Learning Geology What Are Earth Layers Made Of

What Are Earth Layers Made Of Learning Geology The mantle of the earth forms a 2,885 km thick layer surrounding the core. in terms of volume, it is the largest part of the earth. in contrast to the crust, the mantle consists entirely of an ultramafic (dark and dense) rock called peridotite. this means that peridotite, though rare at the earth’s surface, is actually the most abundant rock. The four primary layers are the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. however, geologists subdivide these layers into a complex structure that better describes the earth’s intricate composition and behavior. let’s start with the basic four layer model before delving into greater detail. the 4 basic layers of the earth the crust.

What Is Earth Made Of Learning Geology All the earth’s layers, their structure and composition. 1. crust. temperature: 475 k (∼200°c) at the surface to 1300 k (∼1000°c) thickness: 25 miles (32 km) for continental crust and 3 5 miles (8 km) for oceanic crust. density: ∼ 2830 kg m 3 at the continental crust and ∼ 3000 kg m 3 at the oceanic crust. it is the outermost and. Lithosphere. figure 2.2.5 2.2. 5: map of the major plates and their motions along boundaries. lithos is greek for stone, and the lithosphere is the outermost physical layer of the earth. it is grouped into two types: oceanic and continental. oceanic lithosphere is thin and relatively rigid. University of saskatchewan. earth consists of three main layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core (figure 3.3). the core accounts for almost half of earth’s radius, but it amounts to only 16.1% of earth’s volume. most of earth’s volume (82.5%) is its mantle, and only a small fraction (1.4%) is its crust. figure 3.3 earth’s interior. In order to understand the details of plate tectonics, it is essential to first understand the layers of the earth. in general, the earth can be divided into layers based on chemical composition and physical characteristics. figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: the layers of the earth. physical layers include the lithosphere and asthenosphere; chemical layers.
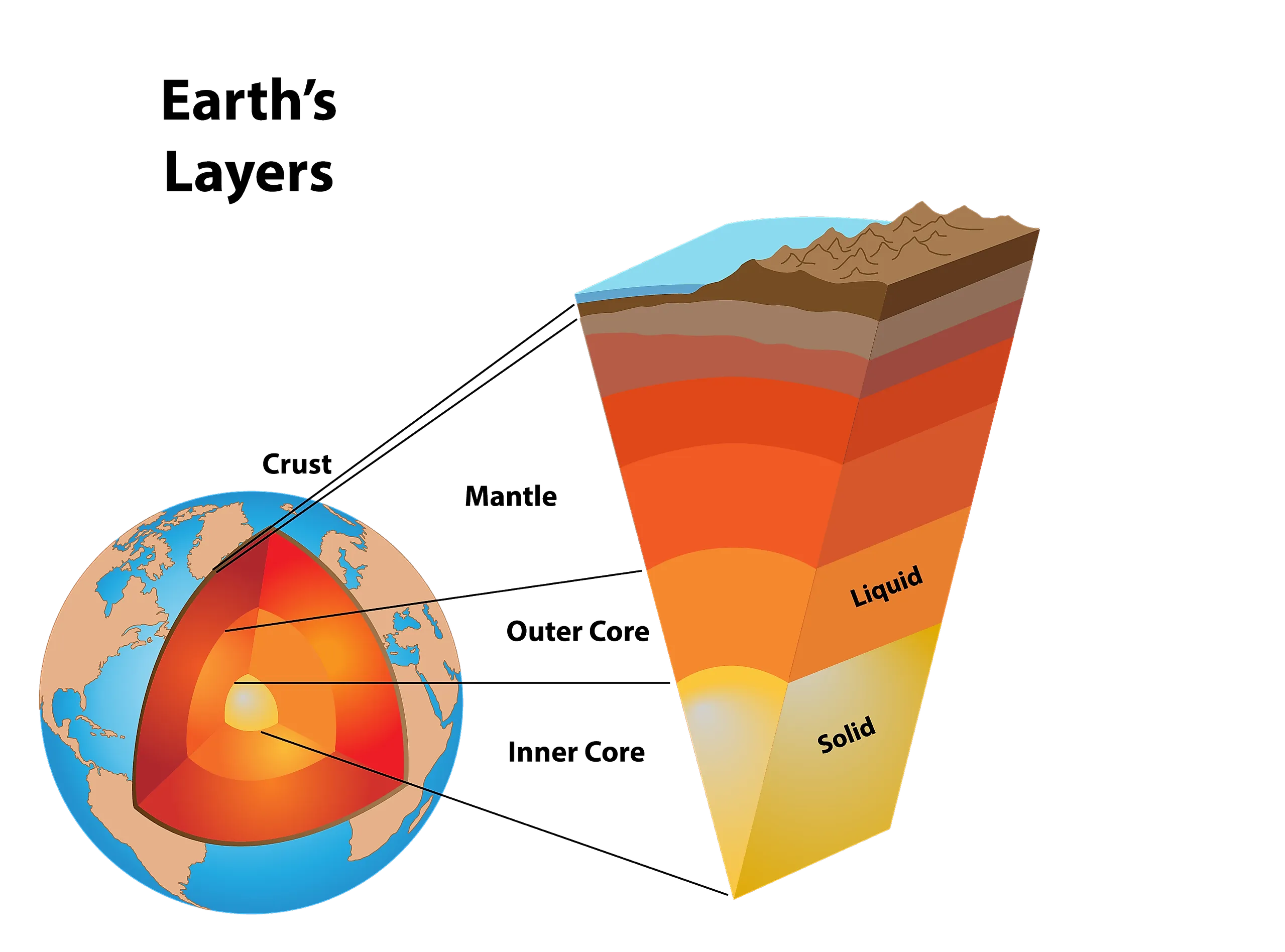
A Diagram Of The Earth S Layers University of saskatchewan. earth consists of three main layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core (figure 3.3). the core accounts for almost half of earth’s radius, but it amounts to only 16.1% of earth’s volume. most of earth’s volume (82.5%) is its mantle, and only a small fraction (1.4%) is its crust. figure 3.3 earth’s interior. In order to understand the details of plate tectonics, it is essential to first understand the layers of the earth. in general, the earth can be divided into layers based on chemical composition and physical characteristics. figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: the layers of the earth. physical layers include the lithosphere and asthenosphere; chemical layers. Earth layering: compositions, properties, locations. the geosphere is a term used to describe the “solid earth” as a means to distinguish it from the hydrosphere (oceans) and the atmosphere. most people recognize that earth’s interior has a kind of layered structure. here, we’ll learn about the classification of the various layers and. The structure of the earth is divided into four major components: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. each layer has a unique chemical composition, physical state, and can impact life on earth's surface. movement in the mantle caused by variations in heat from the core, cause the plates to shift, which can cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. these natural hazards.

Comments are closed.