Nuclear Power Reactors How Does A Nuclear Reactor Work World

Nuclear Power Reactors How Does A Nuclear Reactor Work World Nuclear reactors are the heart of a nuclear power plant. they contain and control nuclear chain reactions that produce heat through a physical process called fission. that heat is used to make steam that spins a turbine to create electricity. with more than 400 commercial reactors worldwide, including 93 in the united states, nuclear power. About 9% of the world's electricity is produced from nuclear energy. most nuclear electricity is generated using just two kinds of reactor. new designs are coming forward and some are in oper improved designs of nuclear power reactors are currently being developed in several countries. newer advanced reactors now being built have simpler.
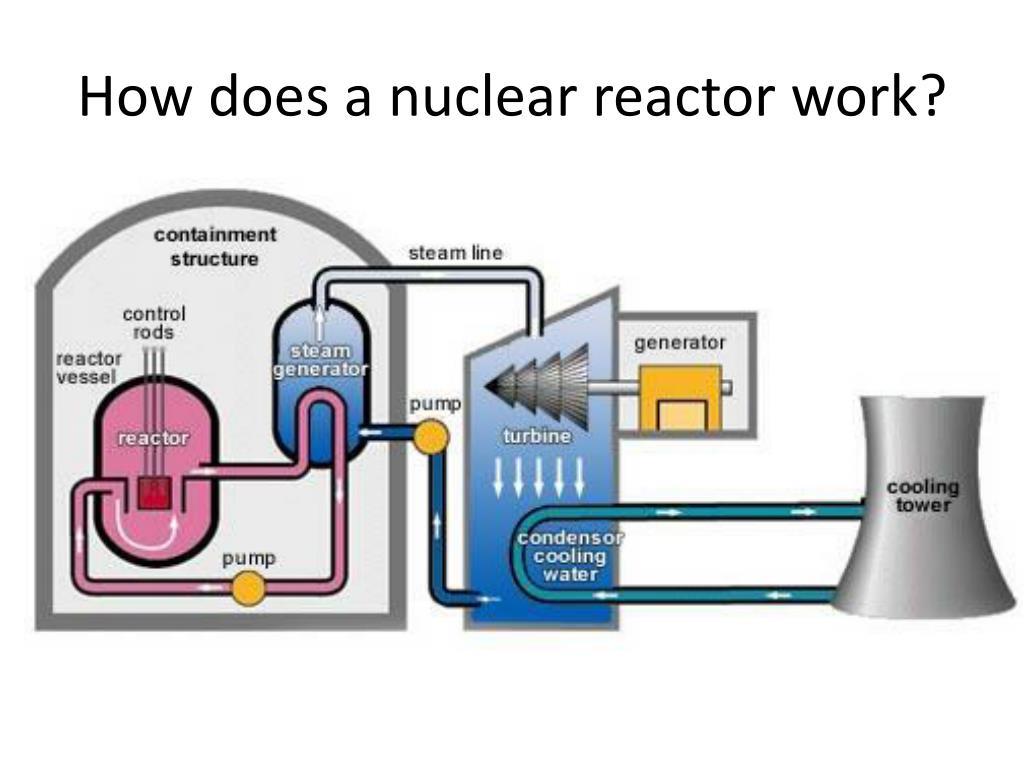
Ppt How Does A Nuclear Reactor Work Powerpoint Presentation Free Nuclear reactors are designed to sustain an ongoing chain reaction of fission; the reactors operating in the u.s. today are filled with a specially designed, solid uranium fuel and surrounded by water, which facilitates the process. when the reactor starts, uranium atoms will split, releasing neutrons and heat. The chernobyl sarcophagus, built to contain the effects of the 1986 disaster. a nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction. nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. when a fissile nucleus like uranium 235 or plutonium 239 absorbs. Nuclear power reactors produce energy by initiating and controlling a sustained nuclear chain reaction. currently, over 400 such reactors in 32 countries provide about 10 per cent of the world’s electricity. the iaea fosters an international information exchange and collaboration on technological innovations in different reactor technologies. Nuclear reactors have one job: to split atoms in a controlled reaction and use the released energy to generate electrical power. over the years, reactors have been viewed as both a miracle and a menace. when the first u.s. commercial reactor went on line in shippingport, pa., in 1956, the technology was hailed as the energy source of the future.

Nuclear Reactor Definition History Components Britannica Nuclear power reactors produce energy by initiating and controlling a sustained nuclear chain reaction. currently, over 400 such reactors in 32 countries provide about 10 per cent of the world’s electricity. the iaea fosters an international information exchange and collaboration on technological innovations in different reactor technologies. Nuclear reactors have one job: to split atoms in a controlled reaction and use the released energy to generate electrical power. over the years, reactors have been viewed as both a miracle and a menace. when the first u.s. commercial reactor went on line in shippingport, pa., in 1956, the technology was hailed as the energy source of the future. So how do nuclear reactors work, and can the atom become "our friend" again? chicago pile 1 (cp 1) was activated, becoming the world's first nuclear reactor. today, 78 years later, 440. Step one: split atoms to create heat. nuclear plants harness the incredible power of nuclear fission to generate heat and energy, which ultimately becomes electricity. fission occurs when a neutron hits a larger atom and splits the atom into two smaller atoms. when a reactor starts, the uranium atoms in the reactor core split, releasing.
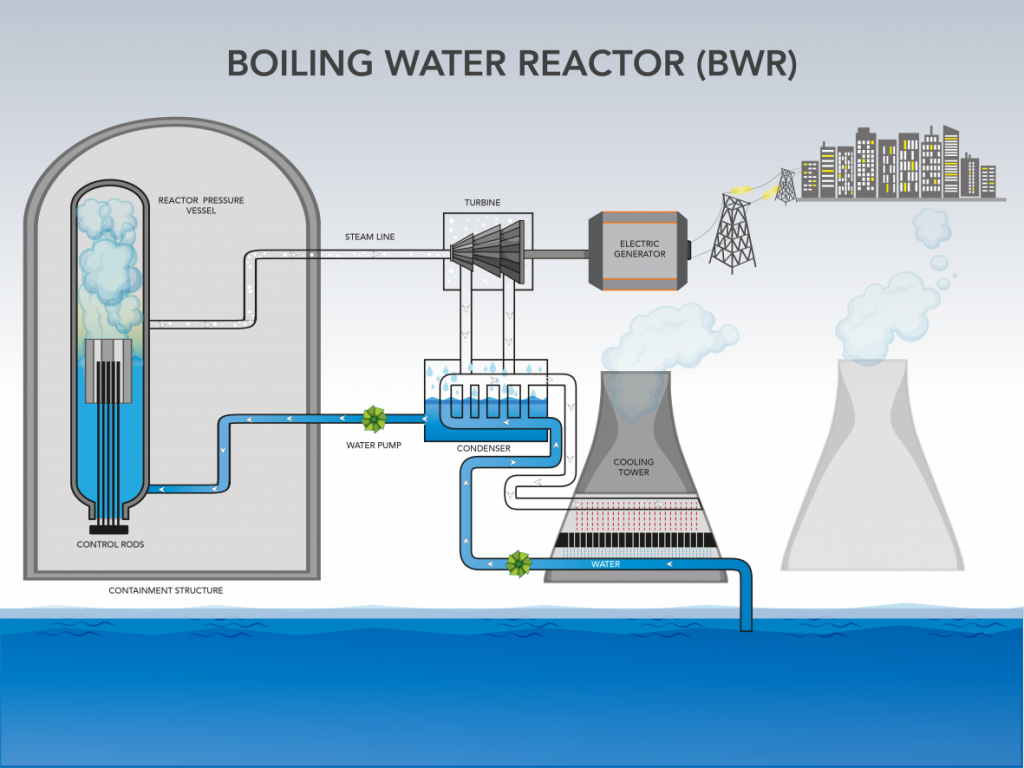
How Do Nuclear Power Plants Work Prv Engineering Blog So how do nuclear reactors work, and can the atom become "our friend" again? chicago pile 1 (cp 1) was activated, becoming the world's first nuclear reactor. today, 78 years later, 440. Step one: split atoms to create heat. nuclear plants harness the incredible power of nuclear fission to generate heat and energy, which ultimately becomes electricity. fission occurs when a neutron hits a larger atom and splits the atom into two smaller atoms. when a reactor starts, the uranium atoms in the reactor core split, releasing.

Comments are closed.