Overview Of Skull Bones

Skull And Facial Bones Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology For Skull. introduction to the bones that make up the skull. the human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. the skull is divided into the braincase (neurocr anium) and the facial skeleton (viscerocranium). The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. it encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones. it is also known as the calvarium.
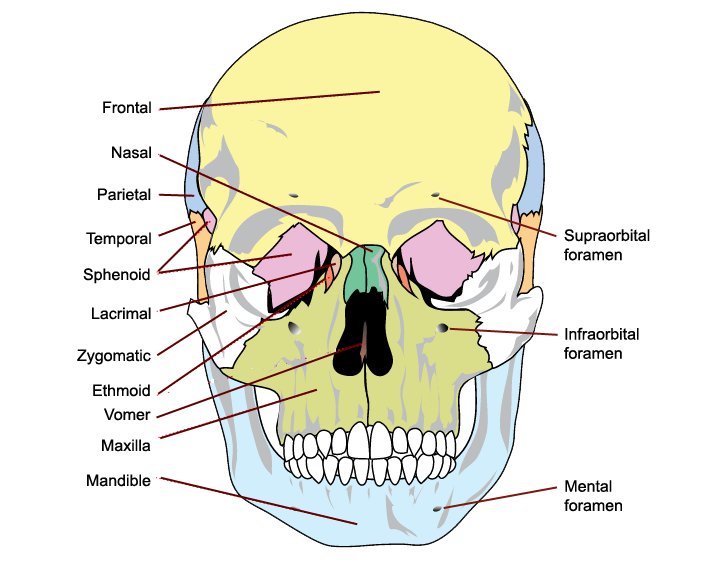
The Bones Of The Skull Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141 Neurocranium. it is the uppermost part of the skull that encircles and protects the brain, as well as the cerebral vasculature and meninges. the hollow space taken up by the brain is called the cranial cavity. the 8 (2 paired and 4 unpaired) bones forming the cranium are called the cranial bones. the cranium is divided into the cranial roof or. Bones of the calvarium. the calvarium, also known as the roof or skull cap, consists of three bones: frontal bones. parietal bones. occipital bones. these bones protect the brain superiorly, but also provide an anchor for important muscles of facial expression and eye movement. the parts of these bones that lie inferior to the brain are. The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. figure 7.3.1 – parts of the skull: the skull consists of the rounded cranium that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures. The bones of the head meet at joint lines called sutures. they are a type of fibrous joint, which are immovable. the 22 bones of the skull can be divided in to two main categories: the cranium and the facial skeleton. the cranium encloses and protects the brain; whereas, the bones of the facial skeleton provides support to facial soft tissues.
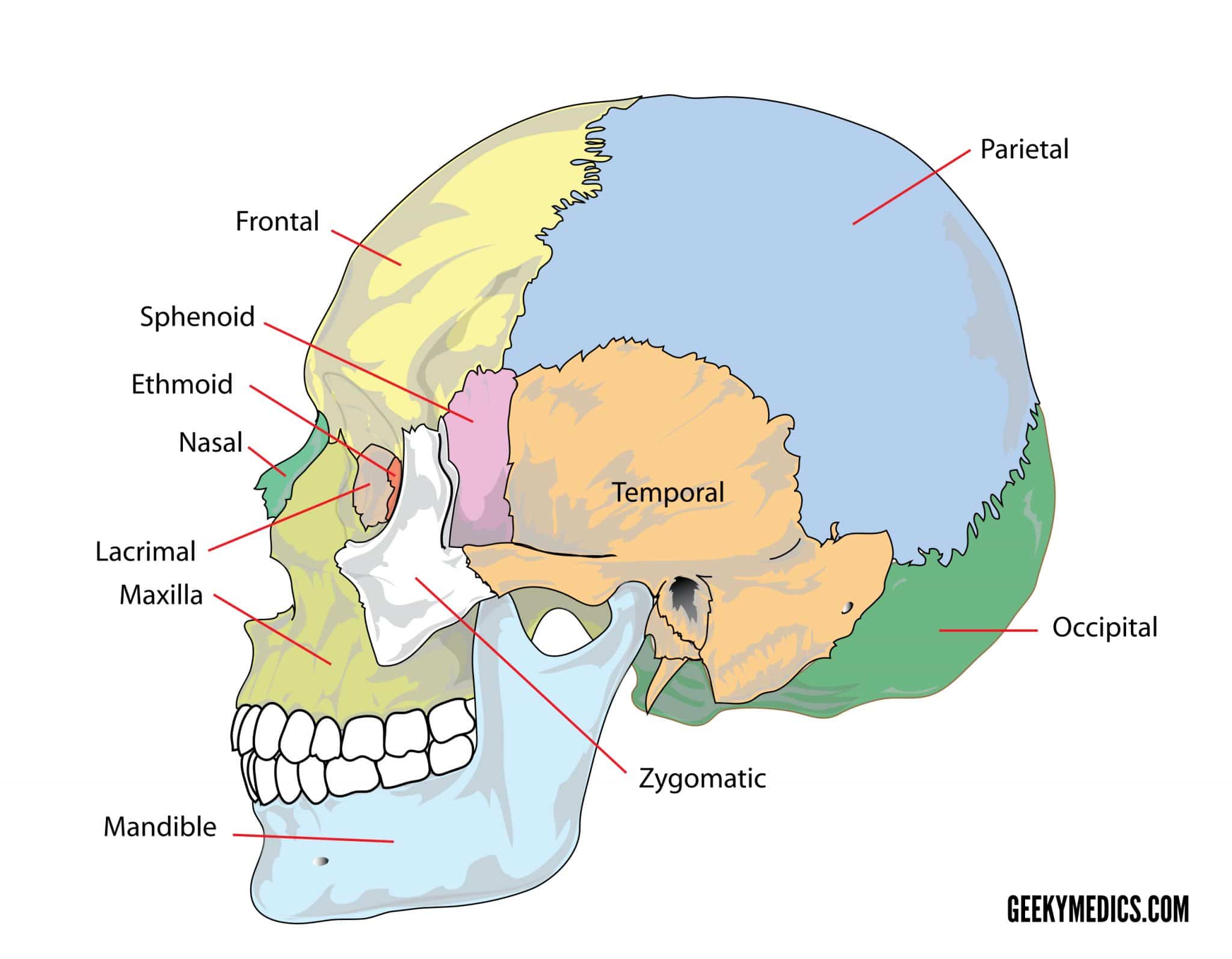
Bones Of The Skull Skull Osteology Anatomy Geeky Medics The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. figure 7.3.1 – parts of the skull: the skull consists of the rounded cranium that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures. The bones of the head meet at joint lines called sutures. they are a type of fibrous joint, which are immovable. the 22 bones of the skull can be divided in to two main categories: the cranium and the facial skeleton. the cranium encloses and protects the brain; whereas, the bones of the facial skeleton provides support to facial soft tissues. The skull contains all the bones of the head and is a shell for the brain and the origins of the central nervous system. a first glance shows that this is one large mass of detailed and irregular bone. upon closer inspection however, it seems that it is intricately constructed of many smaller bone fragment pairs, all unique in shapes and sizes. Neurocranium: the protective vault surrounding the brain and brain stem. the skull supports the musculature and structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. the skull is formed of several bones which, with the exception of the mandible, are joined together by sutures—synarthrodial (immovable) joints.

Bones Of The Skull Overview Diagram Front View Diagram Quizlet The skull contains all the bones of the head and is a shell for the brain and the origins of the central nervous system. a first glance shows that this is one large mass of detailed and irregular bone. upon closer inspection however, it seems that it is intricately constructed of many smaller bone fragment pairs, all unique in shapes and sizes. Neurocranium: the protective vault surrounding the brain and brain stem. the skull supports the musculature and structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. the skull is formed of several bones which, with the exception of the mandible, are joined together by sutures—synarthrodial (immovable) joints.

Comments are closed.