Overview Of Amino Acid Metabolism

General Overview Of Amino Acids Metabolism Scheme Showing The Main An overview of amino acid metabolism. amino acids are degraded to yield nh 4 , which enters the urea cycle, and a carbon skeleton that can enter metabolic pathways to generate atp, glucose, and fatty acids. amino acids are also used to produce no, neurotransmitters, and catecholamines. The number of carbons in the intermediate formed is the same as the number of carbons in the longest chain in the amino acid. these amino acids form the 5c tca intermediate alpha ketoglutarate (2 oxoglutarate) and are shown in figure 18.4.2 18.4. 2. figure 18.4.2 18.4. 2: glucogenic amino acids converted to 5c α ketoglutarate (2 oxoglutarate.
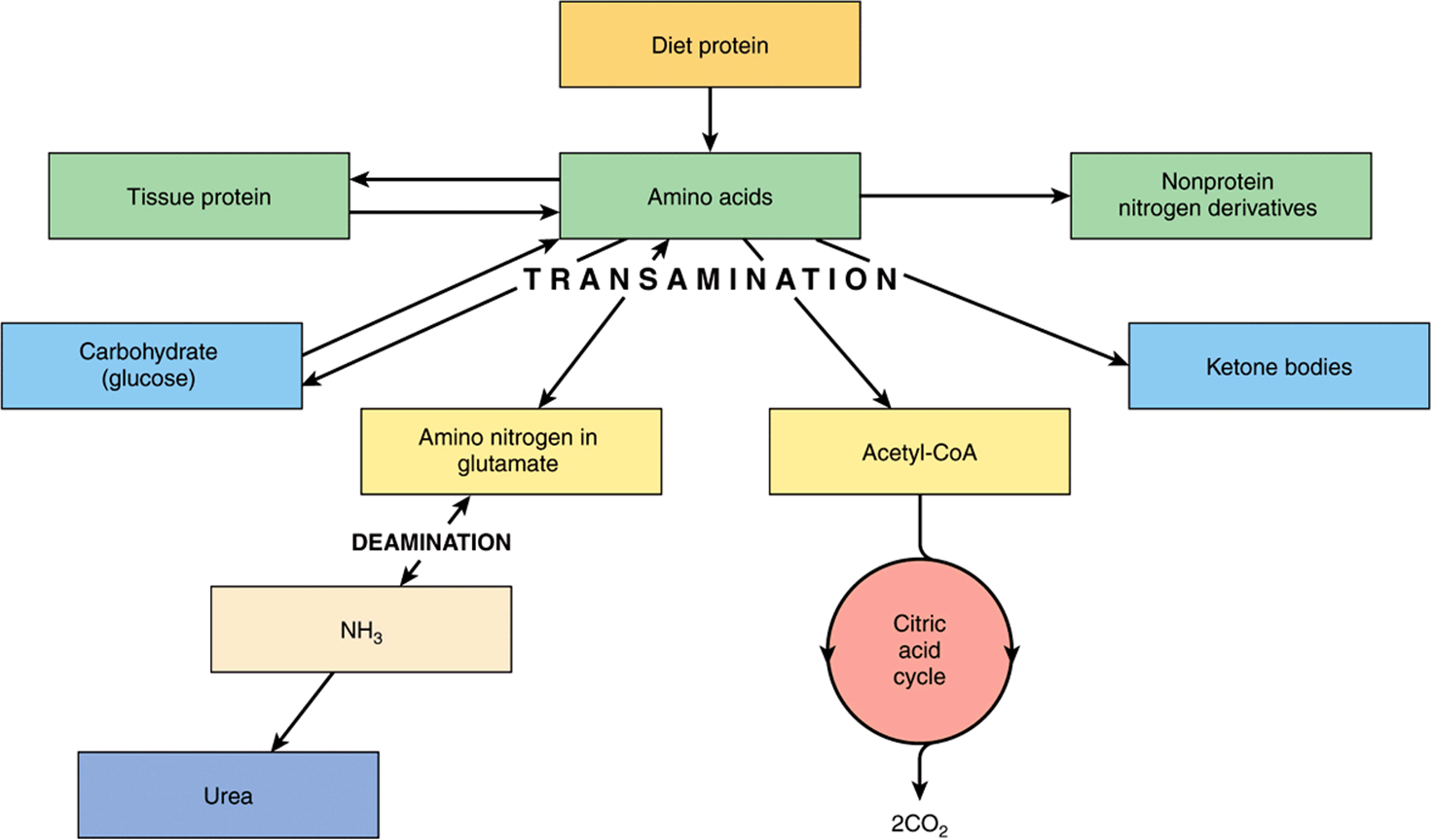
Image Summary. amino acid metabolism refers to the biochemical pathways that produce, break down, and use amino acids. the body uses amino acids to make proteins, enzymes, hormones, and other important molecules. protein synthesis and degradation are both essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body. amino acid oxidation is a process that helps. 234045. 10.1: proteins metabolism. 10.2: amino acids degradation. generally the first step in the breakdown of amino acids is the removal of the amino group, usually through a reaction known as transamination. the carbon skeletons of the amino acids undergo further reactions to form compounds that can either be used for the synthesis of glucose. Amino acids are classified into three groups namely: essential amino acids and nonessential amino acids. essential amino acids. essential amino acids cannot be made by the body. as a result, they must come from food. the 9 essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and. Overview of amino acid metabolism. the human body can obtain amino acids through food digestion and absorption, tissue decomposition, internal synthesis of three ways.

Comments are closed.