Mitosis And Meiosis Stages
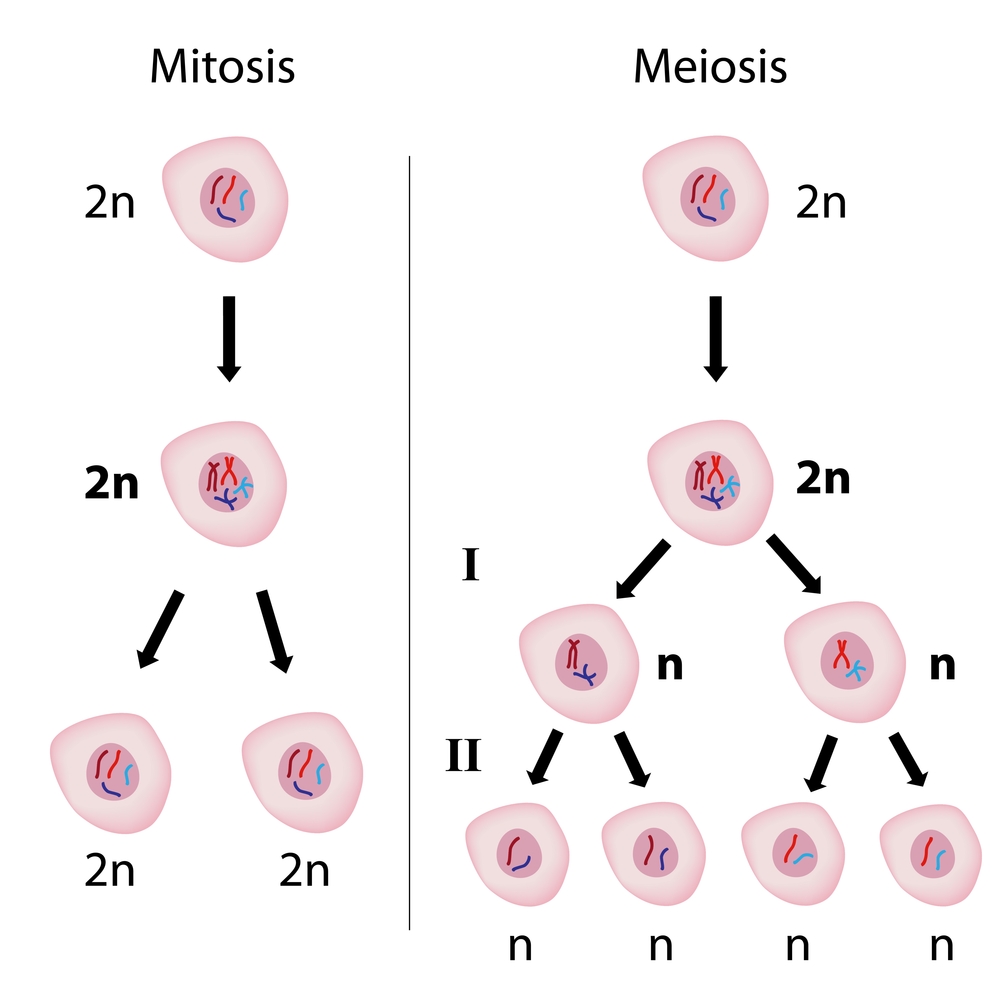
Understand The Cell Cycle Worksheet Edplace Learn the differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division. mitosis produces two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four non identical haploid cells for gamete formation. Before meiosis i starts, the cell goes through interphase. just like in mitosis, the parent cell uses this time to prepare for cell division by gathering nutrients and energy and making a copy of its dna. during the next stages of meiosis, this dna will be switched around during genetic recombination and then divided between four haploid cells.
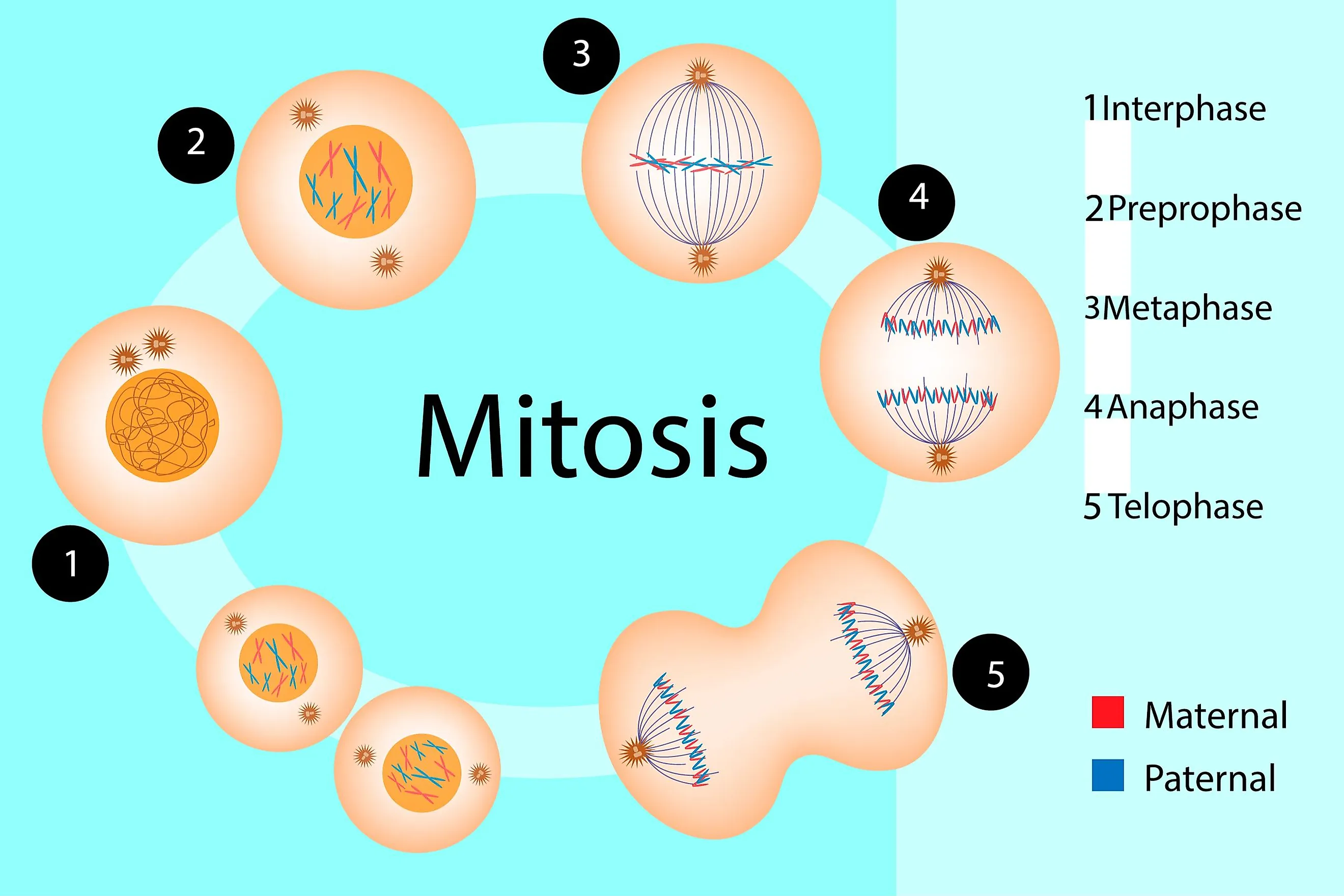
Meiosis Vs Mitosis Cells Learn the differences between mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division in eukaryotes. mitosis produces identical daughter cells for growth and repair, while meiosis produces non identical daughter cells for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. The stages of mitosis vs. meiosis the stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, sometimes followed by cytokinesis. “interphase” is a blanket term which describes all the stages before mitosis, that is: g1, s and g2 phases. The m phase completes the cell cycle. ’m’ could be mitosis or meiosis depending on the type of cell. for the zygote, the goal is to make more somatic cells. therefore, it goes through mitosis and gives rise to two daughter cells. this completes the life cycle of the zygote and starts the lifecycle of the new cells. During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and go to opposite ends of the dividing cell. mitosis ends with 2 identical cells, each with 2n chromosomes and 2x dna content. all eukaryotic cells replicate via mitosis, except germline cells that undergo meiosis (see below) to produce gametes (eggs and sperm).

Meiosis Process The m phase completes the cell cycle. ’m’ could be mitosis or meiosis depending on the type of cell. for the zygote, the goal is to make more somatic cells. therefore, it goes through mitosis and gives rise to two daughter cells. this completes the life cycle of the zygote and starts the lifecycle of the new cells. During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and go to opposite ends of the dividing cell. mitosis ends with 2 identical cells, each with 2n chromosomes and 2x dna content. all eukaryotic cells replicate via mitosis, except germline cells that undergo meiosis (see below) to produce gametes (eggs and sperm). Mitosis occurs in somatic cells; this means that it takes place in all types of cells that are not involved in the production of gametes.prior to each mitotic division, a copy of every chromosome. Learn about the stages of mitosis and cell division, from interphase to cytokinesis, and how they are regulated by proteins and checkpoints. see illustrations of chromosome movements, spindle formation, and cell cycle phases.

Comments are closed.