Oral Ginger Supplementation Adverse Effects With Warfarin

Oral Ginger Supplementation Adverse Effects With Warfarin However, it should also serve as a reminder as to how quickly the anticoagulation effects of warfarin may be impacted. our patient had consumed 48 mg of oral ginger supplement. after stopping the oral ginger supplement entirely and holding her warfarin therapy for 3 days, our patient's inr returned to a therapeutic level. Concurrently, the use of alternative medicines is on the rise. with that, the potential for interactions between them is increasing. ginger has gained popularity in its use. the literature has sparse recent information about the potential conflict between warfarin and ginger. this brief case report discusses the potential scope of the problem.

Pdf Effects Of Oral Ginger Supplementation On The Inr For another 23 (29.5%) herbs or dietary supplements, these were described the inhibition of warfarin effects, while 10 (12.8%) reported no impact on warfarin pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics. these interactions were classified as major in 14 (17.9%) of herbs or dietary supplements, 38 (48.7%) as moderate and 26 (33.3%) as minor. Case report. effects of oral ginger supplementation on the inr. daniel rubin , vishal patel, and eric dietrich. university of florida, gainesville, fl, usa. correspondence should be addressed to. This topic last updated: jan 31, 2024. warfarin and other vitamin k antagonists (vkas, also called coumarins; eg, acenocoumarol, phenprocoumon, fluindione) have been available for decades and are used in various settings. their use is challenging because their therapeutic range is narrow and dosing is affected by many factors including genetic. Abstract. aims: to present an updated overview on the safety of concurrent use of food, herbal or dietary supplement and warfarin. methods: a systematic literature review was performed on 5 databases from inception up to 31 december 2019. these interactions were classified depending on the likelihood of interaction and supporting evidences.

7 Dangerous Side Effects Of Ginger You Should Know Thehealthsite This topic last updated: jan 31, 2024. warfarin and other vitamin k antagonists (vkas, also called coumarins; eg, acenocoumarol, phenprocoumon, fluindione) have been available for decades and are used in various settings. their use is challenging because their therapeutic range is narrow and dosing is affected by many factors including genetic. Abstract. aims: to present an updated overview on the safety of concurrent use of food, herbal or dietary supplement and warfarin. methods: a systematic literature review was performed on 5 databases from inception up to 31 december 2019. these interactions were classified depending on the likelihood of interaction and supporting evidences. A total of 149 articles describing 78 herbs, food or dietary supplements were reported to interact with warfarin. these reports described potentiation with 45 (57.7%) herbs, food or dietary supplements while 23 (29.5%) reported inhibition and 10 (12.8%) reported limited impact on warfarin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Food supplements are usually restricted to lower daily doses than medicinal products and, thus, considered safe. however, depending on individual susceptibility, with conditions such as age or renal impairment, medication, and consumer driven dose changes, there still remains a risk for adverse effects and or interactions.
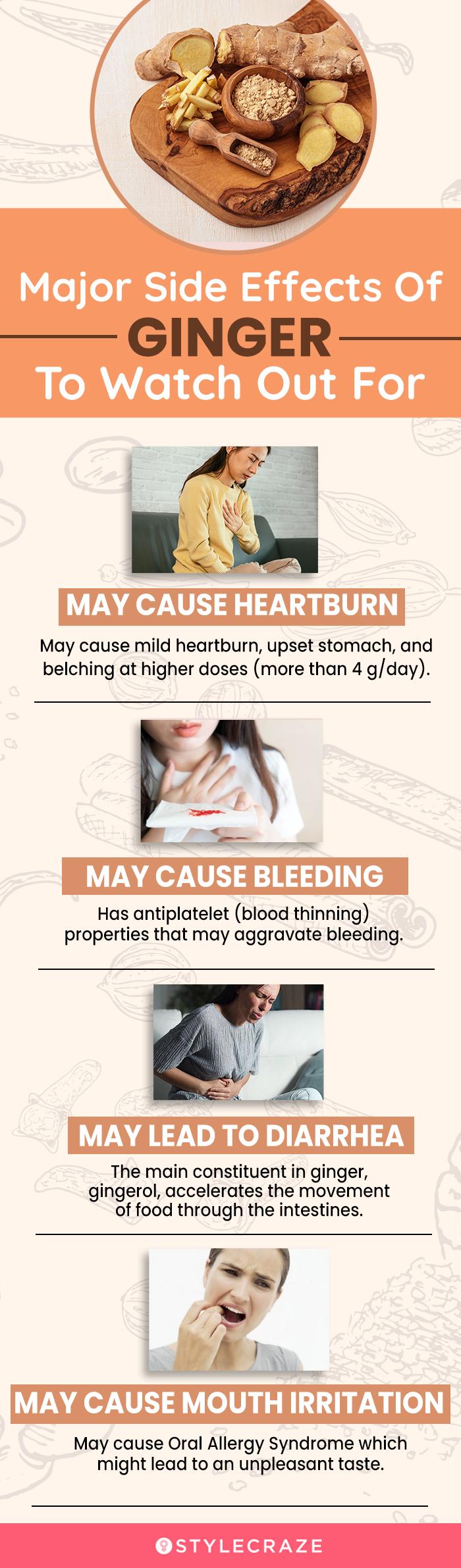
9 Side Effects Of Ginger You Must Know About A total of 149 articles describing 78 herbs, food or dietary supplements were reported to interact with warfarin. these reports described potentiation with 45 (57.7%) herbs, food or dietary supplements while 23 (29.5%) reported inhibition and 10 (12.8%) reported limited impact on warfarin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Food supplements are usually restricted to lower daily doses than medicinal products and, thus, considered safe. however, depending on individual susceptibility, with conditions such as age or renal impairment, medication, and consumer driven dose changes, there still remains a risk for adverse effects and or interactions.

Comments are closed.