Newtons Laws Notes

Newton S Laws Of Motion The rate of change of an object’s momentum equals the force acting upon it or the applied force equal’s an object’s mass times its acceleration. the two equations for newton’s second law are: f = m*a. f = Δp Δt. here, f is the applied force, m is mass, a is acceleration, p is momentum, and t is time. note that the second law tells us. Go ad free for 1 year. newton's laws of motion describe the connection between the forces that act upon an object and the manner in which the object moves. an understanding of forces and their tendency to balance or not balance each other is crucial to understanding how the object will change or not change its state of motion.

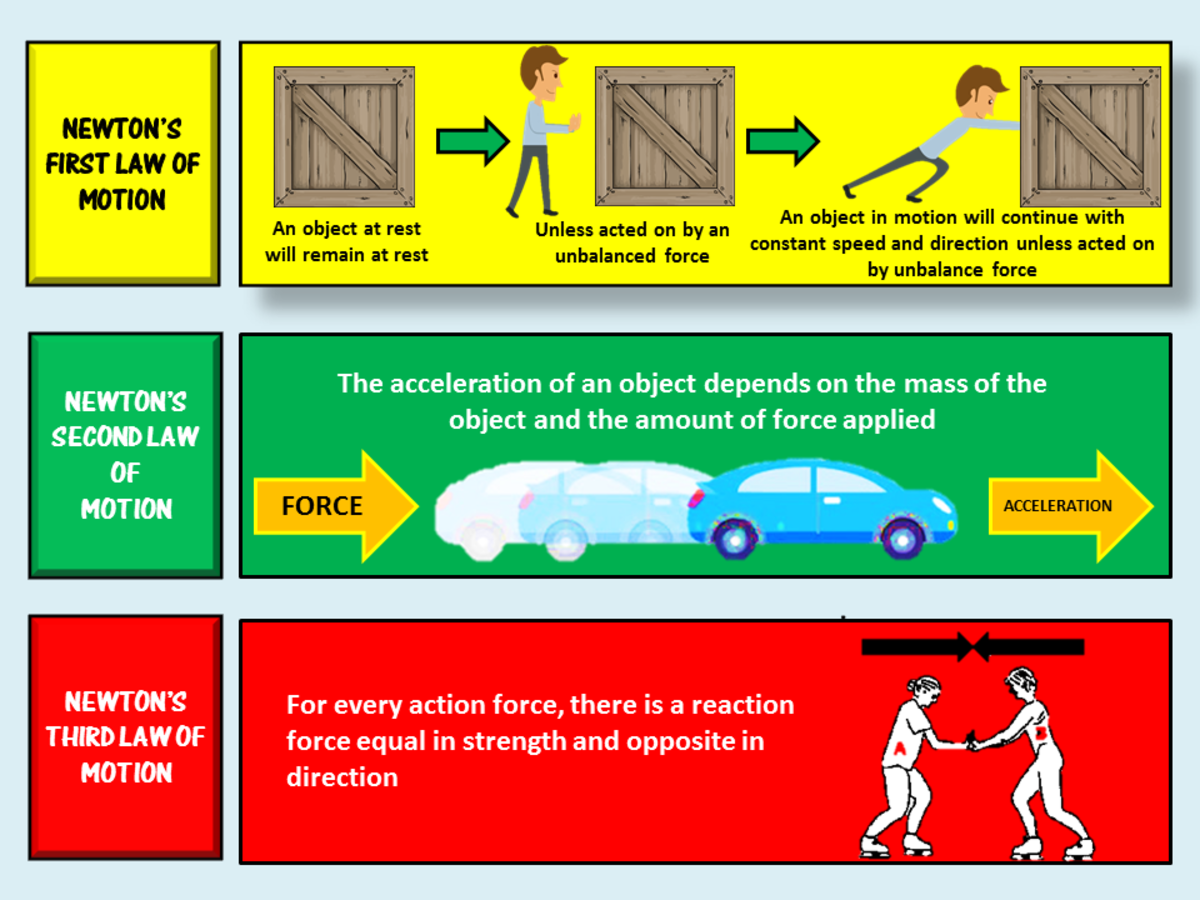
Newton S Laws Of Motion Doodle Notes Bundle Doodle Notes Newtons Newton. si unit of force; 1 n is the force needed to accelerate an object with a mass of 1 kg at a rate of 1 m s 2. newton’s first law of motion. body at rest remains at rest or, if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force; also known as the law of inertia. newton’s second law of motion. Riding a bicycle is an excellent example of newton’s 2nd law. in this example, the bicycle is the mass. the leg muscles pushing on the pedals of the bicycle is the force. you hit a wall with a certain amount of force, and the wall returns that same amount of force. this is an example of newton’s 3rd law. Newton’s laws of motion relate an object’s motion to the forces acting on it. in the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. in the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. in the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude. The study of motion is kinematics, but kinematics only describes the way objects move—their velocity and their acceleration. dynamics considers the forces that affect the motion of moving objects and systems. newton’s laws of motion are the foundation of dynamics. these laws provide an example of the breadth and simplicity of principles.
Newton S 3 Laws Of Motion Explained Owlcation Newton’s laws of motion relate an object’s motion to the forces acting on it. in the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. in the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. in the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude. The study of motion is kinematics, but kinematics only describes the way objects move—their velocity and their acceleration. dynamics considers the forces that affect the motion of moving objects and systems. newton’s laws of motion are the foundation of dynamics. these laws provide an example of the breadth and simplicity of principles. [note 6] newton's third law relates to a more fundamental principle, the conservation of momentum. the latter remains true even in cases where newton's statement does not, for instance when force fields as well as material bodies carry momentum, and when momentum is defined properly, in quantum mechanics as well. Week 2: newton’s laws. week 2 introduction; lesson 4: newton’s laws of motion. 4.1 newton’s first and second laws; 4.2 newton’s third law; 4.3 reference frames; 4.4 non inertial reference frames; lesson 5: gravity. 5.1 universal law of gravitation; 5.2 worked example: gravity superposition; 5.3 gravity at the surface of the earth: the.

Solution Newtons Laws Of Motion Handwritten Notes Studypool [note 6] newton's third law relates to a more fundamental principle, the conservation of momentum. the latter remains true even in cases where newton's statement does not, for instance when force fields as well as material bodies carry momentum, and when momentum is defined properly, in quantum mechanics as well. Week 2: newton’s laws. week 2 introduction; lesson 4: newton’s laws of motion. 4.1 newton’s first and second laws; 4.2 newton’s third law; 4.3 reference frames; 4.4 non inertial reference frames; lesson 5: gravity. 5.1 universal law of gravitation; 5.2 worked example: gravity superposition; 5.3 gravity at the surface of the earth: the.

юааnewtonтащsюаб юааlawsюаб Of Motion 1st And 2nd Summary юааnewtonsюаб юааlawsюаб Physics

Comments are closed.