Non Contact Mode How Afm Works Principle Of Atomic Force Microscopy

What Is Afm Learn About Atomic Force Microscopy Nanoandmore Non contact mode in afm is the safest measurement method where the tip does not touch the sample during the afm scan. for more how afm works series: p. Non contact atomic force microscopy (nc afm), also known as dynamic force microscopy (dfm), is a mode of atomic force microscopy, which itself is a type of scanning probe microscopy. in nc afm a sharp probe is moved close (order of angstroms) to the surface under study, the probe is then raster scanned across the surface, the image is then.

Working Modes Of Afm A Contact Mode B Non Contact Modeо Atomic force microscopy (afm) was developed when people tried to extend. stm technique to investigate the electrically non conductive materials, like. proteins. in 1986, binnig and quate demonstrated for the first time the ideas of afm, which used an ultra small probe tip at the end of a cantilever (phys. rev. letters, 1986, vol. 56, p 930). Atomic force microscopy (afm) is a powerful and versatile scanning probe microscopy technique that has revolutionized nanoscale imaging and measurement. since its invention in 1986 by binnig, quate, and gerber, afm has become an essential tool for researchers in various fields, including physics, chemistry, biology, and materials science. Page id. atomic force microscopy (afm) is a high resolution form of scanning probe microscopy, also known as scanning force microscopy (sfm). the instrument uses a cantilever with a sharp tip at the end to scan over the sample surface (figure 9.2.1). as the probe scans over the sample surface, attractive or repulsive forces between the tip and. Overall, the implication of the above model is that the nc afm image may be considered, in the limit of small a, to be a map of constant interaction force gradient experienced by the tip due to the sample. the non contact mode has the advantage that the tip never makes contact with the sample and therefore cannot disturb or destroy the sample.

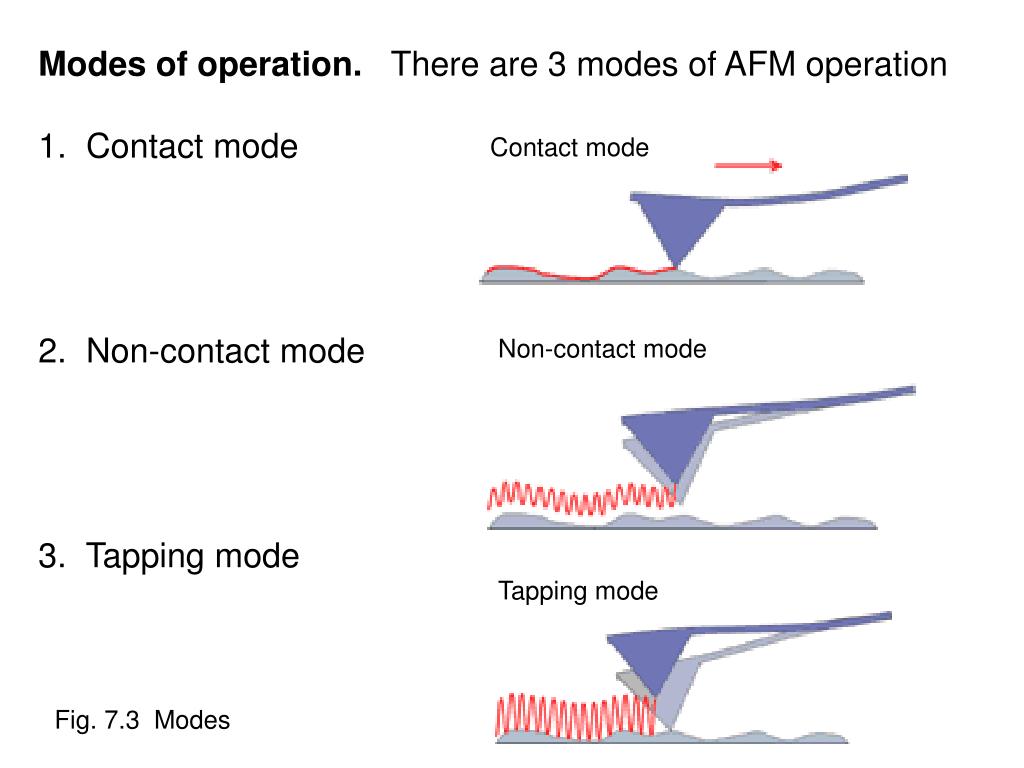
Non Contact Mode How Afm Works Principle Of Atomic Force Microscopy Page id. atomic force microscopy (afm) is a high resolution form of scanning probe microscopy, also known as scanning force microscopy (sfm). the instrument uses a cantilever with a sharp tip at the end to scan over the sample surface (figure 9.2.1). as the probe scans over the sample surface, attractive or repulsive forces between the tip and. Overall, the implication of the above model is that the nc afm image may be considered, in the limit of small a, to be a map of constant interaction force gradient experienced by the tip due to the sample. the non contact mode has the advantage that the tip never makes contact with the sample and therefore cannot disturb or destroy the sample. Afm provides a 3d profile of the surface on a nanoscale, by measuring forces between a sharp probe (<10 nm) and surface at very short distance (0.2 10 nm probe sample separation). the probe is supported on a flexible cantilever. the afm tip “gently” touches the surface and records the small force between the probe and the surface. There are 3 main modes of operation: contact mode, non contact mode, and tapping mode. in contact mode, the tip is brought into physical contact with the sample, and measures a repulsive force. because the force displacement curve is much steeper in this regime, the signal is much larger than the non contact mode.

Helen Greenwood Hansma S Research Afm provides a 3d profile of the surface on a nanoscale, by measuring forces between a sharp probe (<10 nm) and surface at very short distance (0.2 10 nm probe sample separation). the probe is supported on a flexible cantilever. the afm tip “gently” touches the surface and records the small force between the probe and the surface. There are 3 main modes of operation: contact mode, non contact mode, and tapping mode. in contact mode, the tip is brought into physical contact with the sample, and measures a repulsive force. because the force displacement curve is much steeper in this regime, the signal is much larger than the non contact mode.
Ppt Atomic Force Microscopy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download

Comments are closed.