Nitrogen And Hydrogen Covalent Bond
Nitrogen And Hydrogen Covalent Bond Vrogue Co The formula of the carbonate ion is co 32−. the atoms of a polyatomic ion are tightly bonded together and so the entire ion behaves as a single unit. several examples are found in table 3.3.1. nonmetal atoms in polyatomic ions are joined by covalent bonds, but the ion as a whole participates in ionic bonding. These bonds are stronger and much more common than ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon based organic molecules, such as our dna and proteins. covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules like h 2 o, co 2, and o 2. one, two, or three pairs of electrons may be shared, making single.

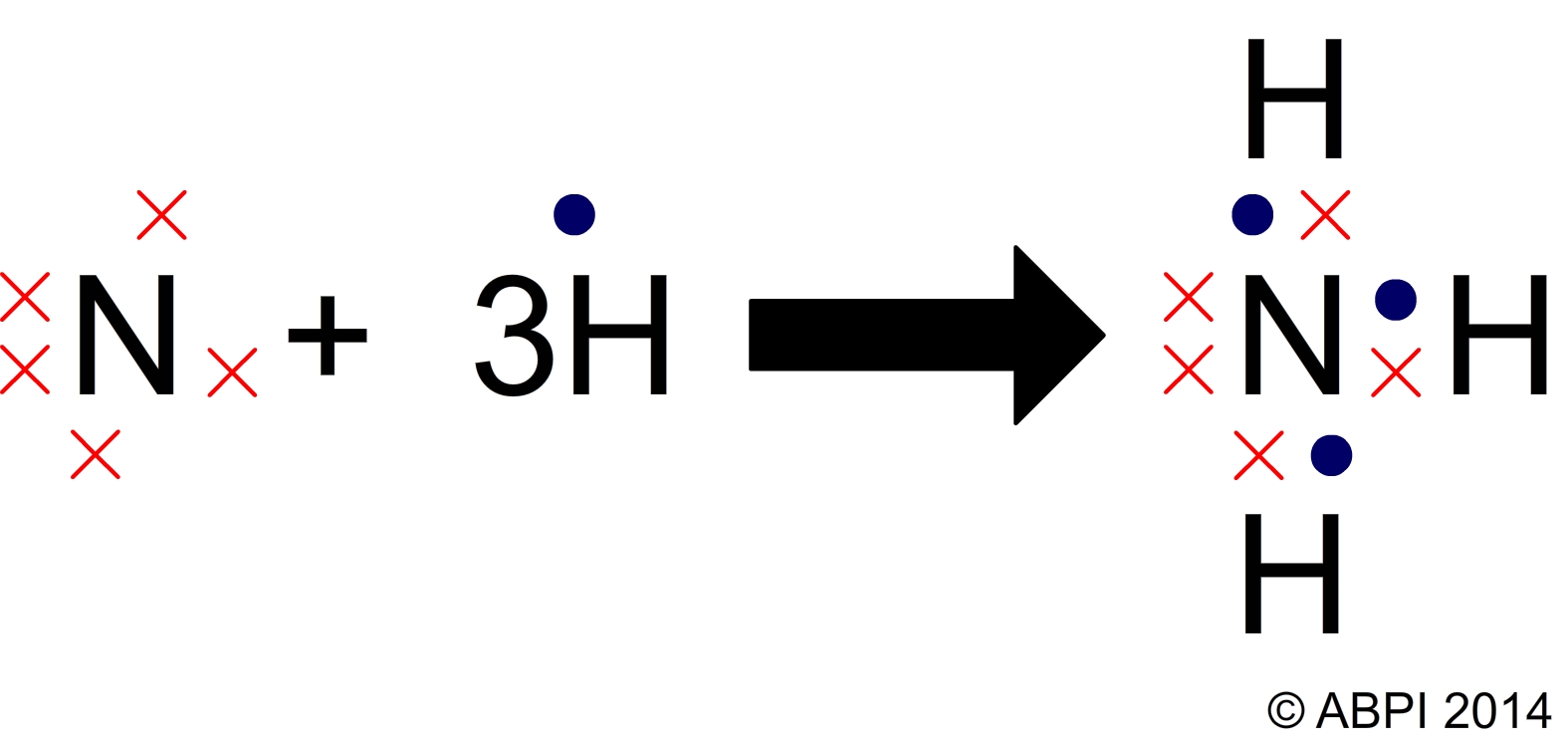
Nitrogen And Hydrogen Bond When analogous bonds in similar compounds are compared, bond length decreases as bond order increases. the bond length data in table 10.2.1 10.2. 1, for example, show that the c–c distance in h 3 c–ch 3 (153.5 pm) is longer than the distance in h 2 c=ch 2 (133.9 pm), which in turn is longer than that in hc≡ch (120.3 pm). Formation of covalent bonds. nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. for example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. figure 7.4 illustrates why this bond is formed. starting on the far right, we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy. Single, double, and triple bonds. covalent bonds exist as single, double, or triple bonds. in a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. hydrogen gas (h 2 or h h) has a single covalent bond, where each hydrogen atom shares its single electron with the other. in a double bond, atoms share two pairs of electrons. Nonmetals like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen form covalent bonds with themselves or other atoms. the number of covalent bonds that they can form is as follows: hydrogen – 1. oxygen – 2. nitrogen – 3. carbon – 4. here are some examples of covalent compounds [1 9]: 1. hydrogen (h 2) hydrogen (h) is the simplest of all elements.
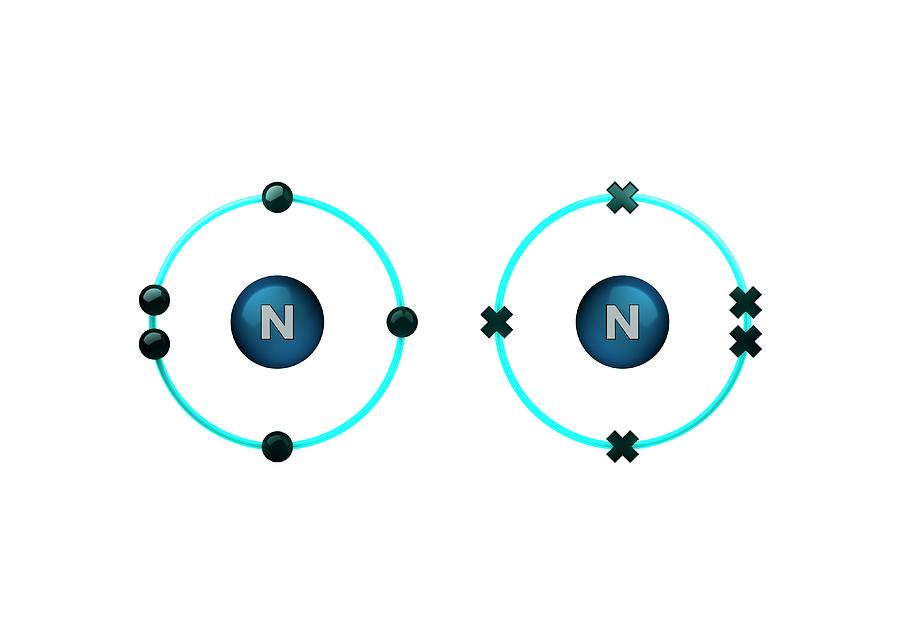
Nitrogen And Hydrogen Covalent Bond Vrogue Co Single, double, and triple bonds. covalent bonds exist as single, double, or triple bonds. in a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. hydrogen gas (h 2 or h h) has a single covalent bond, where each hydrogen atom shares its single electron with the other. in a double bond, atoms share two pairs of electrons. Nonmetals like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen form covalent bonds with themselves or other atoms. the number of covalent bonds that they can form is as follows: hydrogen – 1. oxygen – 2. nitrogen – 3. carbon – 4. here are some examples of covalent compounds [1 9]: 1. hydrogen (h 2) hydrogen (h) is the simplest of all elements. A brief treatment of covalent bonds follows. for full treatment, see chemical bonding: covalent bonds. molecules that have covalent linkages include the inorganic substances hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine, water, and ammonia (h 2, n 2, cl 2, h 2 o, nh 3) together with all organic compounds. in structural representations of molecules, covalent. Learn the basics about the covalent bonding of hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen as a part of the overall topic of properties of matter. the noble gas structure.

Comments are closed.