Maintaining Homeostasis And Listening To Your Body

Maintaining Homeostasis And Listening To Your Body How your body maintains homeostasis. your body’s different systems are responsible for maintaining its optimal steady state. they “listen” on a cellular level for signs of distress. when one of the key variables falls out of the acceptable range, your nervous system detects this deviation and sends a signal to your brain. Your body regulates other chemical mechanisms as well to keep systems in balance. these use hormones as chemical signals—for example, in the case of blood sugar levels. in this situation, the pancreas would release either insulin, when blood sugar levels are high, or glucagon, when blood sugars are low, to maintain homeostasis.
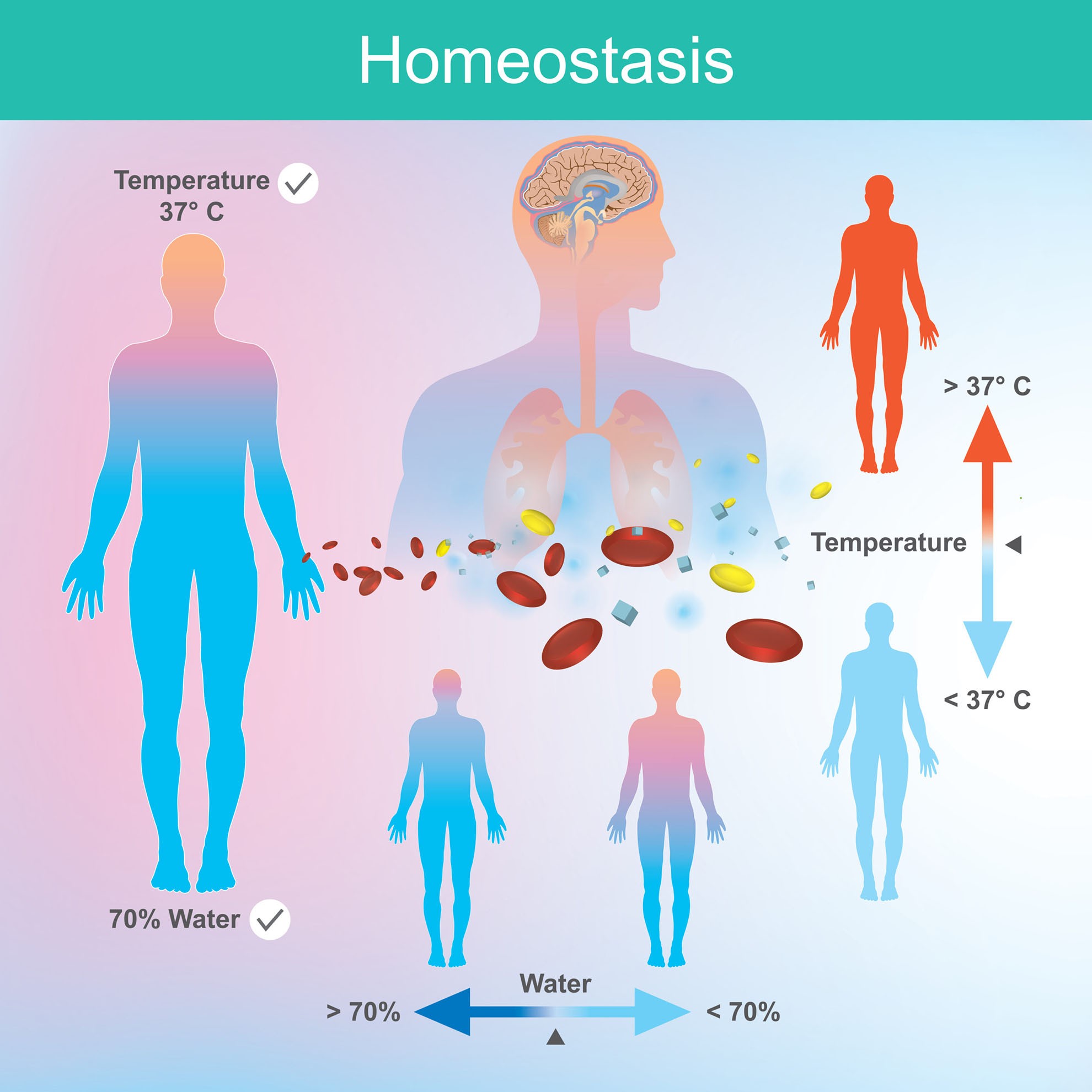
Physiological Homeostasis Biology Online Tutorial Homeostasis of ions. body functions such as regulation of the heartbeat, contraction of muscles, activation of enzymes, and cellular communication require tightly regulated calcium levels. normally, we get a lot of calcium from our diet. the small intestine absorbs calcium from digested food. Significance. homeostasis is a physiological process that keeps the internal environment of a living organism stable and balanced. the constant equilibrium created by homeostasis is vital to the survival of every species. even when the external environment is rapidly changing, homeostasis keeps the body's internal environment constant and steady. This introduction to homeostasis and regulation in the human body is really only a small glimpse into the complex systems that maintain your body’s health. scientists are still working hard to understand the different mechanisms and diseases that affect it. this backgrounder was lasted updated on: august 29th, 2024. Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions. this process involves various biological mechanisms that detect changes, trigger responses, and restore balance. examples of things that homeostasis controls include body temperature, chemical energy, ph levels, oxygen.
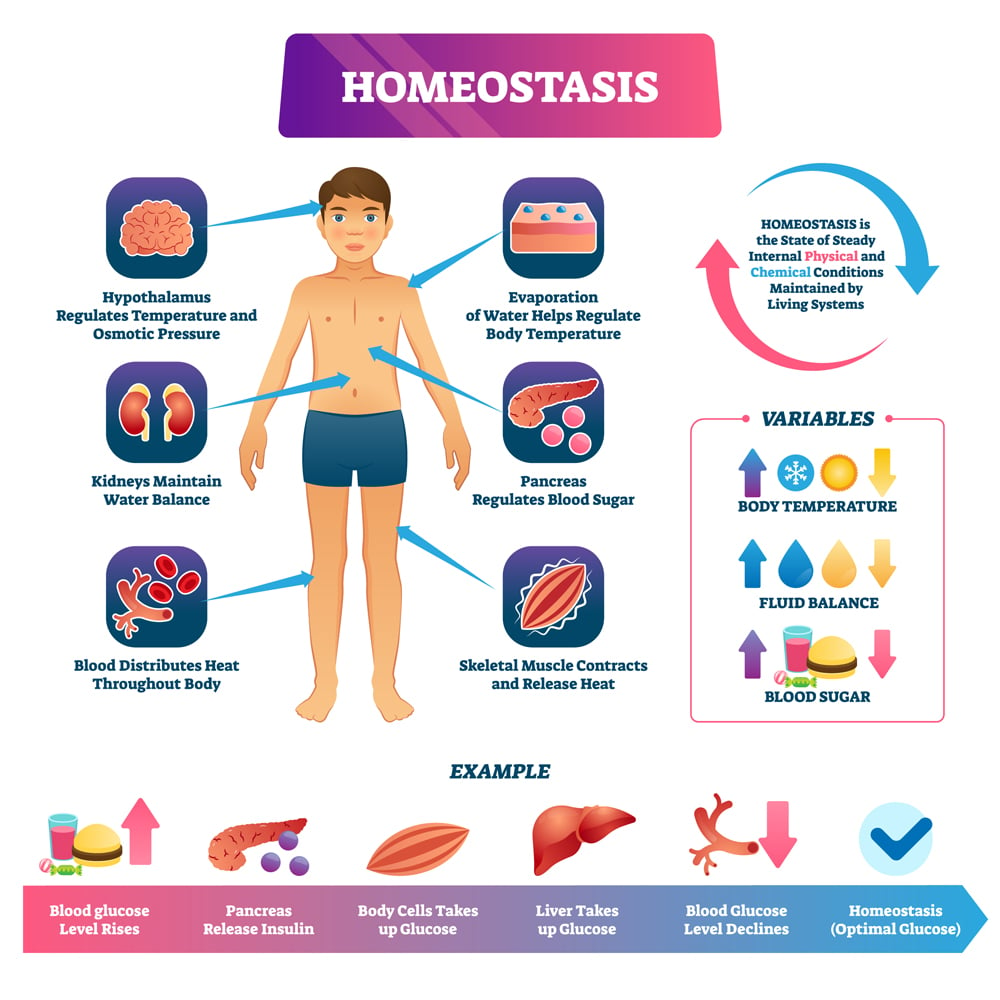
Easy Way To Explain Homeostasis This introduction to homeostasis and regulation in the human body is really only a small glimpse into the complex systems that maintain your body’s health. scientists are still working hard to understand the different mechanisms and diseases that affect it. this backgrounder was lasted updated on: august 29th, 2024. Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions. this process involves various biological mechanisms that detect changes, trigger responses, and restore balance. examples of things that homeostasis controls include body temperature, chemical energy, ph levels, oxygen. Figure 1.3.3 – positive feedback loop: normal childbirth is driven by a positive feedback loop. a positive feedback loop results in a change in the body’s status, rather than a return to homeostasis. the first contractions of labor (the stimulus) push the baby toward the cervix (the lowest part of the uterus). Feedback may be negative or positive. all the feedback mechanisms that maintain homeostasis use negative feedback. biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. figure 10.7.2 10.7. 2: maintaining homeostasis through feedback requires a stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector.

Maintaining Homeostasis And Listening To Your Body Figure 1.3.3 – positive feedback loop: normal childbirth is driven by a positive feedback loop. a positive feedback loop results in a change in the body’s status, rather than a return to homeostasis. the first contractions of labor (the stimulus) push the baby toward the cervix (the lowest part of the uterus). Feedback may be negative or positive. all the feedback mechanisms that maintain homeostasis use negative feedback. biological examples of positive feedback are much less common. figure 10.7.2 10.7. 2: maintaining homeostasis through feedback requires a stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector.

What Is Homeostasis Why Is It So Important For Our Wellbeing

Comments are closed.