Mantle Plume Definition Earth Science The Earth Images Revimage Org

Mantle Plume Definition Earth Science The Earth Images Revimage Org Mantle plumes are an integral aspect of earth’s convection system, yet, difficulty in imaging mantle upwellings led to controversies surrounding their origin, dynamics and composition. this. Abstract. mantle plumes originate at depths near the core−mantle boundary (~2,800 km). as such, they provide invaluable information about the composition of the deep mantle and insight into.

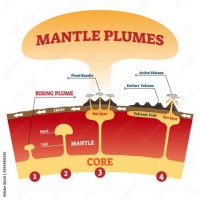
Mantle Plume Earth Science Definition The Earth Images Mantle plume. a superplume generated by cooling processes in the mantle (lvz = low velocity zone) [1] a mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. [2] because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of. Mantle plumes nature.2020 08 18.docx — 19 aug 2020 15:12 — page 2 key messages 1 • thermochemical mantle plumes are an integral part of a dynamic earth’s interior. 2 • many mantle plumes originate from the deepest regions in earth’s mantle. 3 • mantle plumes influence surface processes, including earth’s environment and climate. 1. A mantle plume is an area under the rocky outer layer of earth, called the crust, where magma is hotter than surrounding . magma. heat from this extra hot magma causes melting and thinning of the rocky crust, which leads to widespread volcanic activity on earth’s surface above the plume.while most volcanoes form along tectonic plate. Griffiths, r.w., stirring and structure in mantle starting plumes, earth and planetary science letters 99: 66 (1990). griffiths, r.w., the adjustment of mantle plumes to changes in plate motion, geophysical research letters 16: 437 (1989). gurnis, m, controls of the structure of subducted slabs, nature 335: 317 (1988).

Mantle Plume Definition Earth Science The Earth Images Revimage Org A mantle plume is an area under the rocky outer layer of earth, called the crust, where magma is hotter than surrounding . magma. heat from this extra hot magma causes melting and thinning of the rocky crust, which leads to widespread volcanic activity on earth’s surface above the plume.while most volcanoes form along tectonic plate. Griffiths, r.w., stirring and structure in mantle starting plumes, earth and planetary science letters 99: 66 (1990). griffiths, r.w., the adjustment of mantle plumes to changes in plate motion, geophysical research letters 16: 437 (1989). gurnis, m, controls of the structure of subducted slabs, nature 335: 317 (1988). The history of the hawaiian emperor seamount chain is critical for understanding earth’s interior evolution and plate tectonics. in the classical view, a mantle plume consists of a large head (>2000 km across) and a thin tail (~200 km wide) (6). the plume head generates a large igneous province (lip), such as the ontong java oceanic plateau. The mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth’s interior. the mantle lies between earth’s dense, superheated core and its thin outer layer, the crust. the mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) thick, and makes up a whopping 84 percent of earth’s total volume. as earth began to take shape about 4.5 billion years ago, iron and.

Mantle Plume Earth Science Definition The Earth Images The history of the hawaiian emperor seamount chain is critical for understanding earth’s interior evolution and plate tectonics. in the classical view, a mantle plume consists of a large head (>2000 km across) and a thin tail (~200 km wide) (6). the plume head generates a large igneous province (lip), such as the ontong java oceanic plateau. The mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth’s interior. the mantle lies between earth’s dense, superheated core and its thin outer layer, the crust. the mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) thick, and makes up a whopping 84 percent of earth’s total volume. as earth began to take shape about 4.5 billion years ago, iron and.
Mantle Plume Definition Earth Science The Earth Images Revimage Org

Comments are closed.