Main Sequence Star Definition Chart Characteristics Lesson

Main Sequence Star Definition Chart Characteristics Lesson A main sequence star chart, or hertzsprung russell (hr) diagram, is a chart which shows the relationship between a star's luminosity and their stellar classification, or effective temperature. the. A main sequence star is basically any star during the 'regular' time in its life: it's not newborn and it's not dying, it's just burning in an ordinary stable manner.

Main Sequence Star Definition Chart Characteristics Lesson Main sequence stars fuse hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. about 90 percent of the stars in the universe, including the sun, are main sequence stars. these stars can range from. The main sequence is thus explained as the group of stars of different masses that have reached stable configurations and are generating energy by consuming hydrogen in nuclear reactions. mathematically, a star's luminosity is proportional to the mass to the 3.5 power. in solar units, l = m 3.5. Main sequence stars are fusing hydrogen into helium. these nuclear fusion take place deep in the cores of stars. stars spend about 90% of their lives in this stage. our sun is about 5,000 million years into its 10,000 million year main sequence. one of the fundamental forces in the universe is gravity. it is the force that holds us on earth. The main business of a star is forging heavier elements by fusion; the light we see is just a byproduct of the nuclear reactions. teach astronomy a star joins the main sequence when it begins to generate energy by consuming hydrogen in nuclear reactions deep in its core. prior to that time, the star generates energy primarily by gravitational.
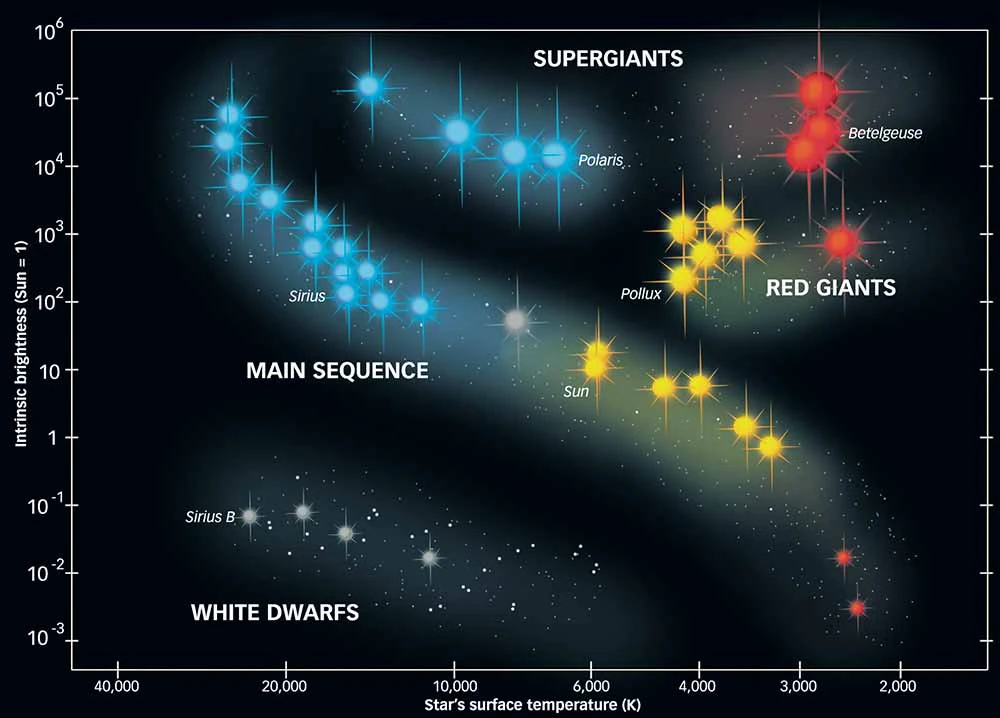
Main Sequence Stars Theoretical Physics Digest Wiki Fandom Powered Main sequence stars are fusing hydrogen into helium. these nuclear fusion take place deep in the cores of stars. stars spend about 90% of their lives in this stage. our sun is about 5,000 million years into its 10,000 million year main sequence. one of the fundamental forces in the universe is gravity. it is the force that holds us on earth. The main business of a star is forging heavier elements by fusion; the light we see is just a byproduct of the nuclear reactions. teach astronomy a star joins the main sequence when it begins to generate energy by consuming hydrogen in nuclear reactions deep in its core. prior to that time, the star generates energy primarily by gravitational. The term “main sequence” refers to the stage in a star’s life cycle when it is fusing hydrogen in its core. ii. characteristics of main sequence stars. main sequence stars come in a variety of sizes, temperatures, and colors. the size of a main sequence star is determined by its mass, with larger stars being more massive. A star whose characteristics place it in a band, called the main sequence, on an h r diagram is called a main sequence star. the hertzsprung russell (h r) diagram is a diagram that plots a star's.

Comments are closed.