Metal Ions With Large Positive Charge And Small Size May Acidify Solution Via Hydrolysis
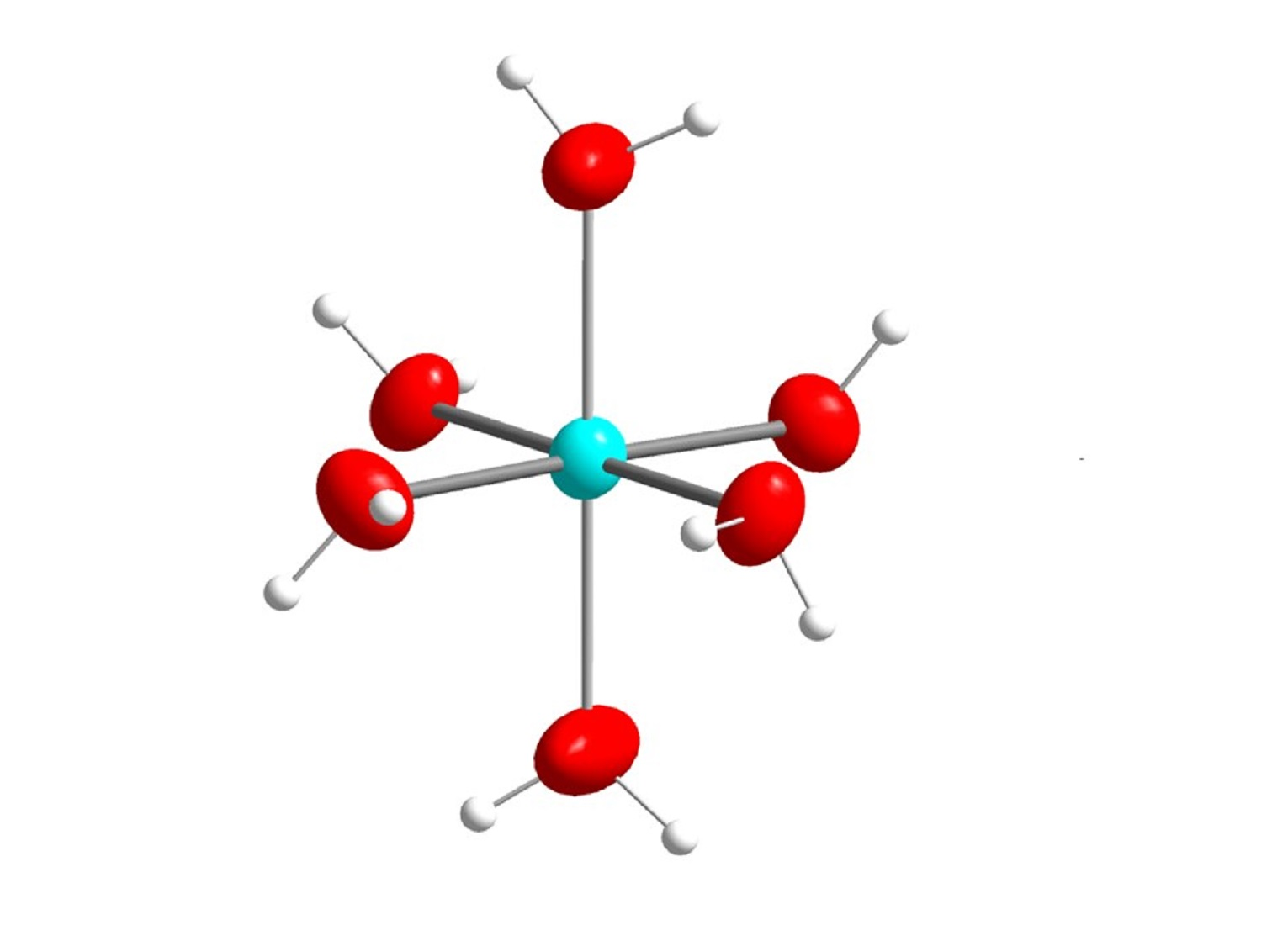
Liquids Free Full Text Structures Of Hydrated Metal Ions In Solid In progresstranscriptin aqueous solution, soluble metal ions are surrounded by a layer of water molecules. small metal ions with large positive charge, 2 o. Burgess, j. metal ions in solution ellis horwood, 1978, pg. 268. 6.3.8: high charge to size ratio metal ions act as brønsted acids in water is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by stephen m. contakes. aqueous solutions of simple salts of metal ions can also be acidic, even though a metal ion.

Formation Of Ion Spm Chemistry Salts that contain small, highly charged metal ions produce acidic solutions in water. the reaction of a salt with water to produce an acidic or a basic solution is called a hydrolysis reaction. 2.7: ions as acids and bases is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. So the ability of a metal cation to hydrolyze water molecules to form acidic solutions is based on the charge of the ion and the size of the atom. the larger atoms will stabilize charge better (i.e. it spreads it out over a larger space). unstable cations form hydroxides or oxides with water molecules and release hydronium ions. Hydrolysis. metal ions in aqueous solution behave as lewis acids. the positive charge on the metal ion draws electron density from the o h bond in the water. this increases the bond's polarity making it easier to break. when the o h bond breaks, an aqueous proton is released producing an acidic solution. Answer. exercise 12.9.1.2 12.9.1. 2. water has a pka p k a of 14. when water is bound to a zn 2 ion in aqueous solution, its pka p k a is lowered to 10. calculate the ph of pure water and the ph of a solution of 0.1 m znso 4. hint. answer. exercise 12.9.1.3 12.9.1. 3.

Natural Sciences Grade 9 Hydrolysis. metal ions in aqueous solution behave as lewis acids. the positive charge on the metal ion draws electron density from the o h bond in the water. this increases the bond's polarity making it easier to break. when the o h bond breaks, an aqueous proton is released producing an acidic solution. Answer. exercise 12.9.1.2 12.9.1. 2. water has a pka p k a of 14. when water is bound to a zn 2 ion in aqueous solution, its pka p k a is lowered to 10. calculate the ph of pure water and the ph of a solution of 0.1 m znso 4. hint. answer. exercise 12.9.1.3 12.9.1. 3. This is depicted in figure 5.5.3 below – note that the charge on the complex ion has reduced from 3 to 2, due to the loss of one positive charge. al(h 2 o) 6 3 (aq) h 2 o(l)⇌ h 3 o (aq) al(h 2 o) 5 (oh) 2 (aq) k a =1.4×10 5 figure 5.5.3. when an aluminum ion reacts with water, the hydrated aluminum ion becomes a weak acid. As shown in figure 15.4.1, the al (h2o)63 al (h 2 o) 6 3 ions involve bonds between a central al atom and the o atoms of the six water molecules. consequently, the bonded water molecules’ o–h bonds are more polar than in nonbonded water molecules, making the bonded molecules more prone to donation of a hydrogen ion:.
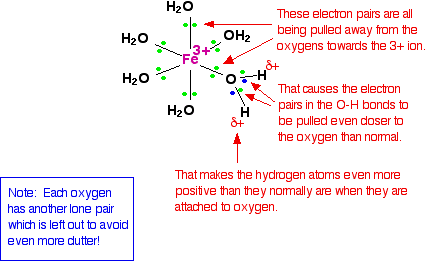
Complex Metal Ions The Acidity Of The Hexaaqua Ions Chemical This is depicted in figure 5.5.3 below – note that the charge on the complex ion has reduced from 3 to 2, due to the loss of one positive charge. al(h 2 o) 6 3 (aq) h 2 o(l)⇌ h 3 o (aq) al(h 2 o) 5 (oh) 2 (aq) k a =1.4×10 5 figure 5.5.3. when an aluminum ion reacts with water, the hydrated aluminum ion becomes a weak acid. As shown in figure 15.4.1, the al (h2o)63 al (h 2 o) 6 3 ions involve bonds between a central al atom and the o atoms of the six water molecules. consequently, the bonded water molecules’ o–h bonds are more polar than in nonbonded water molecules, making the bonded molecules more prone to donation of a hydrogen ion:.

Comments are closed.