Newtons Second Law Forces Motion Physics Fuseschool

Newton S Second Law Forces Motion Physics Fuseschool Youtu In this video, we are going to learn about and practice applying newton’s second law in calculations, relating force, mass and acceleration.creditsanimation. Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. this verbal statement can be expressed in equation form as follows:.
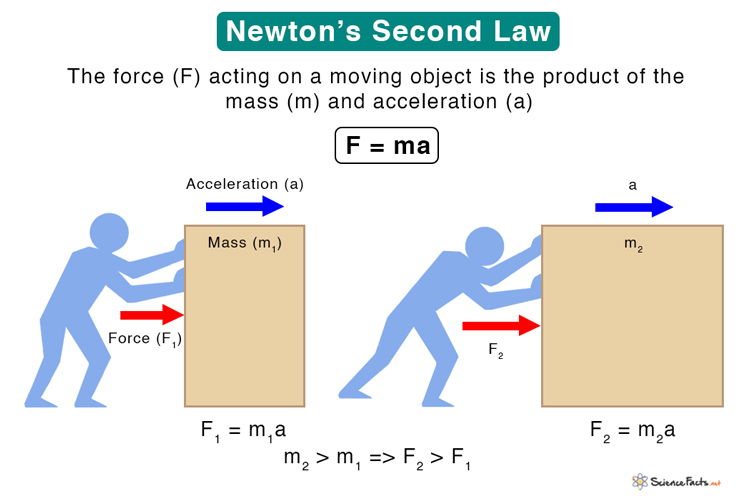
юааnewtonтащsюаб юааsecondюаб юааlawюаб Statement Examples And Equation Newton’s second law states that the magnitude of the net external force on an object is f {\text {net }}=m a . since the object experiences only the downward force of gravity, f {\text {net }}=w. we know that the acceleration of an object due to gravity is g, or a=g. substituting these into newton’s second law gives. This problem involves only motion in the horizontal direction; we are also given the net force, indicated by the single vector, but we can suppress the vector nature and concentrate on applying newton’s second law. since f net and m are given, the acceleration can be calculated directly from newton’s second law as f net = ma. Newton's second law of motion states that f = ma, or net force is equal to mass times acceleration. a larger net force acting on an object causes a larger acceleration, and objects with larger mass require more force to accelerate. both the net force acting on an object and the object's mass determine how the object will accelerate. Explain that, according to newton’s first law, a change in motion is caused by an external force. for instance, a ball that is pitched changes its speed and direction when it is hit by a bat. [bl] [ol] [al] write the equation for newton’s second law and show how it can be solved for all three variables, f, m, and a. explain the practical.

Comments are closed.