Microorganisms In Water Visualization
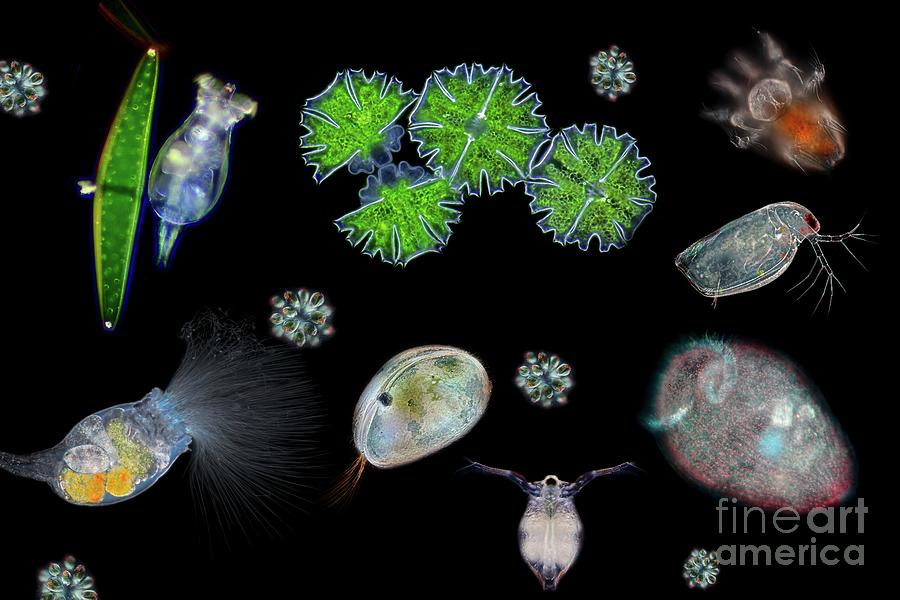
Compilation Of Various Water Microorganisms Photograph By Frank Fox Timeline visualization contained 477 nodes and 2267 connected lines, and the cluster analysis revealed that the research focus of rhizosphere microorganisms of wetland plants differed at different time stages (q = 0.5256 > 0.3, s = 0.8074 > 0.7; fig. 6). at the beginning of the study period (1995–1998), researchers focused on cluster #0. Abstract. the introduction of new approaches for characterizing microbial communities and imaging soil environments has benefited soil microbiology by providing new ways of detecting and locating.
Analysis Of Microorganisms In Water Microscopic Life Forms Stock May be used to identify specific microbes in a mixed population as well as identify non culturable microbes. for example, microscopic techniques are powerful tools used in the identification of microorganisms by visualization of the characteristic structures and for organisms in the vbnc (viable but not culturable) state. Early identification of pathogenic bacteria in food, water, and bodily fluids is very important and yet challenging, owing to sample complexities and large sample volumes that need to be rapidly. Direct microscopic observation of microorganisms is an important tool in many microbial studies. such observations have been reported for protozoa, fungi, inoculated bacteria, and rhizosphere microorganisms but few studies have focused on indigenous bacteria and their spatial relationship within various microhabitats. principles and applications of epifluorescence microscopy and confocal laser. The diverse open source nutrient acquisition strategies of plants highly depend on the participation of rhizosphere microorganisms (lamers et al., 2012). for example, some rhizosphere bacteria increase plant nutrient sources by increasing the bioavailability of insoluble minerals (teng et al., 2018; chawngthu et al., 2020).

Comments are closed.