Maps Of Tectonic Plates Of The World
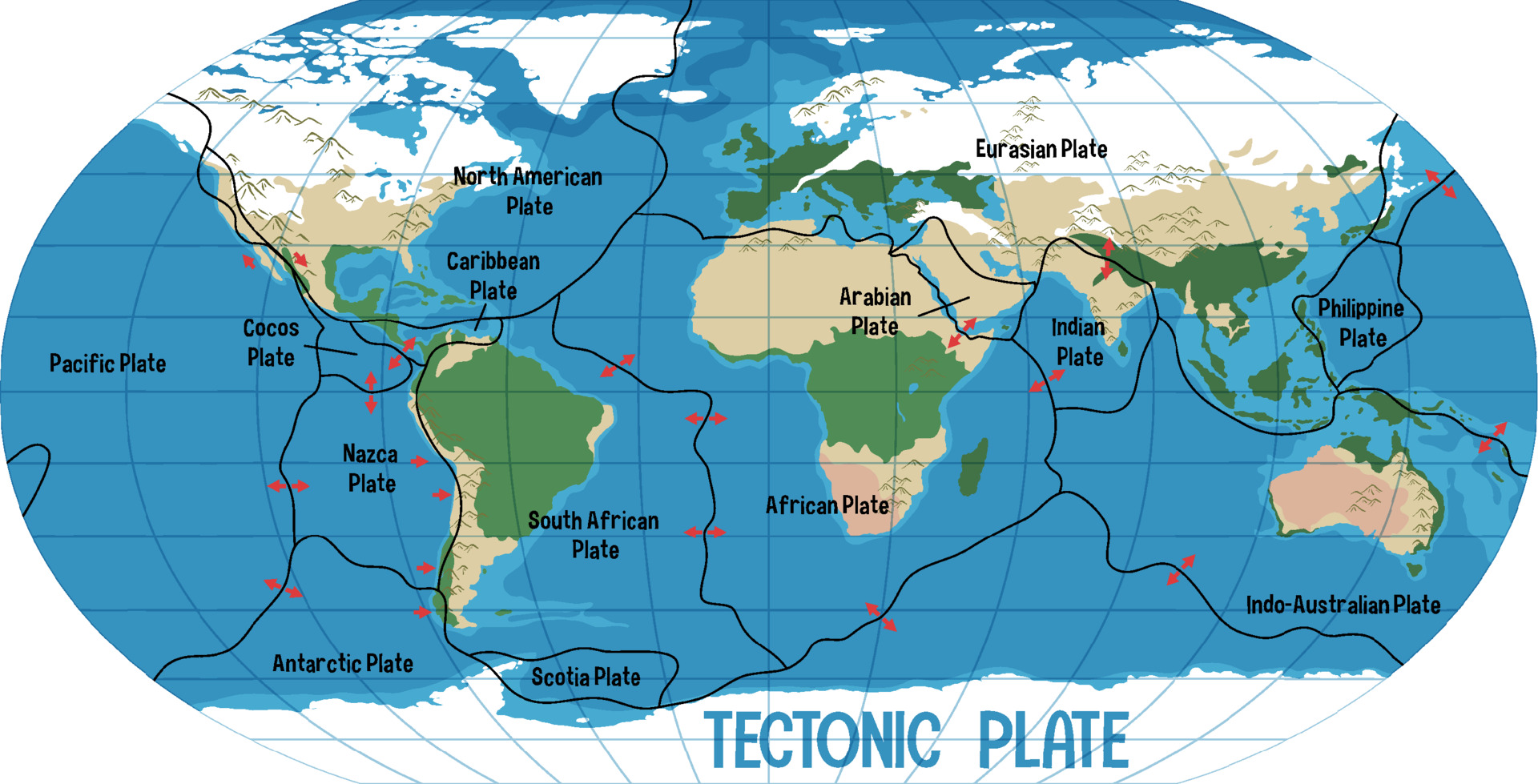
World Map Showing Tectonic Plates Boundaries 3755762 Vector Art At Vecteezy This map shows the major tectonic plates that make up earth’s lithosphere. tectonic plates are massive slabs of solid rock that float on the semi fluid asthenosphere beneath them and move relative to one another. the movement of these plates can cause earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain building, and ocean trench formation. A map of the tectonic plates of the earth showing the different boundary types in different colors. locations where plates collide (convergent boundaries) are shown in red. locations where plates are spreading (divergent boundaries) are shown in yellow. and, locations where plates are sliding past one another are shown in orange.
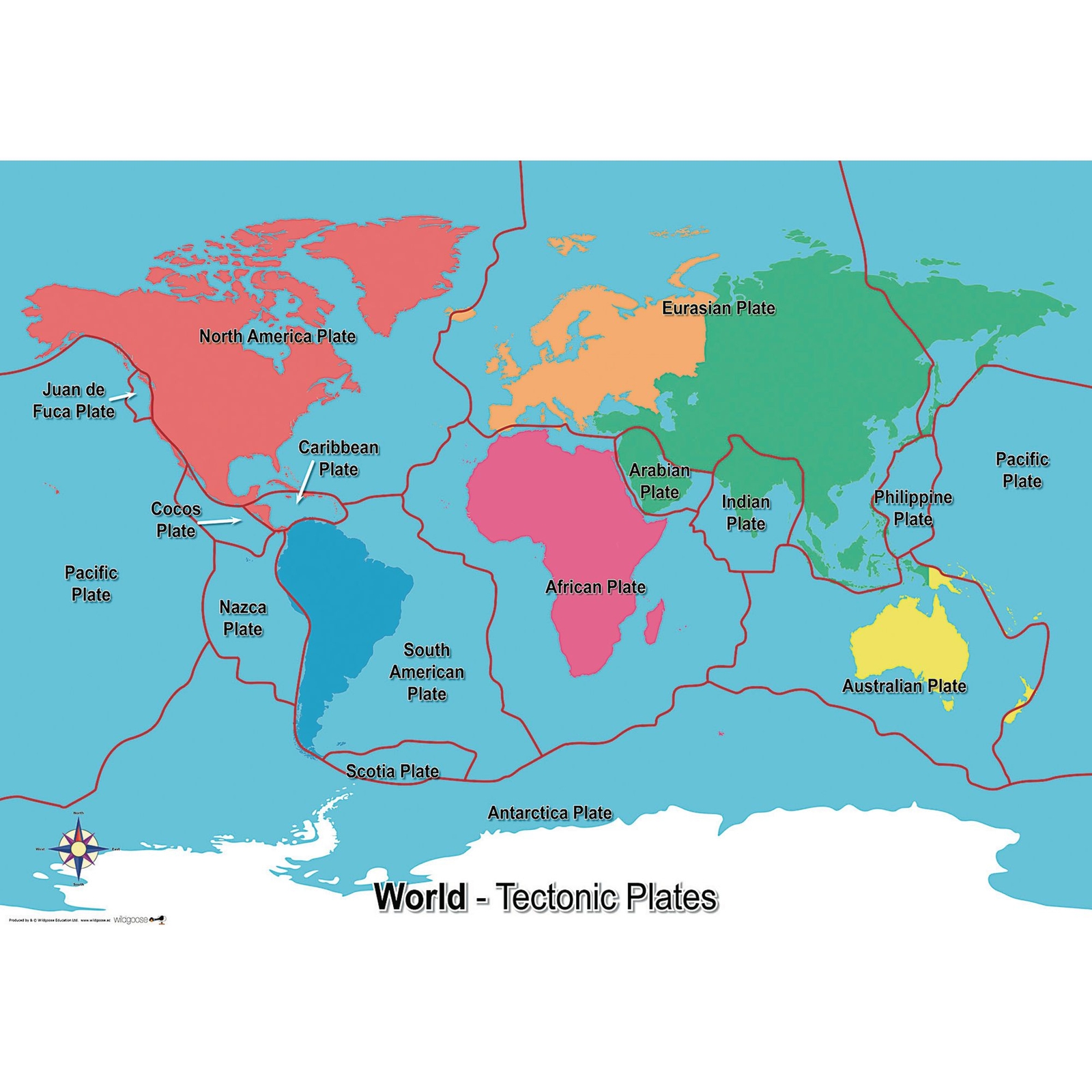
Tectonic Plates Map Tectonic plates, the massive slabs of earth’s lithosphere that help define our continents and ocean, are constantly on the move. plate tectonics is driven by a variety of forces: dynamic movement in the mantle, dense oceanic crust interacting with the ductile asthenosphere, even the rotation of the planet. Updated on january 30, 2020. the 2006 u.s. geological survey map of tectonic plates show 21 of the major plates, as well as their movements and boundaries. convergent (colliding) boundaries are shown as a black line with teeth, divergent (spreading) boundaries as solid red lines, and transform (sliding alongside) boundaries as solid black lines. Cross section view. plate tectonics plus rock formation. features include: plate tectonics. cross section view. rock types. rock sampler tool. temperature and pressure tool. The mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers around 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi). this trench delimits the nazca plate that goes beneath the south american plate. the deepest trench in the world is the mariana trench (or marianas trench). it has a depth of 10,984 m (36,037 ft) with an imprecision of ± 25 m (82 ft).

Adding Tectonic Plates To Your World Map World Building School Cross section view. plate tectonics plus rock formation. features include: plate tectonics. cross section view. rock types. rock sampler tool. temperature and pressure tool. The mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers around 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi). this trench delimits the nazca plate that goes beneath the south american plate. the deepest trench in the world is the mariana trench (or marianas trench). it has a depth of 10,984 m (36,037 ft) with an imprecision of ± 25 m (82 ft). Use this plate boundary map layer to explore how the movement of the plates causes earthquakes, volcanoes, or shapes earth’s landscape. use this map layer in the classroom. tectonic plates and physical features: in this activity, students will analyze maps of tectonic plates to predict the location of physical features. Tectonic plates and plate boundaries (wms) released monday, june 14, 2004. visualizations by: eric sokolowsky. view full credits. the earth's crust is constantly in motion. sections of the crust, called plates, push against each other due to forces from the molten interior of the earth. the areas where these plates collide often have increased.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tectonic-plates--812085686-6fa6768e183f48089901c347962241ff.jpg)
A Map Of Tectonic Plates And Their Boundaries Use this plate boundary map layer to explore how the movement of the plates causes earthquakes, volcanoes, or shapes earth’s landscape. use this map layer in the classroom. tectonic plates and physical features: in this activity, students will analyze maps of tectonic plates to predict the location of physical features. Tectonic plates and plate boundaries (wms) released monday, june 14, 2004. visualizations by: eric sokolowsky. view full credits. the earth's crust is constantly in motion. sections of the crust, called plates, push against each other due to forces from the molten interior of the earth. the areas where these plates collide often have increased.

Comments are closed.