Nuclear Reactor в Energy Knowledgebase
Nuclear Reactor в Energy Knowledgebase Nuclear reactor. a nuclear reactor initiates and controls a fission chain reaction to produce neutrons and or energy. nuclear fission is a process where the nucleus of an atom is split into two or more smaller nuclei, known as fission products. fission of heavy elements (elements with an atomic number greater than 92) results in a reaction that. Tihange nuclear power station in belgium . the use of nuclear energy for power generation became a commercial technology in the 1960s and grew rapidly in some countries around the world during the 1970s and 1980s. key initial countries investing in nuclear energy included canada, france, the soviet union, the united kingdom, and the united states.
Nuclear Steam Turbine в Energy Knowledgebase Small modular reactor (smr) most existing nuclear reactors are big – typically ranging in size from 600 to more than 1,500 mw. new technologies in development promise much smaller reactors ranging in size from 2 to 300 mw. these smaller units could be installed as a single small power plant or as installations of multiple modules to obtain. Nuclear power reactors produce energy by initiating and controlling a sustained nuclear chain reaction. currently, over 400 such reactors in 32 countries provide about 10 per cent of the world’s electricity. the iaea fosters an international information exchange and collaboration on technological innovations in different reactor technologies. Nuclear reactors are designed to sustain an ongoing chain reaction of fission; the reactors operating in the u.s. today are filled with a specially designed, solid uranium fuel and surrounded by water, which facilitates the process. when the reactor starts, uranium atoms will split, releasing neutrons and heat. Figure 1. the core of a nuclear research reactor. [1] a nuclear reactor is a system used to initiate and contain a nuclear chain reaction, and they have many useful applications. these nuclear reactions produce thermal energy through either nuclear fission (in practice) or nuclear fusion (in development). nuclear reactors are primarily used for.

Nuclear Power Reactor Diagram Nuclear reactors are designed to sustain an ongoing chain reaction of fission; the reactors operating in the u.s. today are filled with a specially designed, solid uranium fuel and surrounded by water, which facilitates the process. when the reactor starts, uranium atoms will split, releasing neutrons and heat. Figure 1. the core of a nuclear research reactor. [1] a nuclear reactor is a system used to initiate and contain a nuclear chain reaction, and they have many useful applications. these nuclear reactions produce thermal energy through either nuclear fission (in practice) or nuclear fusion (in development). nuclear reactors are primarily used for. These reactors pump water into the reactor core under high pressure to prevent the water from boiling. the water in the core is heated by nuclear fission and then pumped into tubes inside a heat exchanger. those tubes heat a separate water source to create steam. the steam then turns an electric generator to produce electricity. The nuclear energy knowledge base for advanced modeling and simulation (ne kams) is being developed at the idaho national laboratory in conjunction with bettis laboratory, sandia national laboratories, argonne national laboratory, utah state university and others. the objective of this consortium is to establish a comprehensive and web.
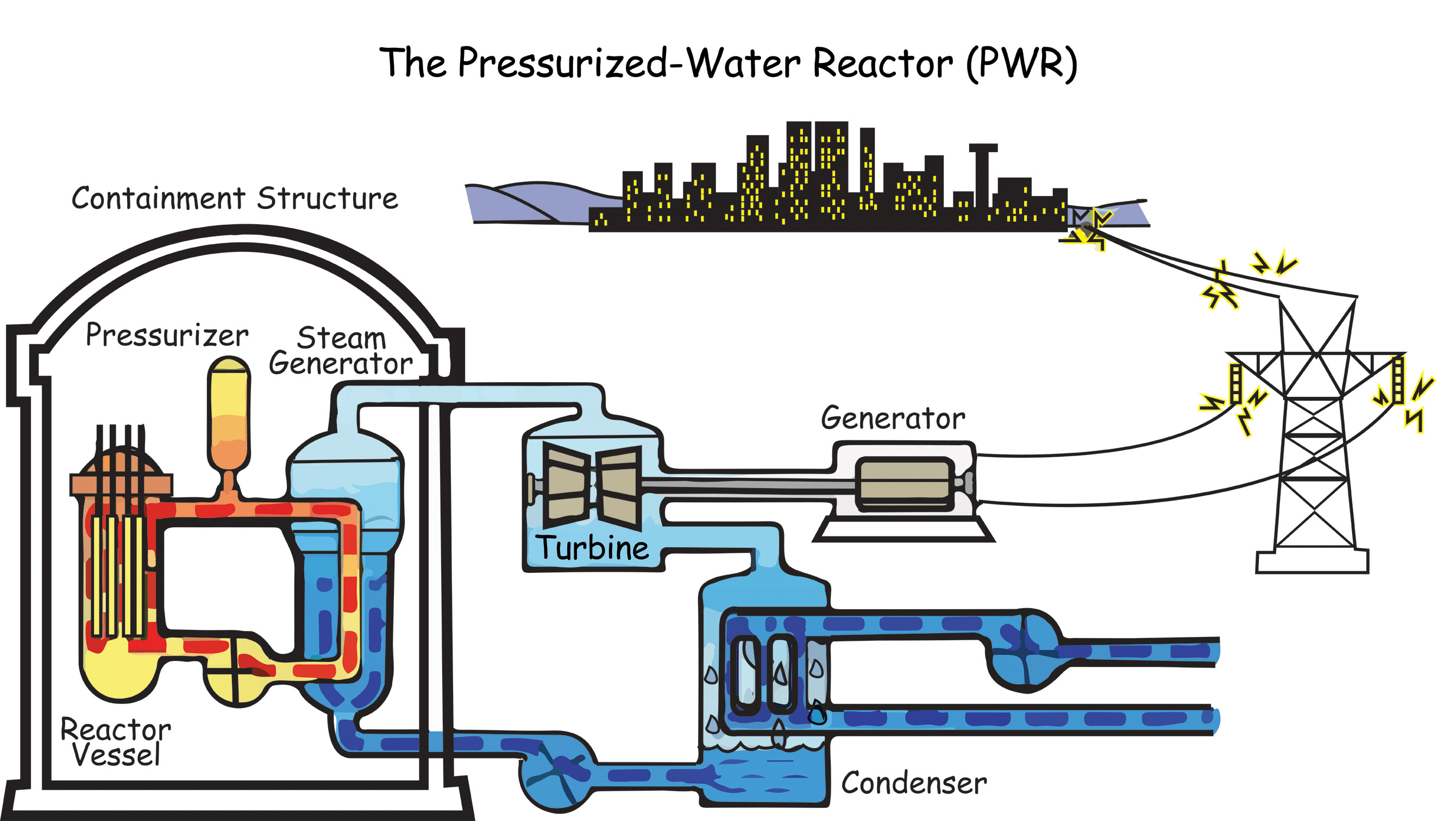
How Does A Nuclear Power Plant Work These reactors pump water into the reactor core under high pressure to prevent the water from boiling. the water in the core is heated by nuclear fission and then pumped into tubes inside a heat exchanger. those tubes heat a separate water source to create steam. the steam then turns an electric generator to produce electricity. The nuclear energy knowledge base for advanced modeling and simulation (ne kams) is being developed at the idaho national laboratory in conjunction with bettis laboratory, sandia national laboratories, argonne national laboratory, utah state university and others. the objective of this consortium is to establish a comprehensive and web.
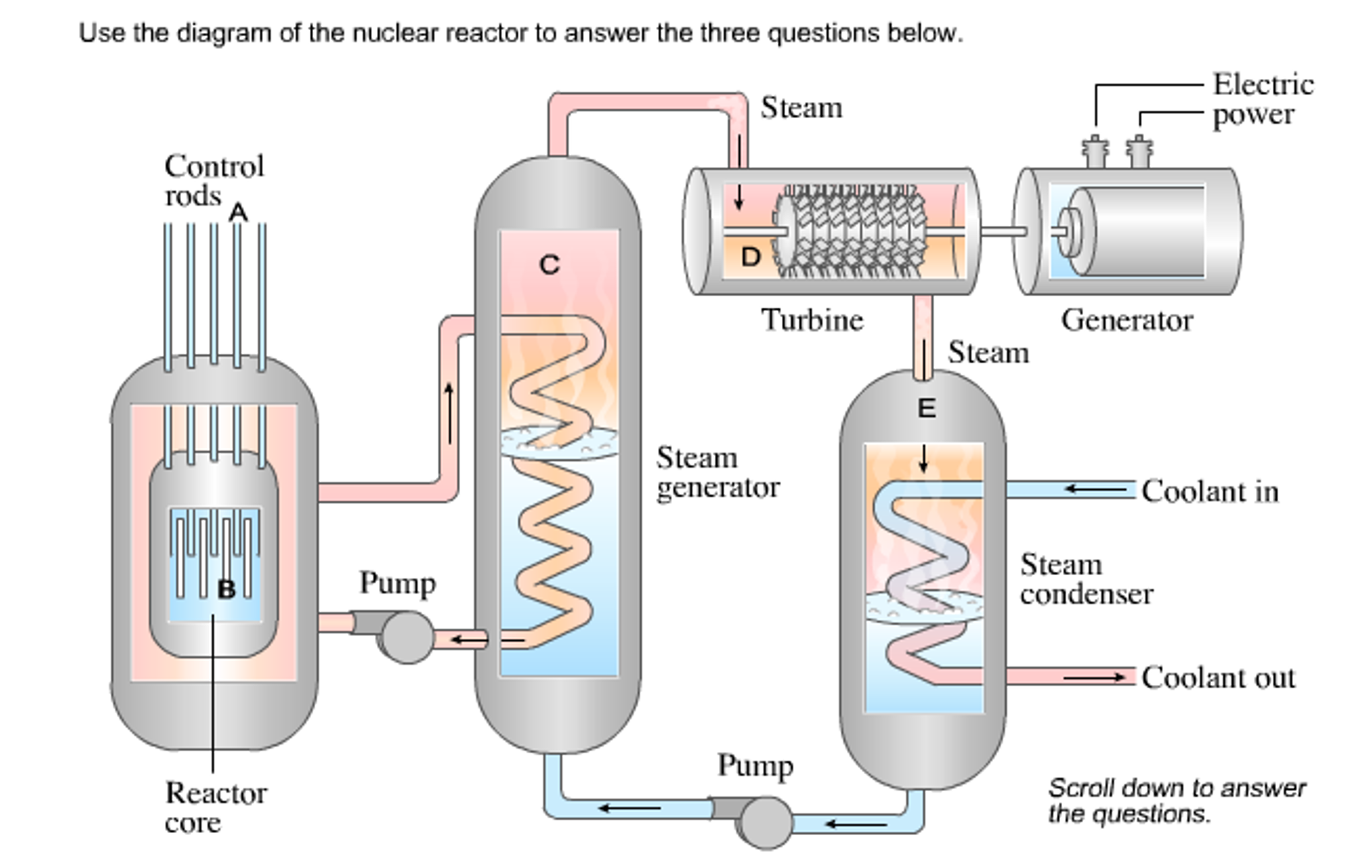
Schematic Diagram Of Nuclear Reactor

Comments are closed.