Keynes Theory Of Investment Multiplier With Diagram
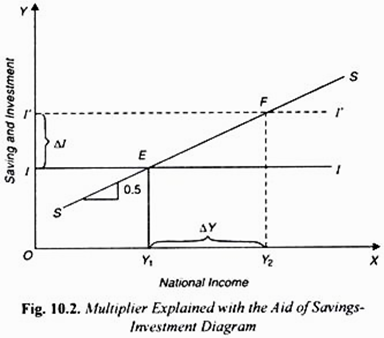
Keynes Theory Of Investment Multiplier With Diagram The below mentioned article provides a complete guide to keynes’ theory of investment multiplier. the concept of investment multiplier: the theory of multiplier occupies an important place in the modern theory of income and employment. the concept of multiplier was first of all developed by f.a. kahn in the early 1930s. but keynes later further refined it. f.a. kahn developed the concept of. Let us make an in depth study of the keynesian theory of investment. according to the classical theory there are three determinants of business investment, viz., (i) cost, (ii) return and (iii) expectations. according to keynes investment decisions are taken by comparing the marginal efficiency of capital (mec) or the yield with the real rate of interest (r). so long as the mec is greater than.
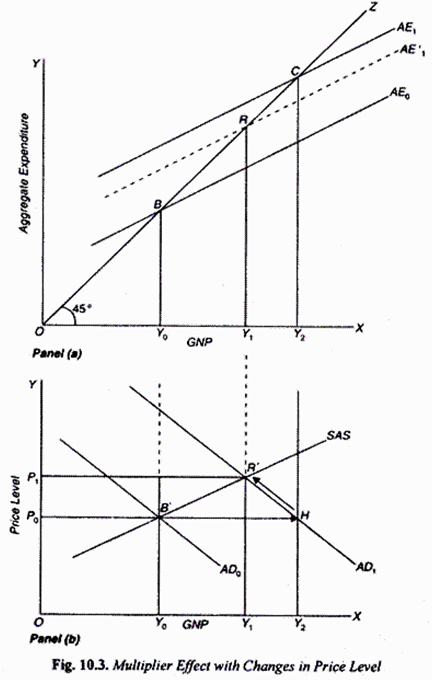
Keynes Theory Of Investment Multiplier With Diagram A keynesian multiplier demonstrates that the economy will flourish as the government increases spending. according to the theory, the net gain is greater than the dollar amount spent. marginal. The keynesian theory states that an increase in production leads to an increase in the level of income and therefore, an increase in spending. the value of mpc allows us to calculate the size of the multiplier using the formula: 1 (1 – mpc) = 1 (1 – 0.5) = 2. it means that every $1 of new income will generate $2 of extra income. The keynesian multiplier model is often graphically represented on the keynesian cross diagram. the name cross comes from the way the model looks. the aggregate demand (or aggregate expenditure) curve or line crosses the 45° curve. the graphical diagram of the model is also called. the expenditure output diagram; the keynesian cross diagram. The simplicity of keynes’ treatment of the multiplier raised certain doubts in the minds of some writers. as george j. stigler has remarked, “the multiplier is the fuzziest part of his (keynes’) general theory.” since then investment multiplier has been the main concept with the improvement of which economists have been preoccupied.

Keynesian Multiplier Overview Components How To Calculate The keynesian multiplier model is often graphically represented on the keynesian cross diagram. the name cross comes from the way the model looks. the aggregate demand (or aggregate expenditure) curve or line crosses the 45° curve. the graphical diagram of the model is also called. the expenditure output diagram; the keynesian cross diagram. The simplicity of keynes’ treatment of the multiplier raised certain doubts in the minds of some writers. as george j. stigler has remarked, “the multiplier is the fuzziest part of his (keynes’) general theory.” since then investment multiplier has been the main concept with the improvement of which economists have been preoccupied. Lesson 4: keynesian economics and its critiques. keynesian economics. risks of keynesian thinking. macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply. keynes’ law and say’s law in the ad as model. aggregate demand in keynesian analysis. the building blocks of keynesian analysis. the phillips curve in the keynesian perspective. When the l evel of investment incre ases by some amount, Äi, th e equili brium level of inc ome will i ncrease by some multiple amount, Äy. the ratio of Äy to Äi is called the investment multiplier. it can be derived, as follows, from the equilibrium condition (y = c i g) together with the consumption equation (c = a by). 1. y = c i.

Comments are closed.