Morphology Cultural Characteristics Of Staphylococcus Aureus

Staphylococcus Aureus Cultural Characteristics Medical Laboratory Staphylococcus: morphology, cultural characteristics, pathogenicity, antibiotic sensitivity. staphylococcus is a genus of gram positive bacteria known for their spherical or grape like clustered shape under a microscope. they are commonly found in various environments, including on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. Introduction. s taphylococcus aureus is a gram positive coccus that colonizes the nasal mucosa and skin of healthy individuals. 1 this organism can cause a wide range of diseases from skin or soft tissue infections to systemic and fatal diseases. 1–3 in particular, methicillin resistant s. aureus (mrsa) is a hazardous organism because of its resistance to multiple antibiotics and biofilm.
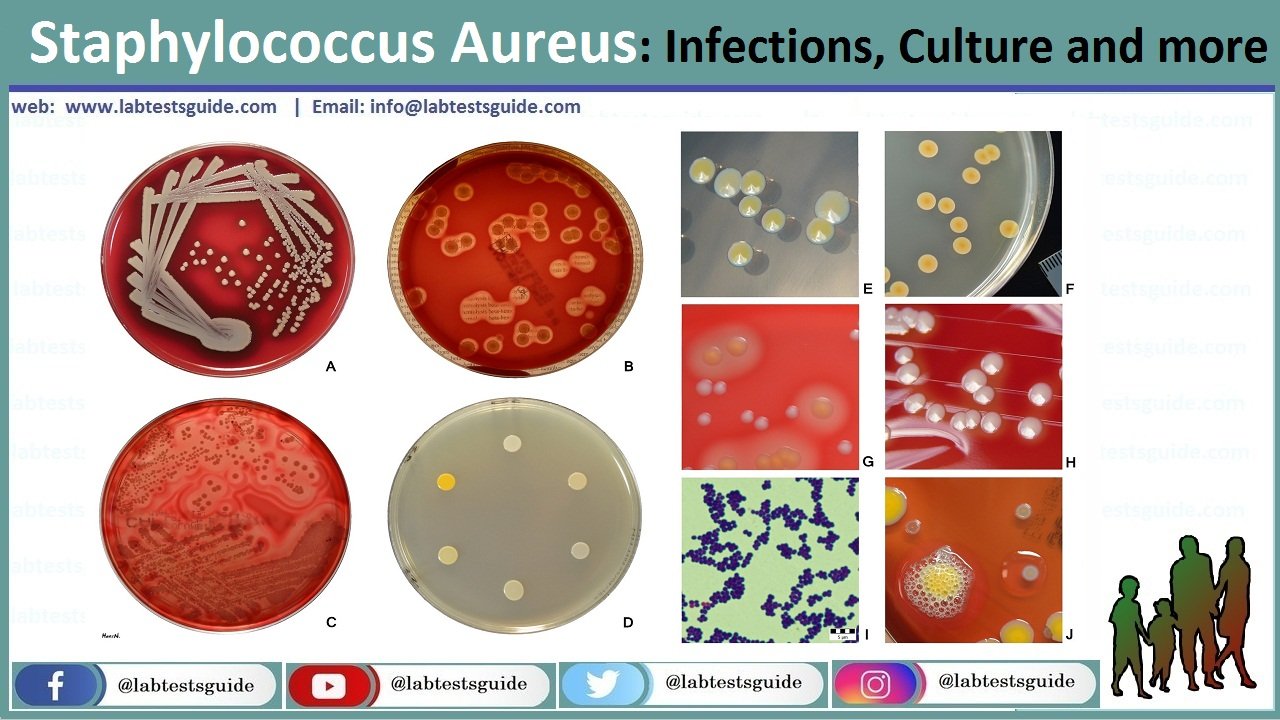
Staphylococcus Aureus Culture Media Cultural characteristics of staphylococcus aureus. staphylococci grow readily on most bacteriologic media under aerobic or microaerophilic conditions. colonies on solid media are round, smooth, raised, and glistening. s. aureus usually forms gray to deep golden yellow colonies. Keywords: staphylococcus aureus, biofilm formation, gene expression, quorum sensing, antimicrobial resistance, pathogenesis, antibiofilm agents. staphylococcus aureus (also denoted as staph. aureus or s. aureus) is a gram positive pathogenic bacterium and is a major cause of different infectious illnesses in humans and animals [1, 2]. Introduction. infections due to staphylococcus aureus present a substantial health problem in the united states (20, 23). s. aureus is a major cause of hospital acquired pneumonia and lower respiratory tract infections and the primary cause of surgical site infections and skin and soft tissue infections (sstis) and is now likely the leading cause of invasive bacterial disease (20, 23). The characteristics used to identify staphylococcus aureus include gram stain morphology, cell morphology, production of catalase, coagulase production, pigment production, susceptibility to.

Cultural Morphological And Biochemical Characterization Of Introduction. infections due to staphylococcus aureus present a substantial health problem in the united states (20, 23). s. aureus is a major cause of hospital acquired pneumonia and lower respiratory tract infections and the primary cause of surgical site infections and skin and soft tissue infections (sstis) and is now likely the leading cause of invasive bacterial disease (20, 23). The characteristics used to identify staphylococcus aureus include gram stain morphology, cell morphology, production of catalase, coagulase production, pigment production, susceptibility to. 2.2. general cultural and biochemical characteristics s. aureus is an aerobic and facultative anaerobic organism that forms fairly large yellow or white colonies on nutrient rich agar media. the yellow colour of the colonies is imparted by carotenoids produced by the organism. the term ‘aureus’ is derived from latin, which refers. Characteristics of <i>staphylococcus aureus< i> infections include biofilm formation, leading to the spread of bacteria to the bloodstream causing sepsis and metastatic infections. in particular, in methicillin resistant <i>s. aureus< i> (mrsa) infections, biofilm formation critically hampers treatm ….

Staphylococcus Aureus Morphology Identification Biochemical Tests 2.2. general cultural and biochemical characteristics s. aureus is an aerobic and facultative anaerobic organism that forms fairly large yellow or white colonies on nutrient rich agar media. the yellow colour of the colonies is imparted by carotenoids produced by the organism. the term ‘aureus’ is derived from latin, which refers. Characteristics of <i>staphylococcus aureus< i> infections include biofilm formation, leading to the spread of bacteria to the bloodstream causing sepsis and metastatic infections. in particular, in methicillin resistant <i>s. aureus< i> (mrsa) infections, biofilm formation critically hampers treatm ….

Comments are closed.