Mike Campbell Blocked And Stratified Randomisation

Mike Campbell Blocked And Stratified Randomisation Youtube This video looks two methods of trying to get a better balance between two groups namely blocked randomisation and stratified randomisation. blocked randomis. Blocked randomisation… this video looks two methods of trying to get a better balance between two groups namely blocked randomisation and stratified randomisation. mike campbell blocked and stratified randomisation on vimeo.
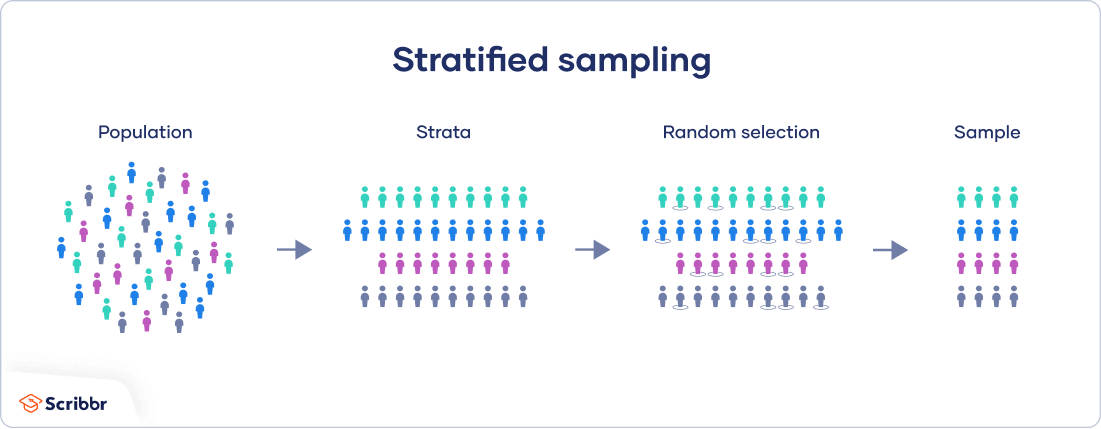
Stratified Sampling A Step By Step Guide With Examples Most participants agreed that stratified block randomisation is a valid and useful method of randomisation. their views reflected the fact that blocks ensured balanced numbers in each group whilst strata can ensure balance with respect to a few characteristics; also, by using randomly permuted blocks, predictability can be greatly reduced. Block randomization. if we consider only the balance in number of subjects in a study involving two treatment groups a and b, then a and b can be repeatedly allocated in a randomized block design with predefined block size. here, a selection bias is inevitable because a researcher or subject can easily predict the allocation of the group. We can describe the efficiency of platform trials with differing arm eligibility by evaluating the proportion of subjects randomized to the standard of care arm. in a two arm study with 1:1 allocation, the proportion randomized to standard of care is 12. in a multi arm trial with k experimental arms and equal allocation, it is 1 k 1. Restrictions during randomisation make it easier for investigators to guess the next allocation. statistical correction of any imbalance in confounders at the end of the study is equally accurate for most trials and would be safer randomised controlled trials commonly use some form of restriction when allocating participants—for example, blocking, stratification, or minimisation.1 2 the main.
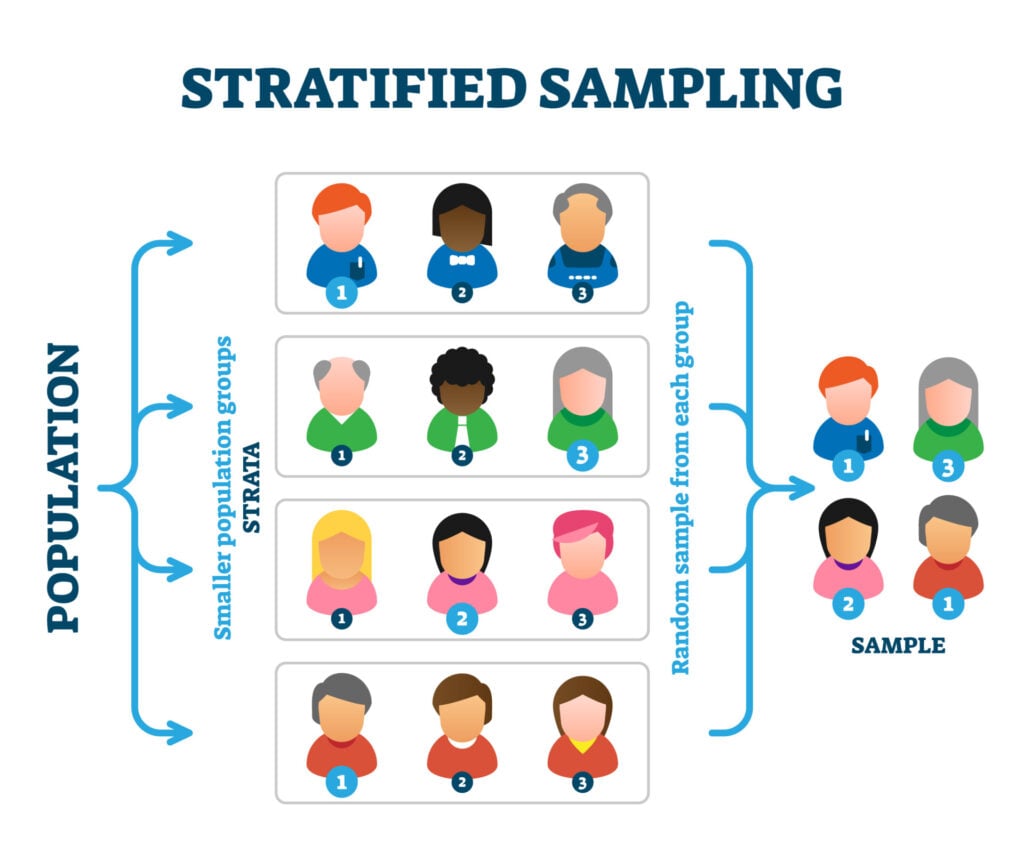
Stratified Random Sampling Definition Method Examples We can describe the efficiency of platform trials with differing arm eligibility by evaluating the proportion of subjects randomized to the standard of care arm. in a two arm study with 1:1 allocation, the proportion randomized to standard of care is 12. in a multi arm trial with k experimental arms and equal allocation, it is 1 k 1. Restrictions during randomisation make it easier for investigators to guess the next allocation. statistical correction of any imbalance in confounders at the end of the study is equally accurate for most trials and would be safer randomised controlled trials commonly use some form of restriction when allocating participants—for example, blocking, stratification, or minimisation.1 2 the main. The randomization method studied is a stratified permuted block permutation. we studied the four methods of allocating blocks to strata described in the previous section, i.e. Stratified blocked randomization consists of generating blocks of treatment allocation (e.g., a block of 4: "abba", meaning the first patient receives treatment a, the second treatment b, etc.). blocks can be of varying size, but one block contains an equal number of treatments a and b in order to achieve balance between groups.

Comments are closed.