Life Cycle Of A Star Explained

Illustrate The Life Cycle Of A Star Learn how stars form, shine and die in different stages depending on their size. find out what happens to a star when it runs out of hydrogen, becomes a red giant, a white dwarf, a black dwarf, a supernova or a black hole. At the first stage of their lives, stars are formed by the gravitational collapse of giant clouds of dust and gas called nebulae. this stage is the start of their life cycle. 2. protostar. a protostar is the result of the gravitational collapse of a nebula. it is the formative phase of a star.
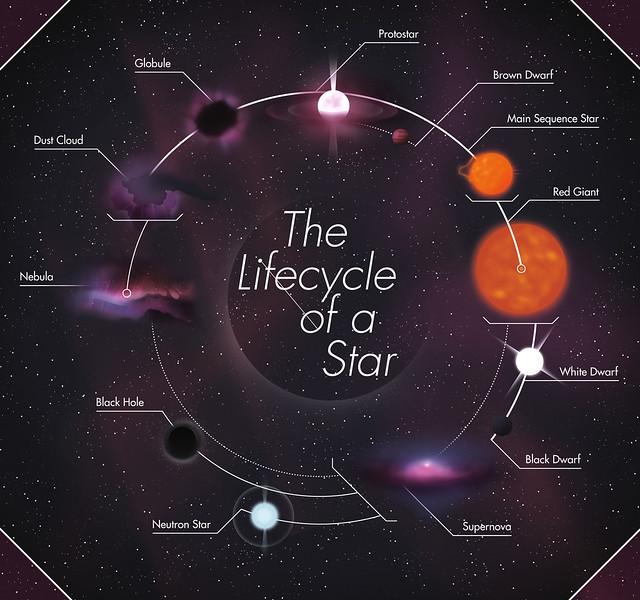
Life Cycle Of A Star Seven Main Stages Of A Star Stellar Evolution Learn how stars form, change and die depending on their size and mass. explore the stages of the life cycle of a star, from nebula to black hole, with diagrams and examples. Massive stars transform into supernovae, neutron stars and black holes while average stars like the sun, end life as a white dwarf surrounded by a disappearing planetary nebula. all stars, irrespective of their size, follow the same 7 stage cycle, they start as a gas cloud and end as a star remnant. 1. giant gas cloud. A hundred years ago, scientists did not know that stars are powered by nuclear fusion, and 50 years ago they did not know that stars are continually forming in the universe. researchers still do not know the details of how clouds of gas and dust collapse to form stars, or why most stars form in groups, or exactly how planetary systems form. All life on earth contains the element carbon, and all carbon was originally formed in the core of a star. stars populate the universe with elements through their “lifecycle”—an ongoing process of formation, burning fuel, and dispersal of material when all the fuel is used up. different stars take different paths, however, depending on.
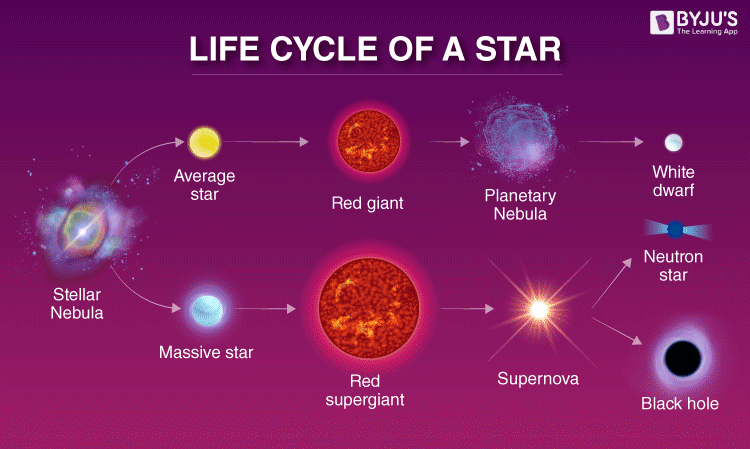
What Is The Life Cycle Of A Typical Star Rc Space A hundred years ago, scientists did not know that stars are powered by nuclear fusion, and 50 years ago they did not know that stars are continually forming in the universe. researchers still do not know the details of how clouds of gas and dust collapse to form stars, or why most stars form in groups, or exactly how planetary systems form. All life on earth contains the element carbon, and all carbon was originally formed in the core of a star. stars populate the universe with elements through their “lifecycle”—an ongoing process of formation, burning fuel, and dispersal of material when all the fuel is used up. different stars take different paths, however, depending on. A star's life cycle is determined by its mass. the larger its mass, the shorter its life cycle. a star's mass is determined by the amount of matter that is available in its nebula, the giant cloud of gas and dust from which it was born. over time, the hydrogen gas in the nebula is pulled together by gravity and it begins to spin. Star formation, evolution, lifecycle: throughout the milky way galaxy (and even near the sun itself), astronomers have discovered stars that are well evolved or even approaching extinction, or both, as well as occasional stars that must be very young or still in the process of formation. evolutionary effects on these stars are not negligible, even for a middle aged star such as the sun. more.

Comments are closed.