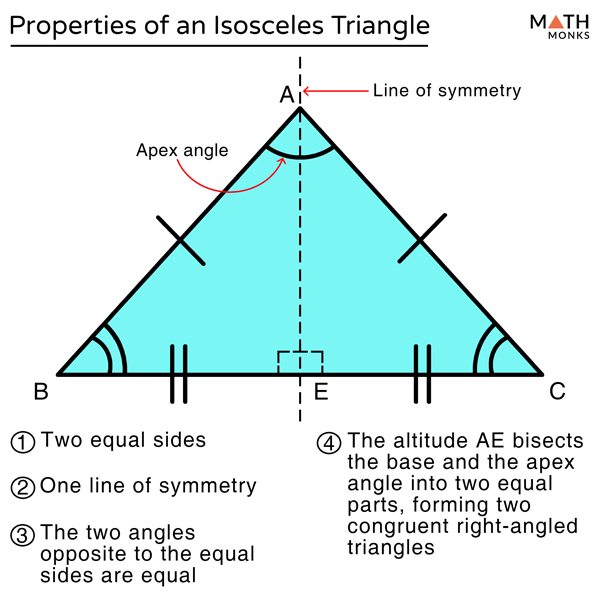
Isosceles Triangle Definition Properties Types Formulas Some pointers about isosceles triangles are: it has two equal sides. it has two equal angles, that is, the base angles. when the third angle is 90 degree, it is called a right isosceles triangle. in this article, we have given two theorems regarding the properties of isosceles triangles along with their proofs. isosceles triangle theorems and. According to the isosceles triangle theorem, if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite to the congruent sides are equal. thus, ∠y = ∠z = 35º. hence the value of x is 35º. example 2: if ∠p and ∠q of ∆pqr are equal to 70º and qr = 7.5 cm, find the value of pr. given that, in ∆pqr, ∠p = ∠q = 70º. An isosceles triangle is a fascinating geometric shape that possesses unique properties and characteristics. it is defined by its distinct symmetry, where two sides of the triangle are of equal length, and the remaining side is different in length. the term “isosceles” is derived from the greek words “isos,” meaning “equal,” and. The key properties of isosceles triangle are: contains two equal sides with the base being the unequal, third side; the angles opposite the two equal sides are equal; when the third angle is 90°, it is called a right isosceles triangle; using the properties of isosceles triangle, the two theorems along with their proofs are given below. what.
Isosceles Triangle Properties Formula Theorems Examples An isosceles triangle is a fascinating geometric shape that possesses unique properties and characteristics. it is defined by its distinct symmetry, where two sides of the triangle are of equal length, and the remaining side is different in length. the term “isosceles” is derived from the greek words “isos,” meaning “equal,” and. The key properties of isosceles triangle are: contains two equal sides with the base being the unequal, third side; the angles opposite the two equal sides are equal; when the third angle is 90°, it is called a right isosceles triangle; using the properties of isosceles triangle, the two theorems along with their proofs are given below. what. Solution: using the formula of area of an isosceles triangle: a = (1 2) b h = 20. given b = 10, to find: lateral side. h = 40 10 = 4. applying pythagora's theorem: a 2 = (b 2) 2 h 2 = √ ( 5 2 4 2) = √41. answer: the lateral side of an isosceles triangle is √41. example 3: calculate the area, altitude, and perimeter of an isosceles. Isosceles acute triangle: an isosceles acute triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are less than 90 degrees, and at least two of its angles are equal in measurement. one example of isosceles acute triangle angles is 50°, 50°, and 80°. isosceles right triangle: this is a right triangle with two legs (and their corresponding angles.

Area Of Isosceles Triangle Formula Definition Examples Solution: using the formula of area of an isosceles triangle: a = (1 2) b h = 20. given b = 10, to find: lateral side. h = 40 10 = 4. applying pythagora's theorem: a 2 = (b 2) 2 h 2 = √ ( 5 2 4 2) = √41. answer: the lateral side of an isosceles triangle is √41. example 3: calculate the area, altitude, and perimeter of an isosceles. Isosceles acute triangle: an isosceles acute triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are less than 90 degrees, and at least two of its angles are equal in measurement. one example of isosceles acute triangle angles is 50°, 50°, and 80°. isosceles right triangle: this is a right triangle with two legs (and their corresponding angles.

Comments are closed.